Contents
- I. Introduction to Urban Biodiversity
- II. Importance of Bees in Urban Environments
- III. Bee Species Found in Urban Areas
- IV. Benefits of Bees for Urban Biodiversity
- V. Threats to Bee Populations in Urban Areas
- VI. Bee Conservation Efforts in Urban Environments
- VII. Frequently Asked Questions about Bees and Urban Biodiversity
I. Introduction to Urban Biodiversity

Welcome to the fascinating world of urban biodiversity! In recent years, cities around the globe have experienced significant growth and development, resulting in an increasing number of people living in urban areas. As a result, the preservation and enhancement of biodiversity within these concrete jungles have become crucial.
Urban biodiversity refers to the variety of plant and animal species that exist within urban environments. Despite initial assumptions that cities are devoid of nature, research has shown that even highly built-up areas can support diverse ecosystems. From parks and gardens to rooftop gardens and green walls, efforts are being made to create habitats for various organisms.
1. The Importance of Urban Biodiversity
Urban biodiversity plays a vital role in maintaining ecological balance within cities. It offers numerous benefits such as improved air quality, reduced noise pollution, enhanced mental well-being for residents, and increased resilience against climate change impacts.
Diverse plant species provide homes for insects like bees, butterflies, and other pollinators essential for crop production and the reproduction of flowering plants. They also help purify the air by absorbing pollutants like carbon dioxide and releasing oxygen into their surroundings.
2. Challenges Faced by Urban Biodiversity
The rapid pace of urbanization poses several challenges to urban biodiversity conservation. Loss or fragmentation of natural habitats due to construction activities reduces available space for wildlife to thrive.
Pollution from vehicular emissions affects both flora and fauna negatively while light pollution disrupts natural cycles such as migration patterns or nocturnal behaviors.
3. Strategies for Promoting Urban Biodiversity
To address these challenges effectively, various strategies are being implemented worldwide:
- Habitat creation and restoration: Creating green spaces like parks, urban forests, and wetlands helps recreate natural habitats for wildlife.
- Community involvement: Engaging residents in conservation efforts through citizen science projects, community gardens, and education programs fosters a sense of ownership and responsibility.
- Sustainable urban planning: Incorporating biodiversity-friendly features into urban design, such as green roofs or permeable surfaces, can help mitigate the negative impacts of development.
II. Importance of Bees in Urban Environments
In recent years, there has been a growing concern about the decline of bees and its impact on urban biodiversity. Bees play a crucial role in maintaining the delicate balance of ecosystems, including those found within cities. Their presence not only enhances the beauty of urban landscapes but also contributes to the overall health and sustainability of our environment.
Pollination: Sustaining Urban Flora
One of the primary reasons bees are vital in urban environments is their role as pollinators. As they collect nectar from flowers, bees inadvertently transfer pollen grains between plants, facilitating cross-pollination. This process is essential for plant reproduction and ensures genetic diversity within species. Without bees, many flowering plants would struggle to reproduce and ultimately decline in numbers.
Biodiversity Support: Enhancing Urban Fauna
The presence of diverse bee species promotes biodiversity by attracting other insects and animals to urban areas. Bees serve as a vital food source for numerous organisms such as birds, bats, and small mammals that rely on them for sustenance. By creating favorable conditions for bee populations to thrive, we indirectly support a broader range of fauna within our cities.
Ecosystem Services: Improving Urban Resilience
Bees contribute significantly to ecosystem services that benefit both humans and nature alike. Through their pollination activities, they bolster agricultural productivity by ensuring higher crop yields. In an urban context where green spaces are limited, this becomes particularly important for community gardens or rooftop farms that rely on adequate pollination to produce healthy fruits and vegetables.
Furthermore, bees help improve air quality by promoting vegetation growth through enhanced pollination efforts. They aid in carbon sequestration while mitigating pollution levels caused by human activities such as vehicle emissions. By playing a role in these ecosystem services, bees contribute to making urban environments more resilient and sustainable.
Education and Awareness: Connecting Humans with Nature
The presence of bees in urban areas provides an excellent opportunity for environmental education and raising awareness among city dwellers. Urban beekeeping initiatives not only promote the well-being of these essential pollinators but also engage communities in learning about the importance of biodiversity conservation. This interaction fosters a sense of responsibility towards nature and encourages individuals to take action to protect bee populations.
III. Bee Species Found in Urban Areas

Urban areas may seem devoid of natural biodiversity, but surprisingly, they support a diverse range of bee species. These industrious insects have adapted to the urban environment and play a crucial role in maintaining urban biodiversity. Let’s explore some of the bee species commonly found in urban areas:
1. Apis mellifera (European Honey Bee)
The European honey bee is perhaps the most well-known and widely recognized species of bees found in both rural and urban settings. Known for their intricate social structure and honey production capabilities, these bees are vital pollinators for many flowering plants.
2. Bombus spp. (Bumblebees)
Bumblebees are large, fuzzy bees known for their distinctive buzzing sound as they fly from flower to flower collecting nectar and pollen. They are highly efficient pollinators due to their ability to vibrate their wings at high frequencies, allowing them to extract more pollen from flowers.
3. Megachile spp.
Megachile bees, commonly known as leafcutter or mason bees, are solitary insects that construct nests using leaves or mud respectively. They play an essential role in plant reproduction by efficiently transferring pollen from one flower to another while visiting various plant species.
4. Halictus spp. (Sweat Bees)
Sweat bees belong to a diverse genus called Halictus and are often attracted to human sweat due to its salt content—thus acquiring their name “sweat” bees! These small-sized solitary bees can be seen visiting a variety of flowers in search of nectar.
5. Osmia spp.
Osmia bees, commonly known as mason or orchard bees, are solitary insects that construct nests in pre-existing cavities like hollow plant stems or abandoned burrows. They are efficient pollinators of fruit trees and are often used in commercial orchards for their pollination services.
6. Andrena spp. (Mining Bees)
Mining bees, belonging to the genus Andrena, are solitary ground-nesting bees that create small tunnels in soil or sand for their nests. These hardworking bees visit a wide range of flowers and contribute significantly to the pollination of both wild plants and garden flowers.
7. Lasioglossum spp. (Sweat Bees)
Sweat bees from the genus Lasioglossum are small-sized solitary bees that also exhibit an affinity towards human sweat due to its salt content. These tiny yet efficient pollinators can be found buzzing around various urban gardens and parks.
In conclusion, urban areas may provide a different landscape compared to natural habitats, but they still support a rich diversity of bee species. Understanding the presence and importance of these bee species is crucial for promoting urban biodiversity conservation efforts and ensuring sustainable ecological balance within cities.
IV. Benefits of Bees for Urban Biodiversity
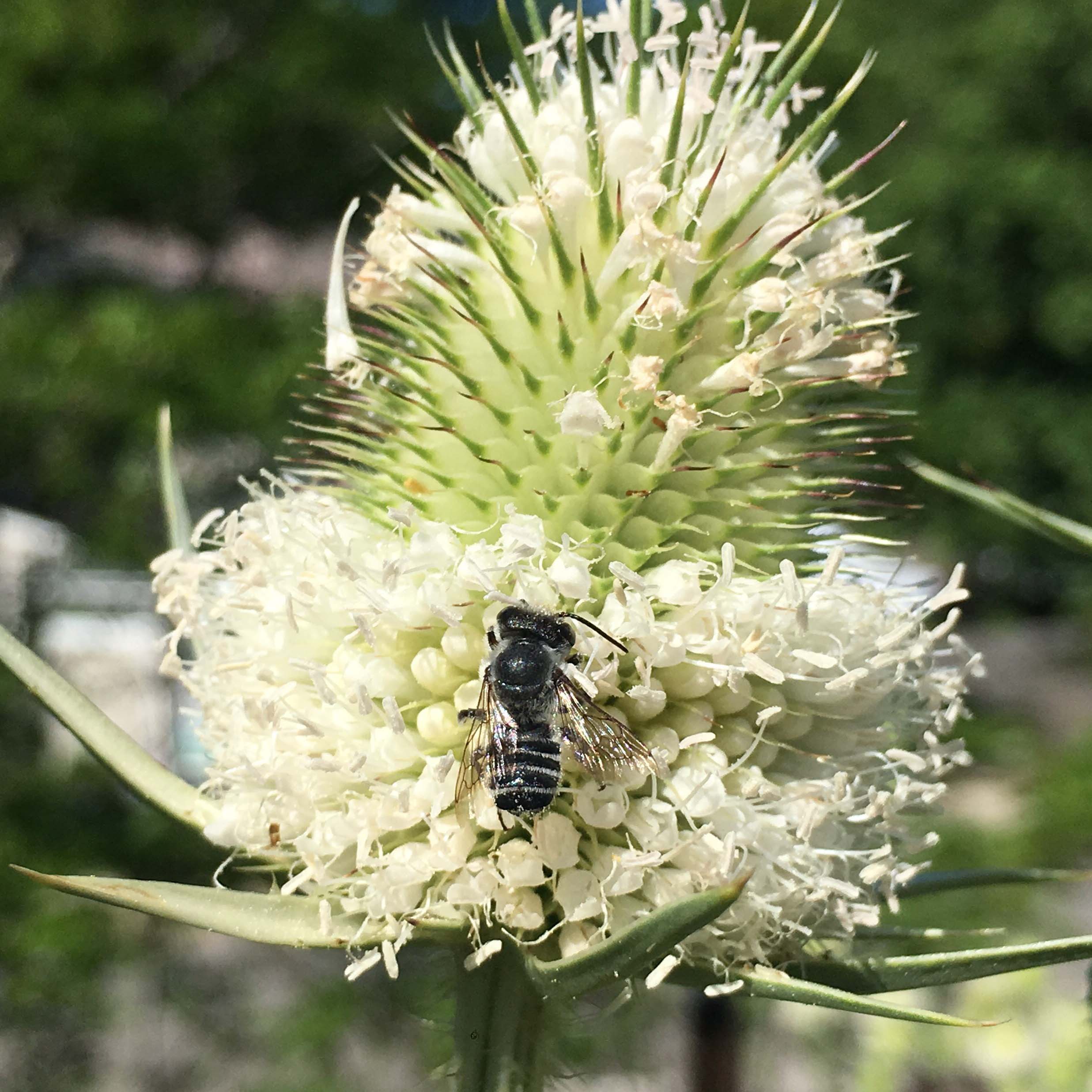

Bees play a crucial role in maintaining urban biodiversity, offering numerous benefits to both the environment and the human population. Their presence and activities contribute to the overall health and well-being of urban ecosystems, making them an essential component of sustainable urban development.
Pollination of Plants
One of the primary benefits bees provide is their role as pollinators. As they move from flower to flower in search of nectar, bees inadvertently transfer pollen grains, enabling plants to reproduce. This process is vital for maintaining plant diversity and ensuring the production of fruits, vegetables, and seeds necessary for sustaining urban green spaces.
Diverse Plant Species
The presence of bees in urban areas promotes the growth and proliferation of diverse plant species. By visiting different flowers across various locations within a cityscape, bees facilitate cross-pollination between plants that might not otherwise occur naturally. This leads to increased genetic diversity among plants, making them more resilient to environmental changes.
Pest Control
Certain bee species also contribute to pest control by preying on insects that damage crops or gardens. For instance, solitary bee species like mason bees actively seek out pests such as aphids or caterpillars that harm plants. By minimizing pest populations naturally without relying on harmful pesticides, these bees help maintain a healthy balance within urban ecosystems.
Ecosystem Services
The presence of bees supports various ecosystem services essential for urban biodiversity conservation. Bees help improve soil quality through their burrowing activities while also promoting water filtration by creating channels in compacted soil. Additionally, their pollination efforts enhance seed dispersal mechanisms necessary for plant colonization in new areas.
Aesthetic Value
Bees also contribute to the aesthetic value of urban spaces. Their buzzing presence and vibrant colors add life and beauty to gardens, parks, and other green areas within cities. The sight of bees gracefully moving from flower to flower can be a source of fascination and joy for onlookers, making urban environments more visually appealing.
V. Threats to Bee Populations in Urban Areas
As urbanization continues to expand rapidly, the bee populations in urban areas face numerous threats that pose significant challenges to their survival and overall biodiversity. While bees play a crucial role in pollination and maintaining ecological balance, the following factors have contributed to the decline of bee populations:
1. Habitat Loss and Fragmentation
The rapid growth of cities has led to extensive habitat loss for bees. The conversion of natural landscapes into concrete jungles eliminates vital foraging grounds, nesting sites, and floral resources necessary for their survival.
2. Pesticide Use
The widespread use of pesticides in urban areas poses a severe threat to bee populations. These chemicals can contaminate nectar and pollen sources, leading to direct mortality or impairing bees’ navigation abilities.
3. Lack of Floral Diversity
In many urban areas, there is a limited variety of flowering plants available for bees due to ornamental plantings that prioritize aesthetics over ecological benefits. This lack of floral diversity reduces the availability of suitable food sources throughout the year.
4. Air Pollution
Elevated levels of air pollution in urban environments can have detrimental effects on bees’ health and reproductive success. Pollutants such as particulate matter can accumulate on flowers, affecting pollination efficiency.
5. Climate Change
The changing climate patterns impact both plant phenology and bee behavior, disrupting their synchrony essential for successful pollination interactions between specific species.
These threats collectively contribute to diminished bee populations within urban areas while also impacting overall biodiversity levels significantly.
Urban planners, policymakers, and communities must work together towards implementing effective strategies that address these challenges:
– Encouraging the creation of green spaces and urban gardens that provide suitable habitats for bees.
– Promoting the use of organic and bee-friendly pest management practices to minimize harmful pesticide exposure.
– Increasing awareness about the importance of native flowering plants and supporting their cultivation in urban landscapes.
– Implementing measures to reduce air pollution levels, such as promoting sustainable transportation options.
By adopting these approaches, we can create a more favorable environment for bees in urban areas, safeguard their populations, and preserve the vital role they play in maintaining biodiversity.
VI. Bee Conservation Efforts in Urban Environments
Bee conservation plays a crucial role in maintaining urban biodiversity, as these industrious insects are not only important pollinators but also indicators of the overall health of our ecosystems. With the rapid expansion of urban areas, it is essential to implement effective strategies to protect and support bee populations within cities.
1. Creating Pollinator-Friendly Gardens
One way to promote bee conservation in urban environments is by establishing pollinator-friendly gardens. These gardens are designed with native flowering plants that provide bees with ample sources of nectar and pollen throughout the year. By incorporating diverse plant species, we can create a continuous food supply for bees and encourage their presence in our cities.
2. Reducing Pesticide Use
Pesticides pose a significant threat to bees’ survival, as they can weaken their immune systems and disrupt their navigation abilities. To protect bee populations, it is crucial to minimize pesticide use in urban areas. Instead, alternative pest control methods such as integrated pest management can be employed to ensure a safer environment for both humans and bees.
3. Installing Bee Hotels
Bee hotels are artificial nesting habitats designed specifically for solitary bee species that do not form hives like honeybees do. These structures consist of drilled wooden blocks or hollow reeds that offer shelter for solitary bees during nesting periods. Installing bee hotels across urban landscapes provides valuable nesting opportunities for these essential pollinators.
4. Educating Communities about Bees
To foster greater understanding and appreciation for bees, educating communities about the importance of these insects is vital. Conducting workshops, organizing educational programs or public events centered around bees can help raise awareness about their role in ecosystem functioning and inspire individuals to take action in bee conservation efforts.
5. Preserving Natural Habitat
Preserving natural habitat within urban environments is crucial for the long-term survival of bees. Urban planners and developers should prioritize green spaces, such as parks, gardens, and nature reserves, which offer suitable habitats for native bee species. By preserving these areas, we can ensure a sustainable urban environment that supports diverse bee populations.
In conclusion, protecting bees in urban environments through various conservation efforts is vital to maintaining biodiversity and ensuring the health of our ecosystems. By creating pollinator-friendly gardens, reducing pesticide use, installing bee hotels, educating communities about bees’ importance and preserving natural habitat, we can contribute to the well-being of both bees and our cities. Together with collective action and awareness, we can create harmonious spaces where humans and bees thrive side by side.
VII. Frequently Asked Questions about Bees and Urban Biodiversity
1. Why are bees important for urban biodiversity?
Bees play a crucial role in pollinating plants, including many of the flowers, fruits, and vegetables that we rely on for food. By pollinating a wide variety of plants, bees contribute to the overall health and diversity of urban ecosystems.
2. How do bees contribute to urban agriculture?
Bees are essential for crop pollination, which ensures higher yields and better quality produce in urban farming settings. They help to transfer pollen from male flower parts to female flower parts, enabling fertilization and fruit production.
3. Can bees thrive in cities with limited green spaces?
Absolutely! While it is true that cities often have limited green spaces compared to rural areas, bees have proven their adaptability by finding nectar and pollen sources even in highly urbanized environments. With proper planning and conservation efforts, it is possible to create bee-friendly habitats within cities.
4. Are all bee species beneficial for urban biodiversity?
Not all bee species provide the same level of benefit when it comes to urban biodiversity. Native solitary bees are particularly important as they often specialize in pollinating specific plant species, contributing significantly to plant diversity within an ecosystem.
5. What challenges do bees face in urban environments?
In cities, some common challenges faced by bees include habitat loss due to development activities or landscaping practices that remove native flora suitable for their food sources; exposure to pesticides used in gardens or public spaces; competition with non-native bee species; climate change effects altering flowering patterns; and lack of nesting sites.
6

Andrew Boyer is an accomplished individual with a deep-rooted passion for bees and their conservation. Born and raised in a small town in Oregon, Andrew developed an early fascination with nature and the environment. He pursued his education at the prestigious University of Oregon, where he obtained a Bachelor’s degree in Environmental Science with a specialization in Entomology. During his time at university, Andrew conducted extensive research on the behavior and ecological impact of bees, earning him recognition from his peers and professors. His dedication to the field led him to internships at local beekeeping associations, where he honed his skills in hive management and honey production. Andrew’s expertise in beekeeping and his commitment to environmental sustainability make him a valuable asset in the conservation of these vital pollinators.
