Contents
- I. Introduction to Beekeeping and Global Sustainability Goals
- II. The Importance of Beekeeping in Achieving Global Sustainability
- III. The Role of Bees in Ecosystem Balance and Biodiversity Preservation
- IV. Beekeeping as a Sustainable Agricultural Practice
- V. Beekeeping and the Conservation of Pollinators
- VI. The Economic Benefits of Beekeeping for Local Communities
- VII. Beekeeping and the Reduction of Pesticide Use
- VIII. Beekeeping and the Promotion of Organic Farming Practices
- IX. Frequently Asked Questions about Beekeeping and Global Sustainability Goals
- 1. Why is beekeeping important for global sustainability goals?
- 2. How does beekeeping contribute to biodiversity conservation?
- 3. Can small-scale beekeepers make a significant difference in global sustainability efforts?
- 4. How does urban beekeeping contribute to sustainable development?
- 5. Are there any risks associated with commercialized industrialized apiculture?
- 6. How can individuals contribute to beekeeping and global sustainability goals?
- 7. What are some challenges faced by beekeepers in achieving sustainability goals?
- 8. How does sustainable beekeeping contribute to poverty alleviation?
- 9. Can traditional knowledge enhance modern sustainable beekeeping practices?
- 10. How does promoting responsible consumption support global sustainability efforts related to beekeeping?
I. Introduction to Beekeeping and Global Sustainability Goals

Beekeeping, also known as apiculture, is the practice of rearing and managing honeybees in artificial hives. This ancient tradition has gained significant importance in recent years due to its crucial role in sustainable development and achieving global sustainability goals.
The Importance of Bees for Ecosystems
Bees play a vital role in pollinating plants, which is essential for the reproduction and survival of numerous plant species. It is estimated that nearly 80% of flowering plants rely on bees or other pollinators for successful pollination. This process leads to the production of fruits, vegetables, seeds, and nuts that form a significant part of our diets.
Furthermore, bees contribute to biodiversity by aiding the cross-pollination between different plant species. This ensures genetic diversity within plant populations, making them more resilient to diseases and environmental changes.
Beekeeping’s Impact on Global Sustainability Goals
Beekeeping aligns with several global sustainability goals set by organizations like the United Nations Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs). Here are some ways beekeeping contributes:
- Poverty Alleviation: Beekeeping offers income-generation opportunities for small-scale farmers in rural areas. By selling honey products such as honeycomb, royal jelly, beeswax candles, or even renting out beehives for crop pollination services.
- Food Security: The increased pollination provided by managed beehives helps enhance crop yields and improve food security globally.
- Ecosystem Preservation: Through bee conservation efforts and habitat restoration initiatives near apiaries (bee farms), beekeepers contribute to preserving ecosystems’ health.
- Climate Change Mitigation: Bees aid in the pollination of trees and plants that sequester carbon dioxide, a greenhouse gas responsible for climate change. Therefore, beekeeping indirectly contributes to mitigating climate change.
The Challenges Faced by Beekeeping
Beekeeping faces several challenges that threaten honeybee populations worldwide. These include:
- Pesticide Use: The use of harmful pesticides in agriculture poses a significant threat to bees’ health and survival.
- Habitat Loss: Urbanization, deforestation, and intensive agricultural practices lead to the destruction of natural habitats for bees.
- Diseases and Pests: Honeybees are susceptible to various diseases and pests, such as Varroa mites, which can devastate entire colonies if left unmanaged.
- Climate Change: Changes in temperature patterns and extreme weather events disrupt the delicate balance required for successful beekeeping.
To address these challenges effectively, it is crucial to promote sustainable beekeeping practices and raise awareness about the importance of bees in achieving global sustainability goals. By supporting beekeepers, implementing pollinator-friendly policies, and reducing pesticide usage through organic farming methods, we can ensure a brighter future for both honeybees and our planet’s sustainability efforts.
II. The Importance of Beekeeping in Achieving Global Sustainability
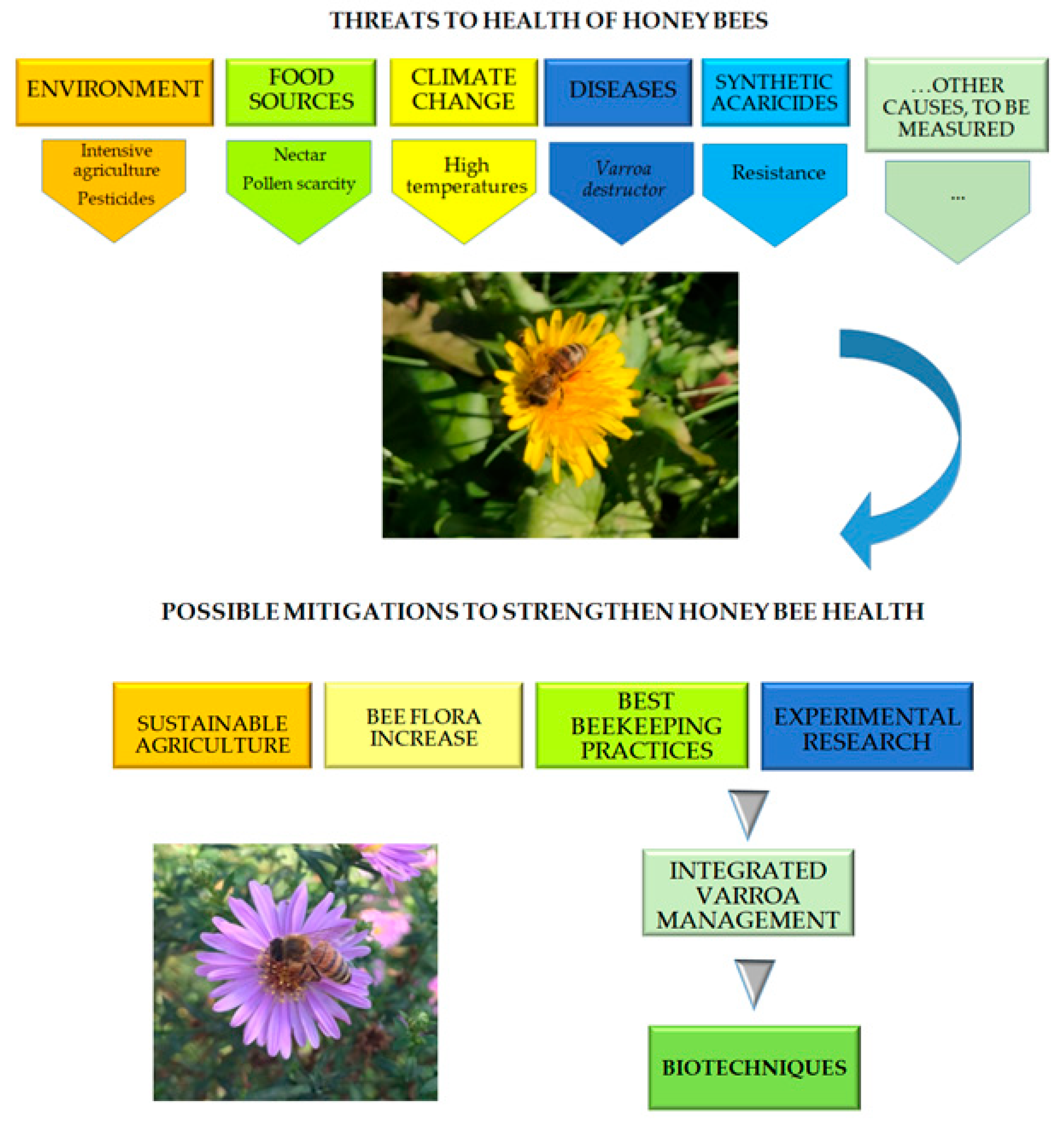
Beekeeping plays a crucial role in achieving global sustainability goals. Bees are not only important for honey production but also for the pollination of crops, which is vital for food security and biodiversity conservation.
Promoting Biodiversity
Beekeeping contributes to the preservation and enhancement of biodiversity. Bees play a pivotal role in pollinating flowering plants, including fruits, vegetables, nuts, and seeds. Without bees, many plant species would struggle to reproduce and eventually decline in numbers or even become extinct. By actively participating in beekeeping practices, we can provide bees with safe habitats and sources of nectar throughout the year.
Enhancing Food Security
One-third of our global food supply relies on pollinators like bees. Through their diligent work as pollinators, bees help fertilize flowers and enable them to produce fruits or seeds. This process ensures that we have an abundant supply of nutritious food such as fruits, vegetables, nuts, and grains. By supporting beekeeping initiatives worldwide, we can contribute to strengthening food security for present and future generations.
Sustainable Agriculture Practices
Beekeepers often adopt sustainable agriculture practices that support ecological balance while minimizing harm to the environment. They prioritize organic farming methods by avoiding harmful pesticides that can be detrimental to both bees’ health and overall ecosystem stability. Beekeepers also encourage crop diversification by growing various types of plants that provide ample nutrition for their colonies throughout different seasons.
Economic Benefits
Aside from its environmental contributions, beekeeping offers significant economic benefits as well. Local economies thrive through honey production and sales-related activities such as apiculture tourism or manufacturing value-added products like beeswax candles or cosmetics made from honey. By supporting beekeepers and consuming their products, we can help stimulate local economies and create employment opportunities.
Preserving Traditional Knowledge
Beekeeping is deeply rooted in many cultures around the world, representing centuries of traditional knowledge passed down through generations. By actively engaging in beekeeping practices, we preserve this cultural heritage while also promoting sustainable land use practices that have been refined over time.
III. The Role of Bees in Ecosystem Balance and Biodiversity Preservation

Bees play a crucial role in maintaining the balance of ecosystems and preserving biodiversity. Their significance goes beyond honey production, as they are essential pollinators for many flowering plants, including crops that provide us with food.
Pollination: A Vital Process
Pollination is a vital process where bees transfer pollen from the male part of a flower to the female part, enabling fertilization and seed production. This process facilitates plant reproduction and ensures genetic diversity within plant populations. Bees are efficient pollinators due to their ability to collect nectar while transferring pollen from flower to flower.
Biodiversity Preservation
Bees contribute significantly to biodiversity preservation by facilitating the reproduction of various plant species. Through their interactions with flowers, they help maintain healthy ecosystems by supporting diverse plant communities. The presence of different plant species creates habitats for other organisms such as insects, birds, and mammals.
Ecosystem Services
Bees provide essential ecosystem services that benefit both humans and wildlife. In addition to pollination, bees also help improve soil fertility through their activities as they visit numerous flowers in search of nectar and pollen. As they move from one flowering plant to another, they inadvertently distribute microorganisms important for soil health.
Food Production
The role of bees in food production cannot be overstated. Many fruits, vegetables, nuts, and oilseeds rely on bee pollination for successful crop yields. Without bees’ assistance in transferring pollen between flowers, these crops would face significant challenges in reproduction leading to reduced harvests or even crop failures.
Threats Faced by Bees
Despite their importance, bees are facing numerous threats that jeopardize their populations. Factors such as habitat loss, pesticide use, climate change, and diseases have led to declines in bee populations worldwide. These challenges not only impact the survival of bees but also disrupt the delicate balance of ecosystems they support.
IV. Beekeeping as a Sustainable Agricultural Practice

Beekeeping, also known as apiculture, is not only a fascinating hobby but also a sustainable agricultural practice that plays a vital role in maintaining global sustainability goals. This ancient practice of rearing and managing honeybees has numerous environmental, economic, and social benefits.
Promoting Biodiversity
Beekeeping contributes significantly to the preservation of biodiversity. Bees are essential pollinators that facilitate the reproduction of flowering plants by transferring pollen grains from male flower parts to female flower parts. As they forage for nectar and pollen, bees inadvertently cross-pollinate various plant species, ensuring their survival and genetic diversity.
Supporting Food Security
The agricultural sector heavily relies on pollinators like bees to ensure food security. Honeybees play an integral role in the pollination of crops such as fruits, vegetables, nuts, and oilseeds. Without adequate pollination services provided by bees, crop yields would suffer tremendously.
Promoting Ecosystem Health
By promoting ecosystem health through pollination activities, beekeeping indirectly helps maintain healthy ecosystems. Pollinated plants provide habitats and food sources for other organisms in the ecosystem chain while contributing to soil fertility and preventing erosion.
Economic Benefits
Beekeeping offers significant economic benefits at both local and global levels. The production of honey is one of the most apparent economic advantages associated with beekeeping. Honey serves as a natural sweetener with various health benefits and has high demand both locally and internationally.
Social Impact
In addition to its environmental benefits, beekeeping positively impacts local communities by providing income-generating opportunities for small-scale farmers or individuals interested in pursuing beekeeping as a profession. It fosters community involvement, knowledge sharing, and cultural preservation.
Beekeeping is an exemplary sustainable agricultural practice that demonstrates the interdependence between humans and nature. By embracing beekeeping practices, individuals can contribute to preserving biodiversity, supporting food security, promoting ecosystem health, reaping economic benefits, and making positive social impacts. It is essential for governments and communities to recognize the significance of beekeeping in achieving global sustainability goals.
V. Beekeeping and the Conservation of Pollinators
Beekeeping plays a crucial role in the conservation of pollinators, contributing to global sustainability goals. Bees, as primary pollinators, are responsible for the fertilization of flowers and plants, ensuring their reproduction and genetic diversity. Without this essential process, ecosystems would suffer significant disruptions.
The Importance of Pollinators
Pollination is vital for a wide array of plant species, including fruits, vegetables, nuts, and seeds. It helps sustain biodiversity by facilitating the reproduction of flowering plants that serve as habitat for other organisms. Additionally, pollination supports food production by enhancing crop yields and improving their quality.
By engaging in cross-pollination activities during their search for nectar and pollen-rich flowers, bees transfer pollen grains from male reproductive organs (anthers) to female reproductive organs (stigmas). This process ensures successful fertilization and subsequent seed formation.
Beekeeping’s Role in Conserving Pollinators
Beekeepers play a vital role in conserving pollinators through beekeeping practices aimed at supporting healthy honeybee populations. They provide suitable habitats for bees by setting up hives or beehives that offer protection from predators and adverse weather conditions.
In addition to providing sheltered spaces for bees to thrive, beekeepers also take measures to ensure adequate nutrition sources throughout the year. They cultivate diverse floral resources near beehives or strategically move them to areas with abundant nectar-producing plants during different seasons.
Furthermore, responsible beekeepers adopt sustainable management techniques that prioritize hive health while minimizing negative impacts on wild bee populations. Regular inspections help identify diseases or pests early on so appropriate measures can be taken promptly without affecting surrounding ecosystems negatively.
Promoting Awareness and Education
Another crucial aspect of beekeeping’s contribution to pollinator conservation lies in promoting awareness and education. Beekeepers often engage with local communities, schools, and environmental organizations to raise awareness about the importance of bees and the need for their protection.
Through educational initiatives, beekeepers help people understand the delicate balance between human activities, biodiversity, and ecosystem health. They emphasize the role individuals can play in creating pollinator-friendly environments by planting native flowering plants, avoiding harmful pesticides, and providing suitable nesting sites for wild bees.
Beekeeping associations also collaborate with researchers to support scientific studies on bees’ behavior, health issues, and habitat requirements. This research helps develop better management practices that benefit both honeybees kept by beekeepers and wild pollinators.
Conclusion
Beekeeping serves as a powerful tool for conserving pollinators while contributing to global sustainability goals. By providing suitable habitats, ensuring nutrition sources year-round, adopting sustainable management techniques, promoting awareness through education initiatives,and supporting scientific research efforts; beekeepers actively contribute to maintaining healthy ecosystems that rely on diverse populations of pollinators like bees.
VI. The Economic Benefits of Beekeeping for Local Communities
Beekeeping, also known as apiculture, not only plays a crucial role in pollination and honey production but also provides significant economic benefits to local communities. Let’s explore how beekeeping contributes to the financial well-being of these communities.
1. Job Creation
Beekeeping offers employment opportunities for individuals within local communities. From beekeepers who manage the hives to workers involved in honey extraction and processing, various jobs are created along the supply chain. This not only helps reduce unemployment rates but also stimulates economic growth in rural areas.
2. Honey Production
Honey is one of the primary products derived from beekeeping and has a high demand both locally and globally. Local communities can capitalize on this by producing quality honey that can be sold directly or through cooperatives or farmer markets. The revenue generated from honey sales can contribute significantly to the income of beekeepers and their communities.
3. Value-added Products
In addition to honey, other value-added products such as beeswax, pollen, royal jelly, propolis, and bee venom can be extracted from beehives. These products have various applications in industries like cosmetics, pharmaceuticals, food supplements, and alternative medicine. By diversifying their product range, beekeepers can tap into different markets and increase their earnings.
4. Ecotourism Opportunities
Beekeeping activities attract tourists who are interested in learning about sustainable agriculture practices and experiencing nature-based tourism activities firsthand. Bee farms or apiaries can serve as educational centers where visitors gain insights into the importance of bees for ecosystem balance while enjoying guided tours or participating in workshops related to hive management or honey tasting sessions.
5. Environmental Benefits
Beekeeping promotes biodiversity and enhances the overall health of ecosystems. By maintaining beehives, local communities contribute to the pollination of plants, which leads to increased agricultural yields for farmers in the vicinity. This indirect economic benefit helps boost crop production and ensures food security at a local level.
VII. Beekeeping and the Reduction of Pesticide Use
Beekeeping plays a crucial role in addressing the issue of pesticide use and promoting sustainable agricultural practices. With the decline in global bee populations, it is more important than ever to focus on reducing pesticide use to protect these vital pollinators.
The Impact of Pesticides on Bees
Pesticides, particularly insecticides, have been linked to significant declines in bee populations worldwide. These chemicals can harm bees directly through contact or ingestion and indirectly by contaminating their food sources and habitat. The exposure to pesticides weakens bees’ immune systems, affects their navigation abilities, disrupts their reproductive cycles, and ultimately leads to colony collapse disorder.
Promoting Integrated Pest Management (IPM)
One approach that can help reduce pesticide use in agriculture is implementing Integrated Pest Management (IPM) strategies. IPM focuses on using a combination of techniques such as biological control methods, crop rotation, habitat manipulation, and targeted pesticide application only when necessary.
The Role of Beekeeping in IPM
Beekeepers play an essential role in IPM by providing natural pest control services for farmers. Honeybees not only pollinate crops but also help suppress pests like aphids and mites through grooming behaviors inside the hive. By maintaining healthy beehives near agricultural fields, beekeepers contribute to reducing the need for synthetic pesticides.
Promoting Organic Farming Practices
Another way beekeeping contributes to reducing pesticide use is through its association with organic farming practices. Organic farmers prioritize using natural pest deterrents such as companion planting or introducing beneficial insects instead of relying on chemical pesticides that can harm bees.
Educating Farmers about Bee-Friendly Practices
Beekeepers can also play a crucial role in educating farmers about the importance of adopting bee-friendly practices. By raising awareness about the detrimental effects of pesticides on bees and offering alternative approaches, beekeepers can help shift agricultural practices towards more sustainable and environmentally friendly methods.
The Importance of Collaboration
Addressing the issue of pesticide use requires collaboration between beekeepers, farmers, policymakers, and researchers. By working together, we can develop innovative solutions that prioritize both agricultural productivity and environmental sustainability while safeguarding our precious pollinators.
VIII. Beekeeping and the Promotion of Organic Farming Practices
Beekeeping plays a vital role in promoting organic farming practices, making it an essential component of global sustainability goals. The symbiotic relationship between bees and plants contributes to the overall health and productivity of agricultural ecosystems.
1. Pollination Services
Bees are crucial pollinators that facilitate the reproduction of flowering plants, including many food crops. Through their foraging activities, bees transfer pollen from male flower parts (anthers) to female parts (stigma), enabling fertilization and subsequent fruit or seed production.
This natural process is fundamental for maintaining biodiversity, ensuring genetic diversity within plant populations, and increasing crop yields. By keeping honeybees or supporting wild bee populations, farmers can enhance pollination services on their farms.
2. Natural Pest Control
Honeybees not only contribute to pollination but also play a role in natural pest control within organic farming systems. Their presence on farms can help reduce pest populations by preying on common crop pests such as aphids and mites.
The use of synthetic pesticides is limited in organic farming practices due to their potential harm to beneficial insects like bees. Therefore, encouraging the presence of honeybees through beekeeping provides a sustainable alternative for pest management without relying heavily on chemical interventions.
3. Soil Fertility Enhancement
Beekeeping promotes soil fertility through the production of honeybee-collected pollen known as “bee bread.” Bee bread contains essential nutrients required by honeybee larvae during their development stages.
In addition to feeding young bees, bee bread also benefits soil health when used as an organic fertilizer rich in nitrogen, phosphorus, potassium, enzymes, and microorganisms that aid decomposition processes and nutrient cycling.
4. Biodiversity Conservation
Beekeeping contributes to the conservation of bee species, including native wild bees that may be threatened by habitat loss and pesticide exposure. By providing suitable habitats and promoting sustainable beekeeping practices, we can help protect these important pollinators.
Furthermore, maintaining diverse plant species on farms to support honeybees and other pollinators also enhances overall biodiversity. This diversity in flora attracts a wide range of beneficial insects, birds, and mammals that contribute to a balanced ecosystem.
5. Education and Awareness
Beekeeping serves as an educational tool to raise awareness about the importance of bees in sustaining agricultural systems. By actively engaging in beekeeping activities, farmers and communities gain firsthand knowledge about the ecological processes involved in pollination and organic farming.
This increased understanding fosters a deeper appreciation for nature’s interconnectedness, inspiring individuals to adopt more sustainable farming practices beyond just beekeeping itself.
In conclusion, integrating beekeeping into organic farming practices aligns with global sustainability goals by enhancing pollination services, natural pest control methods, soil fertility enhancement through the use of bee bread as fertilizer, biodiversity conservation efforts, and raising awareness about ecological processes. Embracing this holistic approach promotes environmentally friendly agriculture while safeguarding our food production systems for future generations
IX. Frequently Asked Questions about Beekeeping and Global Sustainability Goals
1. Why is beekeeping important for global sustainability goals?
Beekeeping plays a crucial role in achieving global sustainability goals due to its positive impact on the environment and food security. Bees are essential pollinators, responsible for fertilizing plants that produce fruits, vegetables, and nuts. By promoting beekeeping practices, we can enhance biodiversity, support ecosystems, and ensure a sustainable supply of food for future generations.
2. How does beekeeping contribute to biodiversity conservation?
Beekeeping helps conserve biodiversity by providing habitats for bees and other pollinators. Beekeepers promote the preservation of natural areas rich in diverse plant species that sustain honeybees’ health and well-being. By maintaining healthy colonies, beekeepers contribute to the overall conservation of various plant species that depend on pollination.
3. Can small-scale beekeepers make a significant difference in global sustainability efforts?
Absolutely! Small-scale beekeepers play a vital role in supporting global sustainability efforts. Their collective impact is substantial as they contribute to local ecosystems’ resilience by increasing pollination rates and fostering biodiversity conservation at a regional level.
4. How does urban beekeeping contribute to sustainable development?
Urban beekeeping offers numerous benefits for sustainable development within cities or urban areas. It promotes green spaces creation or revitalization while contributing to local food production through increased pollination rates in community gardens or rooftop farms.
5. Are there any risks associated with commercialized industrialized apiculture?
The commercialization and industrialization of apiculture present several risks that need careful management to ensure environmental sustainability remains intact: excessive use of pesticides harming bees’ health; spreading diseases due to close proximity of hives; and potential negative impacts on local biodiversity due to monoculture practices for honey production.
6. How can individuals contribute to beekeeping and global sustainability goals?
Individuals can support beekeeping and global sustainability goals by planting pollinator-friendly gardens, avoiding the use of pesticides harmful to bees, supporting local beekeepers by purchasing their products, and raising awareness about the importance of bees in ecosystems.
7. What are some challenges faced by beekeepers in achieving sustainability goals?
Beekeepers face various challenges in achieving sustainability goals, including climate change effects on honeybee populations, pesticide exposure risks, loss of natural habitats due to urbanization or agricultural expansion, and limited access to resources or knowledge for sustainable beekeeping practices.
8. How does sustainable beekeeping contribute to poverty alleviation?
Sustainable beekeeping provides income-generating opportunities for communities living in rural areas or regions with limited economic prospects. By harnessing the potential of honey production and other hive products such as beeswax or propolis, sustainable beekeeping can help alleviate poverty while promoting environmental conservation.
9. Can traditional knowledge enhance modern sustainable beekeeping practices?
Absolutely! Traditional knowledge passed down through generations plays a vital role in shaping modern sustainable beekeeping practices. Indigenous communities often possess valuable insights into maintaining healthy colonies while preserving ecosystems’ balance that can be integrated into contemporary approaches.
Promoting responsible consumption involves making informed choices about purchasing sustainably produced honey products from local sources rather than supporting mass-produced alternatives associated with detrimental environmental impacts. By opting for responsibly sourced honey products, consumers directly contribute to global sustainability efforts linked with ethical apiculture practices.

Andrew Boyer is an accomplished individual with a deep-rooted passion for bees and their conservation. Born and raised in a small town in Oregon, Andrew developed an early fascination with nature and the environment. He pursued his education at the prestigious University of Oregon, where he obtained a Bachelor’s degree in Environmental Science with a specialization in Entomology. During his time at university, Andrew conducted extensive research on the behavior and ecological impact of bees, earning him recognition from his peers and professors. His dedication to the field led him to internships at local beekeeping associations, where he honed his skills in hive management and honey production. Andrew’s expertise in beekeeping and his commitment to environmental sustainability make him a valuable asset in the conservation of these vital pollinators.
