Contents
- I. Introduction to Beekeeping and Sustainable Development
- II. The Role of Beekeeping in Environmental Conservation
- III. Benefits of Beekeeping for Sustainable Development
- IV. Beekeeping Techniques for Sustainable Production
- V. Challenges Faced in Beekeeping for Sustainable Development
- VI. The Importance of Beekeeping Regulations and Standards
- VII. Impact of Beekeeping on Local Economies
- VIII. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) about Beekeeping and Sustainable Development
- 1. Why is beekeeping considered sustainable?
- 2. How does beekeeping contribute to sustainable development?
- 3. Can anyone become a beekeeper?
- 4. Are there any risks involved in beekeeping?
- 5. Is organic honey produced through sustainable practices?
- 6. How can I start my own beehive at home?
- 7. What are the benefits of consuming bee products?
- 8. How can beekeeping contribute to environmental conservation?
- 9. Are there any alternative methods for sustainable pollination?
- 10. How can I support sustainable beekeeping practices as a consumer?
I. Introduction to Beekeeping and Sustainable Development

With the increasing concern for environmental sustainability, beekeeping has emerged as a crucial practice that contributes to sustainable development. Beekeeping, also known as apiculture, involves the maintenance of bee colonies in artificial hives for the production of honey and other bee-related products. However, its impact goes far beyond just honey production.
Beekeeping plays a vital role in sustainable development due to its positive effects on various aspects of the environment and society. Let’s delve into some key reasons why beekeeping is considered essential for sustainable development:
Promoting Biodiversity
Beekeeping encourages biodiversity by supporting pollination activities. Bees are one of the primary pollinators responsible for fertilizing flowers and ensuring plant reproduction. Through their constant movement from one flower to another, bees facilitate cross-pollination, leading to higher crop yields and genetic diversity among plants.
Enhancing Food Security
The pollination services provided by bees are crucial for agricultural productivity. It is estimated that about 75% of global food crops depend on insect pollinators like bees. By enhancing crop yields through effective pollination, beekeeping contributes directly to food security by ensuring an abundant supply of fruits, vegetables, nuts, and seeds.
Preserving Ecosystems
Beekeepers often maintain their colonies in natural habitats or near areas with diverse flora. This practice helps protect ecosystems by providing habitats for wild bees and other beneficial insects that contribute to ecosystem balance and resilience. Furthermore, preserving natural habitats supports wildlife conservation efforts while maintaining ecological harmony.
Economic Empowerment
Beekeeping offers economic opportunities at various levels – from small-scale local farmers to large commercial enterprises – contributing significantly to rural development and poverty reduction. The sale of honey, beeswax, propolis, royal jelly, and other bee-related products provides income for beekeepers and their communities.
Promoting Sustainable Practices
Beekeeping is often practiced using sustainable methods that prioritize the health and well-being of bees. Many beekeepers employ organic practices, avoiding the use of chemical pesticides and antibiotics that can harm bees and contaminate honey. This emphasis on sustainability extends to hive management techniques aimed at minimizing stress on colonies.
Conclusion
Beekeeping plays a vital role in sustainable development by promoting biodiversity, enhancing food security, preserving ecosystems, providing economic empowerment opportunities, and encouraging sustainable practices. By recognizing the importance of beekeeping in achieving environmental sustainability goals, we can contribute to a healthier planet while enjoying the sweet rewards of nature’s pollinators.
II. The Role of Beekeeping in Environmental Conservation
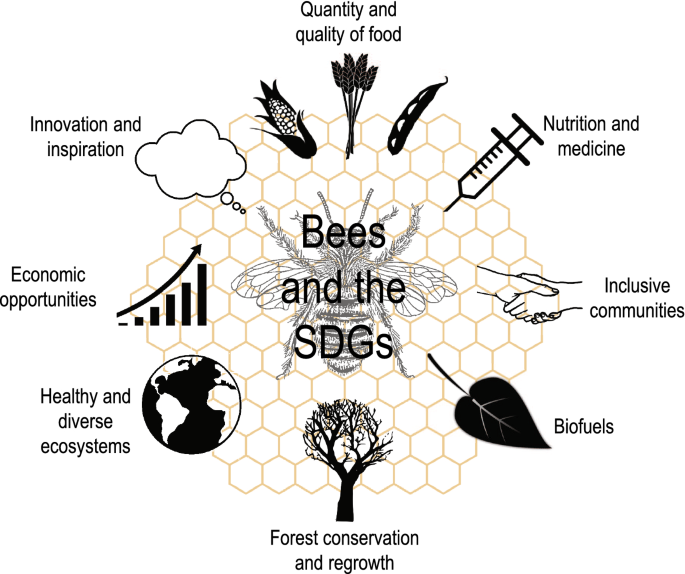
Beekeeping plays a crucial role in environmental conservation, benefiting both the ecosystem and human society. As an ancient practice, beekeeping has evolved to become not only a means of honey production but also an essential contributor to sustainable development and biodiversity preservation.
Pollination and Biodiversity
One significant role that beekeeping fulfills is pollination. Bees are vital pollinators for various flowering plants, including crops and wildflowers. Through their foraging activities, bees transfer pollen from the male parts of flowers to the female parts, enabling fertilization and subsequent seed formation.
This process promotes genetic diversity within plant populations and ensures the survival of numerous species. Without effective pollinators like bees, many plants would struggle to reproduce, leading to a decline in biodiversity.
Ecosystem Stability
Beekeeping contributes to maintaining stable ecosystems by supporting plant growth and food webs. Pollinated plants produce fruits, seeds, nuts, and vegetables that form part of the diet for various animals. In turn, these animals serve as prey for others higher up the food chain.
The loss or decline of crucial plant species due to inadequate pollination can disrupt entire ecosystems by reducing food availability for herbivores or causing imbalances among predator-prey relationships. By promoting healthy bee populations through responsible beekeeping practices, we can help maintain ecosystem stability.
Promoting Sustainable Agriculture
Beekeepers often place their hives near agricultural fields as part of crop-pollination services. This practice benefits farmers by enhancing crop yields through improved fruit set and quality.
In addition to increased productivity levels on individual farms, widespread adoption of beekeeping practices can contribute significantly to sustainable agriculture at large. A diverse range of crops, including those heavily dependent on pollinators, can thrive in an environment with healthy bee populations. This reduces the need for synthetic pesticides and fertilizers, ultimately promoting more sustainable farming practices.
Conservation of Wild Bees
While honeybees are the most well-known bee species associated with beekeeping, wild bees also play a crucial role in pollination. They contribute significantly to natural ecosystems and have unique preferences for specific plants.
Beekeepers can actively participate in the conservation of wild bees by providing suitable habitats and minimizing pesticide use near their apiaries. By creating favorable conditions for wild bees to thrive, beekeepers indirectly support biodiversity preservation by ensuring the survival of all types of pollinators.
In conclusion, beekeeping is far more than just honey production; it is an essential practice for environmental conservation. Through pollination services, ecosystem stability support, promotion of sustainable agriculture, and conservation efforts towards wild bees, responsible beekeeping contributes significantly to maintaining biodiversity and achieving sustainable development goals.
III. Benefits of Beekeeping for Sustainable Development

Beekeeping, also known as apiculture, is the practice of raising and managing bees for honey production and pollination purposes. This ancient tradition not only provides us with delicious honey but also plays a pivotal role in promoting sustainable development. Here are some key benefits of beekeeping:
Promotes Biodiversity
Beekeeping contributes to the preservation and enhancement of biodiversity. Bees are essential pollinators that facilitate the reproduction of various flowering plants, including crops and wildflowers. By actively engaging in beekeeping, we can help safeguard plant species diversity while ensuring healthier ecosystems.
Enhances Food Security
The importance of bees in food production cannot be overstated. Approximately 75% of global food crops rely on pollinators like bees to bear fruit or set seeds. Through their tireless efforts as pollinators, bees enable higher crop yields and increased agricultural productivity. Beekeepers play a crucial role in supporting food security by helping maintain healthy bee populations.
Economic Empowerment
Beekeeping offers economic opportunities for individuals and communities alike. Honey production can generate income through local sales or export markets, providing a sustainable livelihood for beekeepers themselves while contributing to rural development.
Environmental Conservation
Beekeeping aligns with principles of environmental conservation by promoting sustainable land management practices. The presence of beehives encourages farmers to adopt organic farming methods that reduce reliance on harmful pesticides and chemical fertilizers detrimental to both human health and the environment.
Promotes Rural Development
In many rural areas around the world, where alternative sources of income may be limited, beekeeping serves as an important source of revenue generation. It empowers rural communities, particularly women and marginalized groups, by providing them with a means to earn income and improve their overall quality of life.
Supports Ecosystem Stability
Beekeeping contributes to the stability of ecosystems by ensuring the continuity of pollination services. Healthy bee populations help maintain balanced ecological systems, which in turn benefit other wildlife species that rely on pollination for survival.
By recognizing the manifold benefits of beekeeping for sustainable development, we can encourage its widespread adoption. Through responsible apiculture practices and increased awareness about the importance of bees, we can create a more harmonious coexistence between humans and nature while fostering economic growth and environmental conservation.
IV. Beekeeping Techniques for Sustainable Production
Beekeeping is not just a hobby; it plays a crucial role in sustainable development and the preservation of our ecosystem. To ensure the long-term viability of beekeeping practices, it is essential to adopt techniques that promote sustainable production. Here are some effective methods that beekeepers can employ:
1. Organic Beekeeping
Organic beekeeping involves avoiding the use of synthetic chemicals, antibiotics, and pesticides in beehives. Instead, natural remedies like essential oils, organic acids, and biological controls can be used to manage diseases and pests.
2. Integrated Pest Management (IPM)
Implementing IPM strategies helps reduce reliance on chemical treatments while effectively managing pests in beehives. This approach involves monitoring pest populations regularly, using physical barriers, introducing beneficial insects or nematodes as predators or parasites to control pests naturally.
3. Hive Design and Placement
The design and placement of hives significantly impact honeybee health and productivity. Using hive designs that prioritize adequate ventilation, insulation against extreme weather conditions while providing ample space for brood rearing promotes healthy colonies.
4. Pollinator-Friendly Landscaping
Create an environment that supports pollinators by incorporating diverse flowering plants into your landscape design. Planting native flowers with different blooming periods ensures a consistent nectar flow throughout the year.
5. Queen Rearing Techniques
Raising strong queen bees is vital for maintaining healthy colonies capable of withstanding environmental challenges such as disease outbreaks or pesticide exposure.
By selecting breeding stock from colonies exhibiting desirable traits such as docility or resistance to diseases like Varroa mites or American foulbrood, beekeepers can improve the overall health and productivity of their colonies. Techniques such as grafting or instrumental insemination can be used to ensure controlled mating and the propagation of desirable genetic traits.
6. Seasonal Management
Adopting appropriate seasonal management practices is crucial for successful beekeeping. This includes regular hive inspections, monitoring honey stores, assessing colony strength, and taking appropriate measures to prevent swarming or manage varroa mite infestations.
7. Sustainable Harvesting
When it comes to honey harvesting, beekeepers should prioritize sustainable practices that do not harm the bees or compromise their long-term survival. Leaving enough honey for winter feed ensures the bees’ well-being during colder months.
V. Challenges Faced in Beekeeping for Sustainable Development
Beekeeping plays a crucial role in sustainable development by promoting biodiversity, supporting food production, and providing livelihood opportunities. However, beekeepers face several challenges that hinder their efforts towards achieving sustainability. Let’s explore some of the key challenges faced in beekeeping for sustainable development.
1. Pesticide Use and Bee Health
The use of pesticides poses a significant threat to bee health and overall colony survival. Bees are highly sensitive to chemicals used in agriculture, which can lead to direct mortality or weaken their immune systems, making them more susceptible to diseases and pests.
2. Loss of Habitat
The loss of natural habitats due to urbanization and intensive agriculture has a negative impact on bees’ foraging resources. Bees rely on diverse floral resources throughout the year for nectar and pollen collection. The reduction in available floral resources limits their food supply and affects their reproductive success.
3. Climate Change
Climate change brings unpredictable weather patterns, including prolonged droughts or extreme rainfall events that disrupt flowering seasons and affect plant-pollinator interactions. Changes in temperature also influence the timing of honeybee brood development, potentially disrupting colony dynamics.
4. Colony Collapse Disorder (CCD)
Colony Collapse Disorder is a phenomenon where entire honeybee colonies experience rapid population decline or disappearance without any apparent cause. Factors such as pests (e.g., Varroa mites), diseases (e.g., Nosema), poor nutrition, stressors from transportation, and exposure to pesticides can contribute to CCD.
5. Lack of Knowledge and Training
Beekeepers often face challenges due to insufficient knowledge about modern beekeeping techniques and sustainable practices. Adequate training and education on beekeeping management, disease prevention, and the use of sustainable methods are crucial to ensure the long-term success of beekeeping operations.
6. Market Access and Economic Viability
While beekeeping offers potential economic opportunities, accessing markets for honey, beeswax, pollen, or other hive products can be challenging for small-scale beekeepers. Limited market access can hinder their ability to generate sufficient income to sustain their operations.
In conclusion, while beekeeping holds immense potential for sustainable development, it faces various challenges that need to be addressed. From pesticide use and habitat loss to climate change impacts and colony collapse disorder, these challenges require collective efforts from governments, researchers, beekeepers themselves, and society as a whole. By addressing these challenges head-on through policy interventions, research initiatives promoting best practices in beekeeping management,and raising awareness about the importance of bees in our ecosystems we can work towards ensuring a future where both bees and humans thrive together.
VI. The Importance of Beekeeping Regulations and Standards
Beekeeping regulations and standards play a crucial role in ensuring the sustainability and well-being of both beekeepers and honeybees. These guidelines are designed to protect the environment, promote responsible beekeeping practices, and maintain high-quality honey production. Let’s explore why these regulations are essential for the beekeeping industry.
Promoting Environmental Conservation
Beekeeping regulations aim to safeguard the natural habitat of honeybees by promoting environmental conservation. They ensure that bees have access to diverse sources of pollen and nectar, which is vital for their survival. By implementing measures such as pesticide control, land management, and habitat preservation, these regulations help maintain a healthy ecosystem for bees to thrive.
Preventing Disease Outbreaks
Beekeepers face numerous challenges when it comes to protecting their colonies from diseases and pests. Regulations provide guidelines on disease prevention strategies such as regular hive inspections, proper sanitation practices, and quarantine protocols. These measures help prevent the spread of contagious diseases among honeybee populations while maintaining overall hive health.
Ensuring Food Safety
Honey is a valuable agricultural product consumed worldwide. To guarantee food safety standards, beekeeping regulations enforce strict guidelines on hygiene practices during honey extraction, processing, packaging, transportation, and storage. Adhering to these standards ensures that consumers receive safe products free from contaminants or adulteration.
Promoting Ethical Beekeeping Practices
Responsible beekeeping involves treating bees with care and respect throughout their lifecycle. Regulations emphasize ethical practices that prioritize the welfare of bees over commercial interests. This includes providing adequate nutrition sources for bees during seasonal variations or times when there may be scarcity in natural resources.
Fostering Sustainable Honey Production
Beekeeping regulations support sustainable honey production by setting guidelines for harvesting practices. These measures ensure that beekeepers leave enough honey in the hive to sustain the colony through winter, preventing excessive exploitation of honeybee resources. Sustainable practices promote long-term viability of beekeeping operations and contribute to the overall health of honeybee populations.
In conclusion, beekeeping regulations and standards are crucial for maintaining a healthy and sustainable beekeeping industry. By promoting environmental conservation, preventing disease outbreaks, ensuring food safety, promoting ethical practices, and fostering sustainable honey production, these guidelines provide a framework for responsible beekeeping practices. Adhering to these regulations not only benefits bees but also contributes to the preservation of biodiversity and supports the livelihoods of beekeepers around the world.
VII. Impact of Beekeeping on Local Economies
Beekeeping, also known as apiculture, has a significant impact on local economies around the world. This ancient practice of cultivating honeybees and harvesting their honey and other products not only contributes to the sustainability of ecosystems but also provides economic opportunities for individuals and communities.
1. Job Creation
Beekeeping creates numerous employment opportunities within local communities. From beekeepers who manage the hives to technicians who extract honey and other bee products, there is a diverse range of jobs associated with this industry. Additionally, supporting industries such as equipment manufacturers, suppliers of beekeeping tools, and packaging companies further contribute to job creation.
2. Income Generation
The sale of honey, beeswax, pollen, royal jelly, propolis, and other bee-related products generates income for both small-scale beekeepers and larger commercial enterprises. This income can be reinvested in expanding the business or used to support families in rural areas where alternative sources of income may be limited.
3. Tourism Boost
Beekeeping can act as a catalyst for tourism development in certain regions. Visitors are often intrigued by the process of beekeeping and enjoy learning about its benefits while experiencing firsthand interactions with bees in safe environments such as educational apiaries or guided tours at commercial operations. This interest from tourists can stimulate local economies through accommodations, restaurants, transportation services, souvenir shops selling bee-related products.
4. Environmental Conservation
Beekeeping plays a vital role in maintaining biodiversity by ensuring pollination continuity for wild plants that rely on bees for reproduction. As bees visit flowers to collect nectar and pollen for making honey – they inadvertently transfer pollen between flowers leading to fertilization which results in fruit set or seed production. This process is crucial for agriculture as it supports the growth of crops, thereby safeguarding food security and preserving natural habitats.
5. Knowledge Transfer
Beekeeping promotes knowledge transfer within communities as experienced beekeepers share their expertise with younger generations. This passing down of traditional practices ensures the preservation of cultural heritage while also equipping individuals with valuable skills that can be applied in various aspects of life.
VIII. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) about Beekeeping and Sustainable Development
1. Why is beekeeping considered sustainable?
Beekeeping is considered sustainable because it supports the natural environment and biodiversity. Bees play a crucial role in pollination, helping plants reproduce and ensuring food production. By practicing beekeeping, we can help maintain healthy ecosystems and promote sustainability.
2. How does beekeeping contribute to sustainable development?
Beekeeping contributes to sustainable development in several ways. Firstly, it promotes biodiversity by supporting the growth of flowering plants through pollination. Secondly, it provides economic opportunities for local communities, especially in rural areas where bee products such as honey, beeswax, and propolis can be sold for income generation.
3. Can anyone become a beekeeper?
Yes! Anyone with an interest in bees and sustainable practices can become a beekeeper. It requires some knowledge and skills that can be learned through training programs or mentorship from experienced beekeepers.
4. Are there any risks involved in beekeeping?
Like any agricultural activity, there are risks involved in beekeeping. Beekeepers may face challenges such as diseases affecting the health of their colonies or environmental factors that impact honey production or hive survival rates.
5. Is organic honey produced through sustainable practices?
Yes! Organic honey is produced through sustainable practices that prioritize natural methods of pest control without using synthetic chemicals or antibiotics on the hives.
6. How can I start my own beehive at home?
To start your own beehive at home, you will need to research local regulations on keeping bees within residential areas and obtain necessary permits if required. Then, you can purchase or build beehives, acquire a colony of bees from a reputable source, and learn about proper hive management techniques.
7. What are the benefits of consuming bee products?
Bee products such as honey, propolis, and royal jelly have various health benefits. They contain antioxidants, vitamins, minerals, and antimicrobial properties that can boost the immune system and promote overall well-being.
8. How can beekeeping contribute to environmental conservation?
Beekeeping contributes to environmental conservation by supporting pollinator populations and promoting biodiversity. By providing bees with suitable habitats and protecting them from pesticides or other harmful factors, we play a vital role in preserving ecosystems.
9. Are there any alternative methods for sustainable pollination?
While bees are the most efficient natural pollinators, there are alternative methods for sustainable pollination. Some examples include using other insect species like bumblebees or mason bees or employing mechanical means like vibrating devices to mimic bee pollination.
10. How can I support sustainable beekeeping practices as a consumer?
You can support sustainable beekeeping practices as a consumer by purchasing honey or other bee products from local beekeepers who practice ethical and environmentally friendly methods. Additionally, you can create habitats in your garden that attract bees by planting native flowering plants.

Andrew Boyer is an accomplished individual with a deep-rooted passion for bees and their conservation. Born and raised in a small town in Oregon, Andrew developed an early fascination with nature and the environment. He pursued his education at the prestigious University of Oregon, where he obtained a Bachelor’s degree in Environmental Science with a specialization in Entomology. During his time at university, Andrew conducted extensive research on the behavior and ecological impact of bees, earning him recognition from his peers and professors. His dedication to the field led him to internships at local beekeeping associations, where he honed his skills in hive management and honey production. Andrew’s expertise in beekeeping and his commitment to environmental sustainability make him a valuable asset in the conservation of these vital pollinators.
