Contents
- I. Introduction to Beekeeping and Local Regulations
- II. Understanding the Importance of Local Regulations in Beekeeping
- III. Key Factors to Consider When Starting Beekeeping in Your Area
- IV. Navigating the Permitting Process for Beekeeping
- V. Compliance with Zoning and Land Use Regulations for Beekeeping
- VI. Ensuring Safety and Security Measures in Beekeeping Operations
- VII. Best Practices for Maintaining Beehives in Accordance with Local Regulations
- VIII. Frequently Asked Questions about Beekeeping and Local Regulations
- 1. Is beekeeping legal in my area?
- 2. Do I need a permit to keep bees?
- 3. What are the typical zoning requirements for beekeeping?
- 4. Are there any restrictions on hive placement?
- 5.What precautions should I take regarding neighbors?
- 6. Are there any regulations regarding hive maintenance and inspection?
- 7. Can I sell my honey or other bee-related products?
- 8. How can I stay updated with changes in local beekeeping regulations?
- IX. Conclusion: The Role of Local Regulations in Promoting Sustainable Beekeeping Practices
I. Introduction to Beekeeping and Local Regulations
Beekeeping is the practice of raising bees for honey production, pollination services, and other bee-related products. It is not only a rewarding hobby but also an essential agricultural activity that contributes to the sustainability of ecosystems and food production. However, before embarking on your beekeeping journey, it is crucial to familiarize yourself with the local regulations governing this activity.
Understanding Local Regulations
Local regulations play a vital role in ensuring that beekeeping activities are carried out safely and responsibly within a specific area. These regulations vary from one jurisdiction to another, so it’s important to research and understand the rules specific to your location.
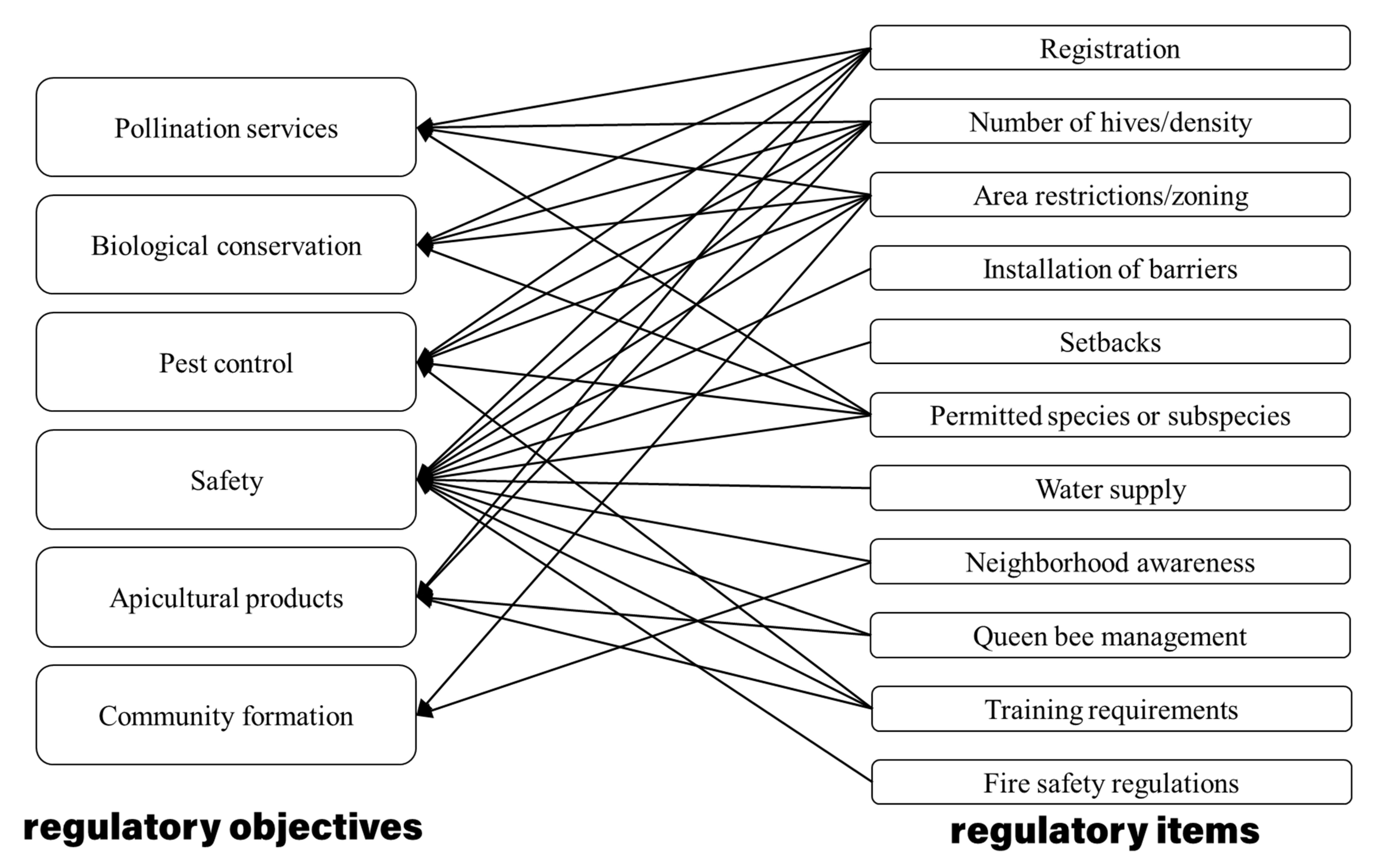
The primary purpose of these regulations is to protect both the beekeepers and the general public. They address concerns such as hive placement, colony density limits, registration requirements, safety protocols, and potential nuisances caused by bees.
Registration Requirements
In many areas, beekeepers are required to register their hives with local authorities or relevant agricultural departments. This registration process helps in monitoring hive locations for disease control purposes and enables authorities to provide necessary assistance during emergencies or natural disasters.
Additionally, some regions may require you to obtain permits or licenses before starting your apiary operation. These permits ensure compliance with zoning restrictions and help maintain harmony with neighboring properties.
Hive Placement Guidelines
The placement of beehives is another critical aspect regulated by local authorities. The guidelines typically specify minimum distances from property lines or habitable structures like houses or schools. Such rules aim at preventing potential conflicts between bees and humans while allowing for efficient management practices.
You might also find recommendations regarding hive orientation (facing south/southeast) for better sunlight exposure or protection against prevailing winds. These guidelines are designed to optimize the conditions for bee colonies and facilitate their productivity.
Safety Protocols and Nuisance Prevention
Local regulations often emphasize safety protocols related to beekeeping. This may include the use of protective clothing, such as veils, gloves, and suits, when working with bees. It is essential to follow these guidelines to minimize the risk of stings and potential allergic reactions.
Nuisance prevention is another crucial aspect covered by local regulations. Beekeepers are typically required to ensure that their bees do not become a nuisance due to excessive swarming or aggressive behavior. Regular hive inspections and maintenance can help prevent issues that may lead to complaints from neighbors or public authorities.
II. Understanding the Importance of Local Regulations in Beekeeping

Beekeeping is an ancient practice that has gained significant popularity in recent years due to its numerous benefits, such as honey production and pollination services. However, it is important for beekeepers to understand and comply with local regulations governing this activity. These regulations are designed to protect both the bees and the surrounding community.
1. Ensuring Safety for Bees
Local regulations often specify guidelines for maintaining proper hive management practices to ensure the well-being of bees. This includes providing adequate food sources, periodic health inspections, and minimizing exposure to harmful pesticides or chemicals. By adhering to these regulations, beekeepers can contribute to the overall health and preservation of bee populations.
2. Preventing Nuisance or Harmful Situations
Beekeeping activities need to be carried out responsibly so as not to create nuisance or harm individuals within the community. Local regulations may outline specific requirements regarding hive placement, distance from residential areas, and measures for controlling swarming behavior. Adhering to these guidelines helps prevent potential conflicts with neighbors and ensures a harmonious coexistence between beekeepers and their surroundings.
3. Protecting Public Health
The safety of public health is another crucial aspect addressed by local beekeeping regulations. These rules often aim at preventing allergic reactions caused by bee stings through proper hive management practices and education programs targeting nearby residents who might have allergies or sensitivities towards bees.
4.Managing Disease Control
Disease control forms an essential part of local beekeeping policies as it helps safeguard honeybee populations from spreading infectious diseases that can devastate entire colonies if left unchecked.
Local authorities may require regular checks for common diseases like Varroa mites or American Foulbrood and may provide guidelines for their proper management. By adhering to these regulations, beekeepers can contribute to the overall health and sustainability of honeybee populations.
5. Environmental Considerations
Local regulations often take into account environmental concerns related to beekeeping activities. These may include restrictions on the use of certain pesticides or chemicals in proximity to beehives, encouraging the planting of bee-friendly flowers, or implementing measures to protect water sources near apiaries from contamination. Such regulations ensure the conservation of natural resources and promote a healthy ecosystem for bees.
III. Key Factors to Consider When Starting Beekeeping in Your Area

Starting beekeeping in your area requires careful consideration of several key factors to ensure the success and well-being of your bees. By understanding these factors, you can create a thriving environment for your bees and reap the rewards of honey production.
1. Climate and Weather Conditions
The climate and weather conditions in your area play a vital role in beekeeping. Bees thrive in certain temperatures, so it’s essential to choose a location that provides adequate warmth during colder months and sufficient shade during hotter months. Research the average temperatures, rainfall patterns, and seasonal changes specific to your region.
2. Available Resources for Foraging
Bee colonies require access to diverse sources of nectar and pollen for their survival. Investigate the availability of flowering plants, trees, or crops that provide ample food sources throughout the year. Ensure there are no harmful pesticides or chemicals used nearby that may harm the bees or contaminate their honey.
3. Local Beekeeping Regulations
Educate yourself about any local regulations or restrictions related to beekeeping in your area. Some regions have specific guidelines on hive placement, maximum number of hives allowed per property, distance from neighboring properties or public spaces, registration requirements, and more.
4. Safety Precautions
Bee stings can be painful and potentially dangerous for individuals with allergies or sensitivities. Take necessary safety precautions by wearing protective gear like veils, gloves, suits when working with bees near hives; this will minimize risks associated with accidental stings.
5. Hive Placement
Selecting an appropriate location for hive placement is crucial for both the productivity of the bees and the convenience of beekeepers. Choose a spot that is easily accessible for regular inspections and maintenance, away from high human traffic areas or potential disturbances, and with enough sunlight for bees to thrive.
6. Bee Breed Selection
Consider the different breeds of honeybees available and their suitability to your local climate and conditions. Some species may be more resilient to certain diseases or better adapted to your specific environment than others. Consult local beekeeping associations or experienced beekeepers for advice on suitable bee breeds.
7. Education and Training
Prioritize learning about proper beekeeping techniques, hive management, disease prevention, pest control methods, and honey extraction processes. Attend workshops, join local beekeeping clubs or associations, read reputable books on the subject matter, watch educational videos online – continuous education will help you become a knowledgeable beekeeper.
By considering these key factors when starting your journey into beekeeping in your area, you can establish a thriving apiary while ensuring the well-being of your bees and compliance with any relevant regulations. Remember that responsible care for your bees will result in healthy colonies that produce delicious honey while supporting local pollination efforts.
Embarking on a journey into beekeeping requires not only enthusiasm but also an understanding of local regulations and permits. To ensure a smooth start to your beekeeping venture, it is crucial to navigate the permitting process effectively. Here are some essential steps to follow:
1. Research Local Regulations
The first step in obtaining a beekeeping permit is to familiarize yourself with the specific regulations in your area. Check with your local government or agricultural department to determine if any restrictions or guidelines exist for keeping bees.
2. Determine Zoning Requirements
Zoning regulations often play a significant role in beekeeping permits. Different areas may have specific zoning requirements that dictate whether you can keep bees on your property, the number of hives allowed, and their placement within your premises.
3. Contact Local Beekeeping Associations
Local beekeeping associations are valuable resources when it comes to understanding the permitting process and complying with local regulations. Reach out to these organizations for guidance, advice, and information on how to obtain necessary permits.
4. Complete Permit Applications
Once you have gathered all relevant information about local regulations, it’s time to complete the permit application forms required by your local authorities or agricultural department.
5. Submit Supporting Documentation
In addition to completing permit applications, you may need to submit supporting documentation such as site plans indicating hive locations, proof of proper hive management techniques (e.g., regular inspections), and evidence of appropriate safety measures like adequate fencing or signage.
6. Pay Any Required Fees
In some cases, there may be fees associated with obtaining a beekeeping permit. Ensure that you are aware of any financial obligations and make the necessary payments promptly to avoid delays in the permitting process.
7. Schedule Inspections
Once your application is submitted, local authorities may schedule inspections to verify your compliance with regulations. Be prepared for these inspections by ensuring that your hives meet all required standards and safety measures.
8. Maintain Communication
Throughout the permitting process, it is important to maintain open lines of communication with local authorities or agricultural departments. Stay updated on the progress of your application and address any concerns or questions they may have promptly.
Navigating the permitting process for beekeeping can seem daunting at first, but with thorough research, adherence to regulations, and effective communication, you can obtain the necessary permits and embark on a successful beekeeping journey.
V. Compliance with Zoning and Land Use Regulations for Beekeeping
When it comes to beekeeping, it is essential to understand and comply with the zoning and land use regulations set by your local authorities. These regulations are put in place to ensure the safety of both beekeepers and the community at large.
1. Understanding Zoning Laws
Zoning laws dictate how land can be used within a specific area. They categorize different zones, such as residential, commercial, or agricultural, each with its own set of rules and restrictions. Before starting a beekeeping operation, it is crucial to determine whether your property falls within a zone that permits this activity.
2. Checking Local Restrictions
In addition to zoning laws, some municipalities may have specific restrictions on beekeeping beyond what general zoning allows. These restrictions could include limitations on the number of hives allowed per property or requirements for hive placement distances from neighboring structures or public areas.
3. Obtaining Permits
In certain areas, obtaining permits or licenses may be necessary before engaging in beekeeping activities legally. This process ensures that you meet all safety standards and have taken necessary precautions to protect both bees and humans.
4. Communicating with Neighbors
Beekeeping involves keeping colonies of bees in close proximity to human dwellings; thus, it’s important to communicate with neighbors about your intentions beforehand. By sharing information about your plans for responsible beekeeping practices and addressing any concerns they might have upfront, you can foster positive relationships within your community.
5. Addressing Safety Concerns
Zoning regulations often prioritize public safety when it comes to potential risks associated with bees escaping from hives or stinging incidents occurring. As a beekeeper, it is crucial to take necessary precautions, such as providing adequate water sources for bees and ensuring proper hive maintenance, to minimize these risks and demonstrate your commitment to safety.
6. Staying Updated
Local regulations can change over time, so it’s important to stay updated on any amendments or new requirements that may affect your beekeeping operation. Regularly check with local authorities or beekeeping associations for any updates or changes in regulations.
By understanding and complying with zoning and land use regulations related to beekeeping, you can ensure a harmonious relationship between your hobby/business and the community while promoting the vital role that bees play in our ecosystem.
VI. Ensuring Safety and Security Measures in Beekeeping Operations
Beekeeping operations require proper safety and security measures to ensure the well-being of both the beekeepers and the bees. By implementing these measures, beekeepers can minimize risks, protect their investment, and contribute to a sustainable beekeeping industry.
1. Protective Gear
One crucial aspect of safety in beekeeping is wearing appropriate protective gear. Beekeepers should always wear a full-body suit, gloves, veil or helmet with a mesh faceguard, and boots. This gear provides essential protection against stings from defensive bees.
2. Handling Techniques
Beekeepers must learn proper handling techniques to minimize stress on the bees during hive inspections or honey harvesting activities. Gentle movements and minimal disruption help maintain hive health while reducing aggression from the colony.
3. Hive Placement
The location of hives also plays a significant role in safety considerations for both humans and bees. Hives should be placed away from high-traffic areas to avoid accidental disturbances or encounters with curious passersby who may not be aware of the potential dangers posed by bees.
4. Regular Inspections
Frequent inspections are necessary for ensuring hive health as well as identifying any signs of diseases or parasites that could harm the colony or spread to nearby hives. Regular inspections allow beekeepers to take prompt action when needed.
5. Pest Management
Pest management is an integral part of maintaining healthy colonies in beekeeping operations. Integrated pest management techniques can help control mites, beetles, wax moths, and other pests without harming the bees themselves or introducing harmful chemicals into the environment.
6. Water Sources
Providing a clean and accessible water source near the beehives is essential for beekeeping safety. Bees require water for cooling the hive, diluting honey, and maintaining humidity levels. Without a nearby water source, bees may venture to neighboring properties or public areas in search of water, potentially resulting in conflicts.
7. Proper Record Keeping
Maintaining accurate records is crucial for both safety and legal compliance in beekeeping. It allows beekeepers to track hive inspections, treatments, honey production, and other important aspects of their operations. These records help identify patterns or issues that need attention while also providing documentation if required by local regulations.
By prioritizing safety and security measures in beekeeping operations, beekeepers can create a conducive environment for healthy colonies while ensuring their own well-being. Remember that adherence to local regulations regarding safety protocols is vital to maintain harmonious relationships with neighbors and authorities alike.
VII. Best Practices for Maintaining Beehives in Accordance with Local Regulations
When it comes to beekeeping, it is crucial to adhere to local regulations and guidelines to ensure the well-being of the bees and maintain a harmonious relationship with your community. Here are some best practices that will help you navigate through these regulations:
1. Familiarize Yourself with Local Laws
Prior to starting your beekeeping journey, take the time to thoroughly research and understand the specific laws and regulations governing beekeeping in your area. This includes permits, hive placement requirements, maximum number of hives allowed, and any restrictions on certain breeds.
2. Register Your Hives
In many jurisdictions, beekeepers are required to register their hives with local agricultural or environmental agencies. This enables authorities to keep track of bee populations and helps prevent the spread of diseases among colonies.
3. Educate Yourself on Bee Health
Maintaining healthy bees is not only important for their well-being but also crucial for preventing potential issues within your community. Stay updated on best practices for disease prevention, pest control methods, proper nutrition, and hive management techniques.
4. Provide Adequate Food Sources
Beekeepers should ensure that there are sufficient food sources available near their apiaries throughout the year. Planting diverse flowering plants in proximity can provide bees with a variety of nectar sources while enhancing biodiversity in your surroundings.
5. Practice Responsible Pest Management
Pests such as varroa mites can have devastating effects on beehive populations if left untreated. Regularly monitor your hives for signs of infestation and employ appropriate pest management strategies approved by local authorities or experienced beekeepers.
6. Hive Hygiene and Maintenance
Regularly inspect your hives for signs of disease, damage, or deterioration. Clean and disinfect equipment between uses to prevent the spread of pathogens. It is also important to maintain proper ventilation and hive insulation to ensure the bees’ comfort during different seasons.
7. Consider Neighbors and Public Safety
Beekeeping in urban or suburban areas requires additional consideration for neighbors and public safety. Place your hives in suitable locations away from high foot traffic areas, provide adequate barriers if necessary, and communicate with neighbors about your beekeeping activities to address any concerns they may have.
8. Continual Learning
Beekeeping is a lifelong learning process, so it’s important to stay informed about new research findings, emerging best practices, and changes in local regulations related to beekeeping. Attend workshops or join local beekeeping associations where you can exchange knowledge with experienced beekeepers.
By following these best practices while adhering to local regulations, you can enjoy a successful journey as a responsible beekeeper while contributing positively to both the environment and your community.
VIII. Frequently Asked Questions about Beekeeping and Local Regulations
Here are some common questions people have regarding beekeeping and the local regulations that govern it:
1. Is beekeeping legal in my area?
The legality of beekeeping varies depending on your location. It is essential to research and understand the local regulations related to keeping bees before you start. Contact your local government or agricultural department for information on permits, restrictions, and guidelines specific to your area.
2. Do I need a permit to keep bees?
Many regions require beekeepers to obtain a permit or license before starting their operations, even if they own private property. These permits help authorities track the number of hives in an area, ensure proper hive management practices, and prevent any potential issues with neighboring properties or public safety concerns.
3. What are the typical zoning requirements for beekeeping?
Zoning requirements differ from place to place but generally revolve around keeping bees at safe distances from neighboring properties or public spaces such as schools and parks. Zoning regulations may also specify minimum lot sizes for beekeeping activities.
4. Are there any restrictions on hive placement?
The placement of beehives is often regulated due to potential nuisance factors like noise, odor, or excessive swarming that could impact nearby residences or businesses adversely.
5.What precautions should I take regarding neighbors?
To maintain good relationships with your neighbors while practicing beekeeping, it’s advisable to inform them about your intentions beforehand—sharing information about honeybees’ gentle nature and explaining how you plan to manage your hives responsibly can help alleviate any concerns they may have.
6. Are there any regulations regarding hive maintenance and inspection?
Local authorities may have guidelines in place to ensure the proper care, inspection, and maintenance of beehives. These regulations aim to prevent the spread of diseases or pests that could harm honeybee populations or other agricultural activities.
In many areas, selling homemade honey and other bee-related products is allowed but may require additional permits, certifications, or inspections to ensure food safety standards are met.
8. How can I stay updated with changes in local beekeeping regulations?
To stay informed about any updates or changes in local beekeeping regulations, it is recommended to join local beekeeping associations or organizations. They can provide you with the latest information and resources related to your area’s specific rules and guidelines.
These frequently asked questions will give you a good starting point for understanding the relationship between beekeeping and local regulations. However, it is crucial to consult your local authorities directly for accurate and up-to-date information pertaining specifically to your location.
IX. Conclusion: The Role of Local Regulations in Promoting Sustainable Beekeeping Practices
Firstly, local regulations help establish guidelines for beekeepers regarding hive placement and management practices. This ensures that bees have access to adequate food sources and water while minimizing any potential negative impact on neighboring communities.
Secondly, these regulations often require beekeepers to register their hives with local authorities. This registration process helps create a database of active apiaries within the area, enabling better monitoring and disease control measures. It also facilitates communication between beekeepers and relevant authorities for educational purposes or in case of emergencies.
“By implementing local regulations that support sustainable beekeeping practices, communities can contribute to the conservation of pollinators.”
Promoting Pollinator-Friendly Landscapes
Local regulations can encourage landowners to create pollinator-friendly landscapes by incorporating native plants that provide diverse sources of pollen and nectar throughout the year. By doing so, they not only support honeybees but also other essential pollinators such as butterflies and wild bees.
Educating Beekeepers on Best Practices
A key aspect of sustainable beekeeping is ensuring that practitioners are well-informed about best management practices. Local regulations can mandate educational programs or workshops for aspiring or experienced beekeepers. These initiatives can cover topics such as hive health maintenance, disease prevention strategies, responsible pesticide use, swarm management techniques, and honey extraction methods.
Collaboration with Farmers
Farmers play a significant role in supporting healthy honeybee populations through responsible agricultural practices. Local regulations can encourage collaboration between beekeepers and farmers, promoting the use of bee-friendly farming methods that reduce or eliminate the use of harmful pesticides and herbicides.
Monitoring and Enforcement
Finally, local regulations should include provisions for monitoring compliance with sustainable beekeeping practices. Regular inspections by designated authorities can help identify any violations or potential risks to honeybee health. Strict enforcement measures may also be necessary to deter illegal activities that could harm both bees and their habitats.

Andrew Boyer is an accomplished individual with a deep-rooted passion for bees and their conservation. Born and raised in a small town in Oregon, Andrew developed an early fascination with nature and the environment. He pursued his education at the prestigious University of Oregon, where he obtained a Bachelor’s degree in Environmental Science with a specialization in Entomology. During his time at university, Andrew conducted extensive research on the behavior and ecological impact of bees, earning him recognition from his peers and professors. His dedication to the field led him to internships at local beekeeping associations, where he honed his skills in hive management and honey production. Andrew’s expertise in beekeeping and his commitment to environmental sustainability make him a valuable asset in the conservation of these vital pollinators.
