Contents
- I. Introduction to Beekeeping and Eco-Friendly Practices
- II. Benefits of Beekeeping for the Environment
- III. Importance of Eco-Friendly Beekeeping Practices
- IV. Essential Tools and Equipment for Eco-Friendly Beekeeping
- V. Sustainable Beekeeping Techniques for a Healthy Bee Colony
- VI. The Role of Organic Beekeeping in Promoting Biodiversity
- VII. Beekeeping and Pollination: Enhancing Crop Yield and Quality
- VIII. Common Challenges in Beekeeping and How to Address Them
- IX. Frequently Asked Questions about Beekeeping and Eco-Friendly Practices
- 1. How can I start my own beekeeping operation?
- 2. Are there any specific requirements for maintaining eco-friendly practices in beekeeping?
- 3. Can I keep bees even if I live in an urban area?
- 4. What are some benefits of keeping bees?
- 5. How can I contribute to saving the bees?
- 6. Are there any risks or challenges associated with beekeeping?
- 7. How much time does beekeeping require?
- 8. Can children get involved in beekeeping?
- 9. What should I do if I find a swarm of bees on my property?
- 10. Is it possible to keep bees without harvesting their honey?
I. Introduction to Beekeeping and Eco-Friendly Practices

Beekeeping, also known as apiculture, is the practice of rearing and managing honey bees for various purposes, such as honey production, pollination services, and beeswax utilization. It is not only a fascinating hobby but also an essential agricultural activity that contributes to our ecosystem’s sustainability.
As we become more aware of the impact of human activities on the environment, eco-friendly practices in beekeeping have gained significant attention. These practices focus on ensuring the well-being of bees while minimizing any adverse effects on nature.
1. Importance of Beekeeping
Beekeeping plays a crucial role in pollination – a process vital for plant reproduction. Bees transfer pollen from one flower to another, enabling fertilization and seed formation. This process supports biodiversity by facilitating the growth and survival of various plants.
In addition to pollination services, beekeepers collect honey produced by bees. Honey has been used for centuries as a natural sweetener with numerous health benefits due to its antioxidant properties.
2. Eco-Friendly Beekeeping Practices
Eco-friendly beekeeping involves implementing sustainable methods that promote bee health and preserve the environment. Here are some key practices:
a) Organic Beekeeping
Organic beekeepers avoid using synthetic chemicals or antibiotics when treating diseases or pests affecting beehives. Instead, they rely on natural remedies like essential oils or organic acids.
b) Providing Diverse Forage
Beekeepers can create healthy environments for their colonies by planting diverse flowering plants that provide abundant nectar and pollen sources throughout the year. This ensures access to balanced nutrition for bees.
c) Natural Comb Building
Allowing bees to build their own comb using beeswax foundation sheets instead of pre-made plastic or wired frames promotes natural behavior and minimizes exposure to potentially harmful substances.
d) Integrated Pest Management
Beekeepers can implement integrated pest management (IPM) techniques to control pests without relying solely on chemical treatments. This approach includes regular monitoring, selective breeding of resistant bee strains, and implementing physical barriers.
3. Benefits of Eco-Friendly Beekeeping
Eco-friendly beekeeping practices yield various benefits:
– Improved bee health: By avoiding the use of harmful chemicals, bees can thrive in a more natural and healthy environment, reducing colony losses and promoting stronger populations.
– Conservation of biodiversity: Providing diverse forage options helps support a wider range of plant species, contributing to overall ecosystem health.
– Sustainable honey production: Eco-friendly practices ensure the production of high-quality honey while maintaining the delicate balance between human activities and ecological systems.
II. Benefits of Beekeeping for the Environment

Beekeeping not only provides us with delicious honey and other bee products but also plays a crucial role in maintaining a healthy environment. Here are some significant benefits that beekeeping brings to the environment:
Pollination of Plants
One of the most vital services that bees provide is pollination. As they fly from flower to flower collecting nectar, bees inadvertently transfer pollen grains, enabling plants to reproduce. This process is essential for the growth and proliferation of various plant species, including fruits, vegetables, and flowers. Without bees’ pollination efforts, many crops would suffer reduced yields or fail altogether.
Biodiversity Preservation
Beekeeping promotes biodiversity by supporting the survival and propagation of different plant species. Bees are known to visit a wide range of flowering plants in search of nectar and pollen. By interacting with diverse plant species, they contribute to maintaining a balanced ecosystem where different plants can thrive.
Environmental Conservation
Beekeepers prioritize sustainable practices that aim to protect both bees and their habitats. They often create dedicated spaces for beehives within natural landscapes or set up apiaries in urban areas where green spaces are limited. These efforts not only help conserve local ecosystems but also contribute to greening initiatives by providing necessary habitats for bees.
Improved Air Quality
The presence of thriving bee populations leads to improved air quality due to increased vegetation growth as a result of effective pollination processes. As more plants flourish through successful pollination, they absorb carbon dioxide from the atmosphere while releasing oxygen back into it – reducing greenhouse gases and improving air quality overall.
Pesticide Reduction
Beekeepers who practice organic beekeeping methods often avoid using harmful pesticides and chemicals in their hives. This approach helps protect bees from the adverse effects of these substances and prevents their accumulation in the environment. By promoting pesticide reduction, beekeeping contributes to maintaining a healthier and more sustainable ecosystem.
III. Importance of Eco-Friendly Beekeeping Practices

Eco-friendly beekeeping practices play a crucial role in preserving the delicate balance of our ecosystem and ensuring the well-being of both bees and humans. These practices prioritize sustainability, biodiversity, and the reduction of negative environmental impacts. Let’s explore why these practices are so important:
Promoting Bee Health
Eco-friendly beekeeping practices focus on providing optimal conditions for bee health and vitality. By avoiding the use of harmful pesticides, artificial additives, or antibiotics in beehives, we can protect bees from unnecessary harm. This helps maintain strong colonies with robust immune systems that are better equipped to combat diseases and pests.
Preserving Biodiversity
Beekeeping is not just about honey production; it also plays a vital role in pollination. Bees are essential pollinators responsible for fertilizing numerous plants that make up our diverse ecosystem. By adopting eco-friendly practices, we ensure that bees have access to a variety of nectar-rich flowers throughout the year, promoting biodiversity and supporting plant reproduction.
Reducing Chemical Contamination
Eco-friendly beekeepers avoid using synthetic chemicals that can contaminate honey and other hive products. This is beneficial for consumers who seek natural and untainted honey as well as for the environment at large. By avoiding chemical contamination, we contribute to cleaner air, water sources, and overall ecological balance.
Safeguarding Bee Habitat
Beekeepers committed to eco-friendly practices understand the importance of providing suitable habitats for their colonies. They create spaces where bees can thrive by planting native flora that supply abundant food sources throughout different seasons. Moreover, they strive to minimize disruptions during hive inspections or honey harvesting processes to reduce stress on bees.
Supporting Sustainable Agriculture
Eco-friendly beekeeping practices align with sustainable agricultural methods. Bees play a critical role in the pollination of crops, ensuring higher yields and better quality produce. By promoting eco-friendly beekeeping, we contribute to sustainable agriculture practices that benefit both farmers and consumers.
In conclusion, adopting eco-friendly beekeeping practices is not just about being environmentally conscious; it is also essential for the survival of bees and the health of our ecosystem. Prioritizing bee health, preserving biodiversity, reducing chemical contamination, safeguarding habitats, and supporting sustainable agriculture are all vital components of responsible beekeeping. Let us all strive to protect these incredible creatures by practicing eco-friendly techniques that ensure their well-being for generations to come.
IV. Essential Tools and Equipment for Eco-Friendly Beekeeping
When it comes to eco-friendly beekeeping, having the right tools and equipment is crucial. Not only does it ensure the well-being of your bees, but it also promotes sustainable practices that protect the environment. Here are some essential tools and equipment you’ll need for your eco-friendly beekeeping endeavors:
Hive Components
The hive is the heart of your beekeeping operation, so investing in high-quality components is essential. Opt for wooden hives made from sustainably sourced materials, as they provide insulation and a natural environment for your bees. Ensure proper ventilation by using screened bottom boards and top covers.
Frames with Foundation
Frames with foundation sheets provide stability to the honeycomb structure within the hive. Look for foundation sheets made from natural beeswax or organic plastic foundations instead of chemically treated ones that could harm your bees.
Bee Suits and Protective Gear
Your safety should never be compromised when working with bees, so wearing appropriate protective gear is a must. Invest in high-quality bee suits made from organic cotton or other sustainable materials that offer full-body coverage while allowing breathability.
Hive Tool
A hive tool is an indispensable accessory used to pry open hives, separate frames, scrape off excess propolis or wax, and perform various other tasks during inspections. Choose stainless steel hive tools as they are durable and easy to clean without leaving behind any harmful residues.
Smoker
A smoker helps calm down bees during inspections by emitting cool smoke into the hive entrance. Opt for smokers fueled by organic smoker fuel such as dried herbs or untreated wood chips instead of chemical-laden options that can contaminate the hive.
Bee Brush
A soft-bristled bee brush is useful for gently sweeping bees away from frames and other surfaces. Look for brushes made from natural materials like horsehair or plant fibers to avoid synthetic materials that could potentially harm the bees.
Feeder
In certain situations, you may need to provide supplemental feeding to your bees. Choose feeders made from food-grade plastic or glass instead of those containing harmful chemicals like BPA. This ensures the safety of your bees while minimizing environmental impact.
Remember, eco-friendly beekeeping is all about sustainable practices that protect both your bees and the environment. By investing in these essential tools and equipment made from eco-friendly materials, you are taking a significant step towards creating a harmonious relationship with nature while reaping the rewards of healthy honeybee colonies.
V. Sustainable Beekeeping Techniques for a Healthy Bee Colony
Sustainable beekeeping is crucial for maintaining healthy bee colonies and ensuring their long-term survival. By implementing eco-friendly practices, beekeepers can support the well-being of bees while also protecting the environment. Here are some sustainable techniques that can contribute to a thriving bee colony:
1. Natural Pest Control Methods
Instead of resorting to chemical pesticides that can harm bees and other beneficial insects, opt for natural pest control methods. For instance, introducing predator insects like ladybugs or using essential oils with insect-repellent properties can help keep pests at bay.
2. Providing Sufficient Food Sources
Bee colonies require ample food sources throughout the year to maintain their health and productivity. Plant diverse flowering plants in your vicinity to ensure a continuous supply of nectar and pollen. Incorporating native plants in your garden will attract local pollinators as well.
3. Avoiding Harmful Chemicals
Beekeepers should avoid using chemicals such as herbicides and fungicides near beehives or on blooming plants as they can contaminate nectar and pollen. Be cautious about what you introduce into the environment surrounding your hives, choosing organic alternatives whenever possible.
4. Regular Monitoring of Hive Health
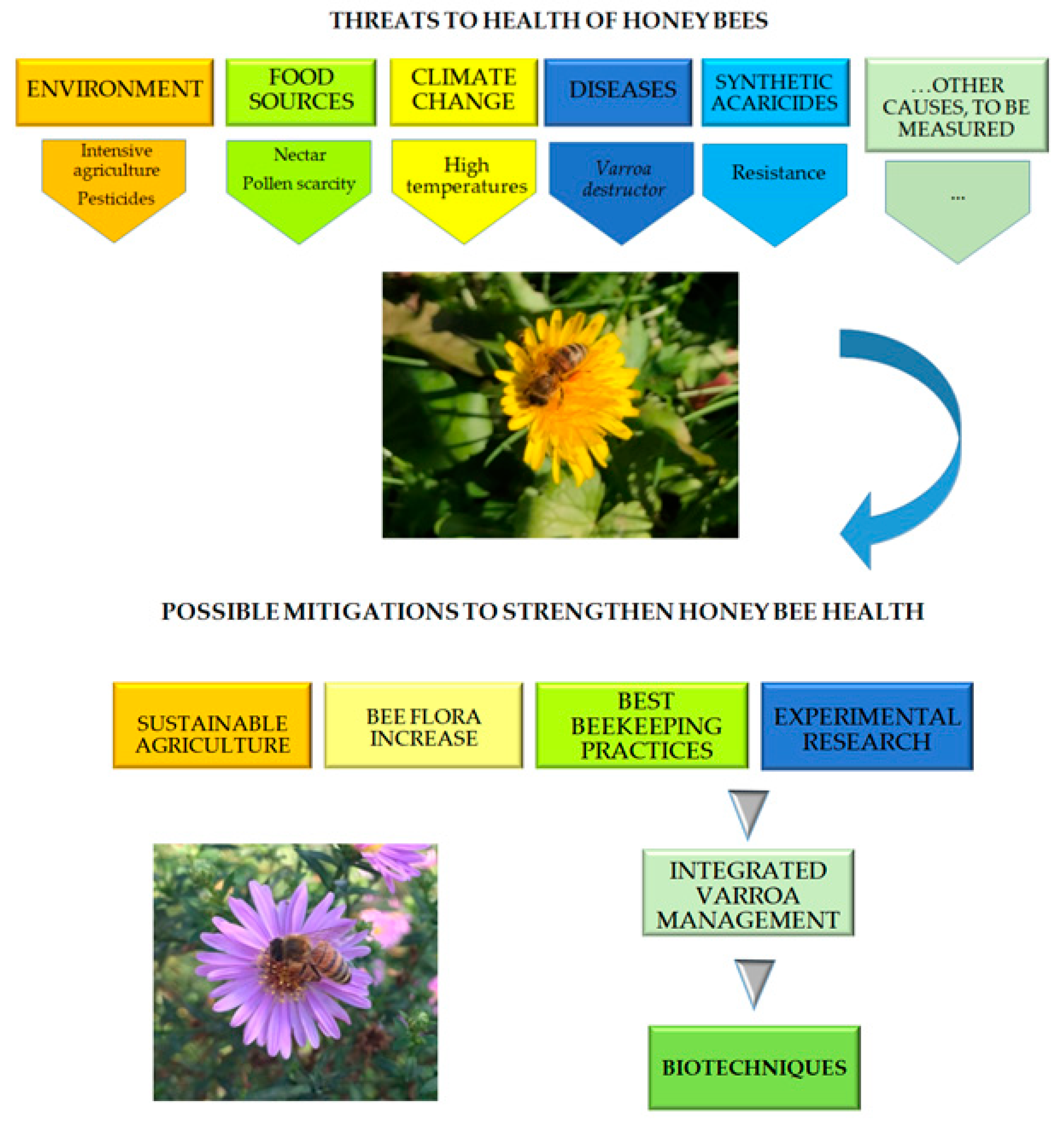
Frequent inspections are necessary to monitor the overall health of a bee colony. Look out for signs of diseases or parasites such as Varroa mites, which can weaken and decimate hives if left untreated.
5. Swarm Prevention Techniques
To prevent swarming – when a portion of the colony leaves with the queen – implement swarm prevention techniques like providing sufficient space within the hive or performing artificial swarming. This helps maintain the population and prevents overcrowding.
6. Promoting Genetic Diversity
Maintaining genetic diversity within a bee colony is vital for their resilience against diseases and pests. Introduce new queen bees from different genetic lineages to prevent inbreeding and enhance overall colony vigor.
7. Sustainable Hive Design
Utilize eco-friendly hive designs that prioritize the well-being of bees. Opt for hives made from sustainable materials, provide proper insulation, and ensure good ventilation to create a comfortable environment for the colony.
8. Collaboration with Local Beekeeping Communities
Engage with local beekeeping communities or associations to exchange knowledge and experiences on sustainable practices. Collaborating with others can provide valuable insights into regional challenges and effective solutions.
By adopting these sustainable beekeeping techniques, you can contribute to the health and vitality of your bee colonies while playing a part in conserving these essential pollinators for generations to come.
VI. The Role of Organic Beekeeping in Promoting Biodiversity
Beekeeping plays a significant role in promoting biodiversity, and when done organically, it becomes even more beneficial for the environment. Organic beekeeping focuses on maintaining healthy bee colonies without the use of synthetic chemicals or antibiotics. This approach not only ensures the well-being of bees but also contributes to a thriving ecosystem.
1. Preservation of Natural Habitat
Organic beekeepers prioritize preserving natural habitats for bees by providing them with suitable environments to thrive. They refrain from using harmful pesticides that can contaminate plants and compromise their pollen and nectar quality. By protecting native flora, organic beekeeping helps sustain diverse plant species that are crucial for sustaining other wildlife populations.
2. Pollination and Plant Propagation
Bee pollination is vital for plant propagation, contributing to increased crop yields and enhancing genetic diversity among plants. Organic beekeepers play a critical role in ensuring effective pollination by maintaining healthy colonies free from chemical exposure. As bees visit various flowers in search of nectar, they transfer pollen grains across different plants, aiding their reproduction.
3. Conservation of Bee Genetic Diversity
Organic beekeeping practices aim to preserve genetic diversity within honeybee populations instead of relying on monocultures or imported varieties that may be susceptible to diseases or pests. By allowing natural selection processes to occur, organic beekeepers help maintain resilient colonies capable of adapting to changing environmental conditions.
4.Supporting Wild Bee Populations
In addition to managed honeybees, wild bees also play a crucial role in pollination efforts worldwide. Organic beekeepers create habitats that support both managed and wild bees by offering diverse food sources throughout the year while avoiding harmful chemicals detrimental to these essential pollinators. The presence of organic beekeeping operations can contribute to the overall health and abundance of wild bee populations.
5. Enhanced Ecosystem Resilience
The use of organic practices in beekeeping promotes a more resilient ecosystem by reducing chemical contamination and supporting diverse plant and animal species. By avoiding pesticides, organic beekeepers prevent the accumulation of harmful substances in soil and water bodies, thereby benefiting other organisms that rely on these resources.
VII. Beekeeping and Pollination: Enhancing Crop Yield and Quality
Beekeeping plays a vital role in enhancing crop yield and quality through the process of pollination. Bees, with their remarkable ability to transfer pollen from male to female flowers, contribute significantly to the reproduction of various plant species.
The Importance of Pollination
Pollination is essential for the fertilization of plants, enabling them to produce fruits, vegetables, nuts, and seeds. It is estimated that nearly 75% of all crops depend on pollinators like bees for successful reproduction.
When bees visit flowers in search of nectar or pollen, they inadvertently pick up grains of pollen on their bodies. As they move from one flower to another, some amount of this pollen is transferred onto the stigma—the female reproductive organ—of each flower they visit.
Enhanced Crop Yield
The presence of bees in agricultural fields greatly enhances crop yield. Increased levels of pollination lead to better fertilization rates and higher fruit-set percentages. This results in larger harvests with improved quality.
Studies have shown that bee-pollinated crops such as apples, almonds, blueberries, cherries, melons, and cucumbers exhibit a significant increase in size compared to those relying solely on wind or self-pollination methods.
Promoting Biodiversity
Beekeeping also contributes to biodiversity conservation by maintaining healthy populations of pollinators. By providing suitable habitats for bees within agricultural landscapes or nearby natural areas such as forests and meadows, beekeepers help sustain diverse ecosystems.
Diverse ecosystems support not only honeybees but also other wild bee species that serve as important pollinators alongside managed colonies. These wild species play a crucial role in pollination, especially in areas where honeybee populations are scarce.
Improved Crop Quality
Besides enhancing crop yield, bee pollination also improves the quality of fruits and vegetables. Pollinated plants produce larger, more uniform, and visually appealing fruits with better taste and nutritional value.
The transfer of pollen triggers hormonal changes within flowers that stimulate the development of fruiting structures. This process ensures proper seed formation and influences the size, shape, color, sweetness, and texture of the resulting produce.
Supporting Sustainable Agriculture
Beekeeping aligns with eco-friendly practices as it promotes sustainable agriculture. By relying on bees for pollination instead of synthetic methods or expensive manual labor, farmers reduce their reliance on chemical inputs while maximizing crop productivity.
Fostering a healthy partnership between beekeepers and farmers helps create a mutually beneficial ecosystem where both parties work together to ensure optimal crop growth while preserving natural resources.
In conclusion, beekeeping is an essential practice that enhances crop yield and quality through efficient pollination. Its contribution to biodiversity conservation and sustainable agriculture makes it a valuable component in eco-friendly farming practices. By recognizing the importance of bees as vital pollinators, we can collectively work towards creating a harmonious relationship between humans and nature for a thriving agricultural landscape.
VIII. Common Challenges in Beekeeping and How to Address Them
Beekeeping can be a rewarding and fulfilling hobby, but it also comes with its fair share of challenges. Whether you are a beginner or an experienced beekeeper, it’s important to be aware of these common issues and know how to address them effectively. In this section, we will discuss some of the most prevalent challenges in beekeeping and provide practical solutions.
Predators and Pests
One of the biggest challenges faced by beekeepers is dealing with predators and pests that can harm or destroy beehives. Common threats include bears, skunks, raccoons, mice, ants, wax moths, varroa mites, and small hive beetles. To protect your hives from these invaders:
- Use sturdy hive stands at least 18 inches off the ground to deter larger predators.
- Install entrance reducers or mouse guards during vulnerable periods.
- Maintain cleanliness in your apiary by regularly cleaning equipment to prevent wax moth infestations.
- Treat hives for varroa mites using approved methods such as organic acids or essential oils.
- Monitor hives frequently for signs of pests or diseases so that you can take immediate action if necessary.
Climate Challenges
The climate plays a crucial role in beekeeping success. Extreme temperatures or sudden weather changes can have negative effects on bees’ health and productivity. Here are some measures you can take:
- Select bee breeds that are well-adapted to your region’s climate conditions.
- Provide adequate shade during hot summer days by placing hives under trees or using shade cloth covers.
- In colder regions, insulate hives with materials such as foam or straw to protect bees from harsh winter conditions.
- Ensure proper ventilation in the hive to prevent excessive heat buildup or moisture accumulation.
Lack of Forage
A lack of available nectar and pollen can pose a challenge for beekeepers, especially in urban or agricultural areas where monoculture crops dominate. To address this issue:
- Create a diverse and bee-friendly environment by planting a variety of flowering plants that bloom at different times throughout the year.
- Encourage your local community to reduce pesticide use, as it can harm both bees and their food sources.
- Consider establishing partnerships with nearby farms or landowners who are willing to provide additional forage opportunities for your bees.
Disease Management
Bee colonies are susceptible to various diseases, including American foulbrood, European foulbrood, chalkbrood, and Nosema. To effectively manage these diseases:
- Practice good hygiene by regularly cleaning and sterilizing equipment.
- Promote strong colony health through regular inspections and monitoring for signs of disease.
- If an infection is detected, follow recommended treatment protocols provided by local authorities or experienced beekeepers in your area.
By addressing these common challenges head-on, you can ensure the well-being of your bees and increase your chances of successful beekeeping. Remember that each situation may require its own unique approach, so always stay informed about current best practices in the industry!
IX. Frequently Asked Questions about Beekeeping and Eco-Friendly Practices
Here are some common questions people have about beekeeping and eco-friendly practices:
1. How can I start my own beekeeping operation?
To start your own beekeeping operation, you will need to research local regulations, obtain the necessary permits, invest in the right equipment (such as beehives and protective clothing), and educate yourself on proper hive management techniques. It’s also recommended to join a local beekeeping association or take part in workshops to learn from experienced beekeepers.
2. Are there any specific requirements for maintaining eco-friendly practices in beekeeping?
Absolutely! To maintain eco-friendly practices in beekeeping, it is important to avoid using harmful pesticides or chemicals near the bees’ habitat as they can harm the bees and contaminate their honey. Additionally, providing a diverse range of flowering plants throughout the year helps support pollinators by providing them with ample food sources.
3. Can I keep bees even if I live in an urban area?
Absolutely! Urban beekeeping has gained popularity over recent years due to its positive impact on local ecosystems and food production. However, before starting an urban beehive, it’s crucial to check local regulations regarding hive placement and obtain any necessary permissions from your local council or homeowner’s association.
4. What are some benefits of keeping bees?
Besides producing delicious honey, keeping bees offers numerous benefits such as increased pollination for nearby gardens or crops, improved biodiversity due to increased plant diversity around beehives, potential income from selling honey or other hive products like beeswax candles or propolis-based skincare products.
5. How can I contribute to saving the bees?
There are several ways you can contribute to saving the bees. Planting bee-friendly flowers and avoiding pesticide use in your garden, supporting local beekeepers by purchasing their honey and hive products, spreading awareness about the importance of pollinators, and creating bee-friendly habitats in urban areas are all impactful steps you can take.
6. Are there any risks or challenges associated with beekeeping?
Beekeeping does come with certain risks and challenges. Bee stings are a common concern, so proper protective clothing is essential. Additionally, colony health issues such as Varroa mites or diseases can impact hive productivity. Regular monitoring, proper management techniques, and seeking advice from experienced beekeepers can help mitigate these risks.
7. How much time does beekeeping require?
The time commitment for beekeeping varies depending on factors such as the number of hives you have and the specific tasks required during each season. Initially, setting up beehives will require more time investment; however, once established, routine inspections might only take a few hours per month.
8. Can children get involved in beekeeping?
Absolutely! Beekeeping can be an educational and enriching activity for children when done under adult supervision. It helps them learn about nature’s interconnectedness while fostering a sense of responsibility towards environmental conservation.
9. What should I do if I find a swarm of bees on my property?
If you encounter a swarm of bees on your property, it’s best to contact your local beekeeper association or pest control professionals who specialize in safely removing swarms without harming the bees.
10. Is it possible to keep bees without harvesting their honey?
Absolutely! Some beekeepers choose not to harvest honey and instead focus on providing a safe habitat for bees while supporting local pollinators. This approach can be beneficial for those primarily interested in promoting the welfare of bees and their role in the ecosystem.

Andrew Boyer is an accomplished individual with a deep-rooted passion for bees and their conservation. Born and raised in a small town in Oregon, Andrew developed an early fascination with nature and the environment. He pursued his education at the prestigious University of Oregon, where he obtained a Bachelor’s degree in Environmental Science with a specialization in Entomology. During his time at university, Andrew conducted extensive research on the behavior and ecological impact of bees, earning him recognition from his peers and professors. His dedication to the field led him to internships at local beekeeping associations, where he honed his skills in hive management and honey production. Andrew’s expertise in beekeeping and his commitment to environmental sustainability make him a valuable asset in the conservation of these vital pollinators.
