Contents
- I. Introduction to Beekeeping and Ecological Restoration
- II. Importance of Bees in Ecological Restoration
- III. Benefits of Beekeeping for Ecological Restoration
- IV. Beekeeping Techniques for Ecological Restoration
- V. Beekeeping and Pollinator Conservation
- VI. Role of Bees in Plant Biodiversity and Ecosystem Health
- VII. The Relationship between Beekeeping and Sustainable Agriculture
- VIII. Beekeeping as a Tool for Habitat Restoration
- IX. Challenges and Solutions in Beekeeping for Ecological Restoration
I. Introduction to Beekeeping and Ecological Restoration
Welcome to the fascinating world of beekeeping and ecological restoration! In recent years, there has been a growing interest in these interconnected practices, driven by a deep concern for the environment and the need to preserve our delicate ecosystems. Beekeeping not only provides us with honey and other valuable products but also plays a vital role in pollination, contributing to the health of plants and biodiversity.
Beekeeping is an ancient practice that dates back thousands of years. It involves maintaining colonies of bees in man-made hives, providing them with suitable conditions for their survival and reproduction. Bees are remarkable creatures known for their highly organized social structure and incredible work ethic.
Ecological restoration, on the other hand, focuses on repairing or rehabilitating damaged ecosystems through various techniques such as habitat creation, reforestation, wetland restoration, or reintroduction of native species. This holistic approach aims to bring balance back to our natural landscapes while addressing environmental issues like habitat loss, pollution, or climate change.
The Importance of Beekeeping
Beekeeping has immense significance both economically and ecologically. From an economic standpoint, it provides income opportunities for beekeepers who can sell honey products such as raw honeycomb or beeswax candles. Additionally, commercial pollination services offered by beekeepers contribute significantly to agricultural productivity by ensuring crop pollination.
From an ecological perspective, bees play a crucial role as pollinators. As they visit flowers in search of nectar and pollen for their survival needs (and hive production), they inadvertently transfer pollen from one flower to another – facilitating fertilization that leads to fruit set and seed production. Without bees’ diligent efforts in pollinating flowering plants worldwide across various ecosystems – both natural habitats like forests as well as human-managed landscapes like farms – many plant species would struggle to reproduce.
The Benefits of Ecological Restoration
Ecological restoration is essential for reversing the damage caused by human activities and restoring balance to ecosystems. By actively rehabilitating degraded areas, we can enhance biodiversity, improve water quality, prevent soil erosion, and create habitats for endangered species. Moreover, restoration projects contribute to carbon sequestration and help mitigate climate change by promoting the growth of forests and other vegetation that absorb greenhouse gases.
Through ecological restoration efforts, we can also reconnect people with nature and foster a sense of stewardship towards the environment. By engaging communities in conservation initiatives and providing opportunities for hands-on involvement in habitat restoration projects, we can raise awareness about environmental issues and inspire individuals to take action.
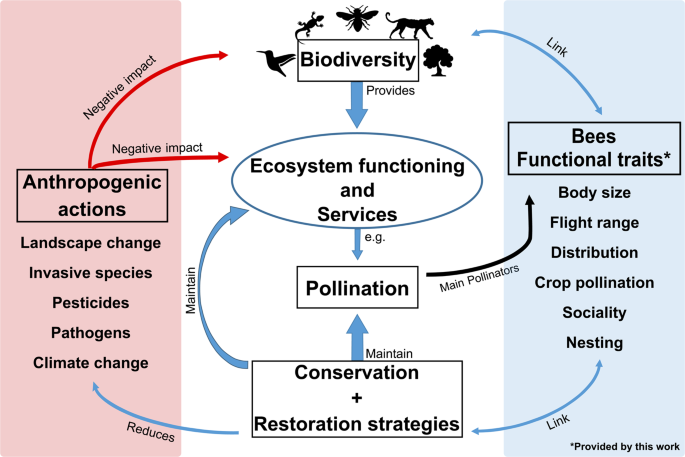
II. Importance of Bees in Ecological Restoration

Bees are not just buzzing insects that produce honey; they play a vital role in ecological restoration. These small creatures have a significant impact on the health and balance of our ecosystems, making them crucial for the preservation of biodiversity and overall environmental well-being.
Pollination: A Key Role
One of the most critical contributions bees make to ecological restoration is their role as pollinators. As they fly from flower to flower in search of nectar and pollen, bees transfer pollen grains, enabling plants to reproduce. This process is essential for the production of fruits, vegetables, seeds, and nuts.
In fact, around 80% of flowering plants depend on pollinators like bees for reproduction. Without their assistance, many plant species would struggle to survive or face extinction. This loss would disrupt entire food chains and negatively impact both wildlife populations and human agriculture.
Biodiversity Preservation
Bees also contribute significantly to preserving biodiversity by promoting genetic diversity among plant populations. As they visit various flowers in search of resources, bees inadvertently cross-pollinate different varieties within the same species.
This cross-pollination process helps prevent genetic bottlenecks by introducing new gene combinations into plant populations. Genetic diversity allows plants to adapt better to changing environmental conditions such as climate change or disease outbreaks.
Habitat Creation
In addition to their essential role as pollinators, bees actively participate in creating habitats that facilitate ecological restoration efforts. Many bee species build nests or hives using materials found in natural environments such as wood cavities or soil burrows.
These nesting activities help increase habitat complexity and provide shelter for other organisms like insects or small mammals that rely on these structures for survival. By creating suitable habitats, bees contribute to the overall health and stability of ecosystems.
Indicators of Environmental Health
Bees can act as indicators of environmental health due to their sensitivity to changes in ecosystems. Their decline or absence in an area can signal ecological imbalances, including pollution, habitat destruction, or pesticide usage.
Monitoring bee populations can provide valuable insights into the overall state of an ecosystem and help identify potential environmental issues that require attention. By focusing on protecting and conserving bees, we indirectly safeguard other species and promote a healthier environment for all.
III. Benefits of Beekeeping for Ecological Restoration
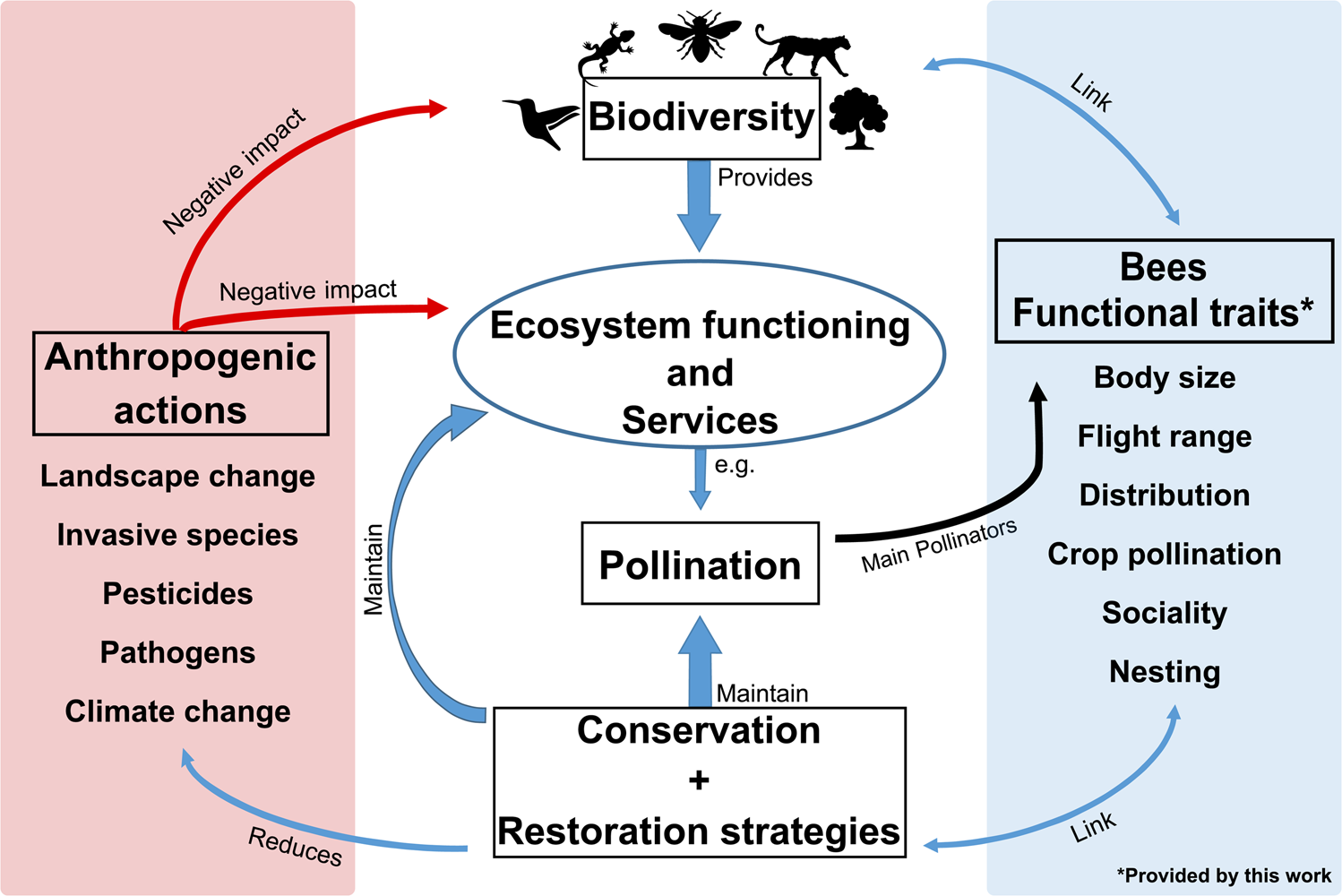
Beekeeping is not only a rewarding hobby or business venture, but it also plays a crucial role in ecological restoration. By promoting the growth and well-being of bee populations, we can achieve significant benefits for our environment and biodiversity.
Pollination Support
Beekeeping contributes to the pollination of various plant species, including fruit trees, vegetables, and flowering plants. Bees are natural pollinators and play a vital role in fertilizing plants by transferring pollen from male to female flower parts. This process leads to increased fruit set, better crop yields, and improved plant health. By engaging in beekeeping practices, we can ensure the continuation of this essential ecosystem service.
Biodiversity Conservation
Through their pollination activities, bees help maintain biodiversity by supporting the reproduction and survival of numerous plant species. When bees visit flowers for nectar collection or pollen gathering, they inadvertently transfer pollen between flowers of different plants. This cross-pollination facilitates genetic diversity within plant populations and helps sustain ecosystems that depend on diverse flora.
Habitat Preservation
As beekeepers create suitable habitats for their colonies near farms or gardens through the provision of beehives or apiaries, they indirectly contribute to habitat preservation efforts. By providing safe spaces for bees to thrive and establish their colonies close to areas where crops or flowering plants require pollination support, beekeepers help preserve natural habitats that might otherwise be disrupted due to urbanization or agricultural expansion.
Educational Opportunities
Beekeeping offers educational opportunities for individuals interested in learning about ecology and environmental conservation firsthand. By becoming involved in beekeeping activities such as hive maintenance or honey production processes like extraction and processing techniques; people develop a deeper understanding of how these insects interact with their surroundings and contribute to the balance of ecosystems.
Local Economy Boost
Beekeeping can also have positive impacts on local economies. It provides opportunities for small-scale entrepreneurs to generate income through the sale of honey, beeswax, pollen, propolis, royal jelly, and other bee-related products. Additionally, the presence of healthy bee populations enhances agricultural productivity and crop yields in nearby areas, leading to economic growth for farmers and food producers.
In conclusion, engaging in beekeeping practices not only benefits individuals through honey production or personal enjoyment but also contributes significantly to ecological restoration efforts. By supporting pollination services provided by bees and promoting biodiversity conservation while preserving habitats, we can create a positive impact on our environment and local communities.
IV. Beekeeping Techniques for Ecological Restoration

Beekeeping can play a crucial role in ecological restoration, helping to support the local ecosystem and promote biodiversity. By implementing certain techniques, beekeepers can contribute to the restoration of damaged habitats and create a more sustainable environment for both bees and other wildlife.
1. Native Plant Selection
One effective technique is to focus on planting native flowers and plants within the beekeeping areas. Native plants provide essential nectar and pollen sources that are well-suited for local bees, ensuring their health and vitality. By choosing indigenous species, you can help restore the natural balance of your region’s flora while providing an abundant food supply for your bees.
2. Creating Habitat Diversity
In addition to planting native plants, it’s vital to create a diverse habitat that offers various nesting sites for different bee species. This includes providing suitable nesting materials such as hollow logs or wooden blocks with drilled holes of varying sizes. Incorporating diverse vegetation structures like shrubs, trees, meadows, and water sources will attract a wider range of pollinators.
3. Integrated Pest Management
To ensure the health of your honeybees without harming other beneficial insects or contaminating the environment with harmful chemicals, adopt integrated pest management (IPM) practices. IPM involves regularly monitoring hives for pests or diseases and using non-toxic methods like mechanical controls or biological agents when necessary.
4. Conservation-oriented Beekeeping Practices
Beekeepers can further contribute to ecological restoration by adopting conservation-oriented practices such as swarm prevention techniques instead of splitting colonies artificially; this allows bees to engage in their natural reproductive behavior while minimizing human intervention.
5. Providing Water Sources
Water is essential for bees, especially during hot summer months. By creating water sources like shallow birdbaths or small ponds near the beekeeping area, you can help sustain the bees’ hydration needs while attracting other beneficial insects and wildlife to your garden.
Incorporating these techniques into your beekeeping practices not only benefits the environment but also enhances honey production. By embracing ecological restoration principles, you contribute to a healthier ecosystem that supports pollinators and promotes biodiversity in your local community.
V. Beekeeping and Pollinator Conservation
Beekeeping plays a crucial role in pollinator conservation, as bees are essential for ecosystem health and food production. By engaging in responsible beekeeping practices, beekeepers can contribute to the preservation of these vital pollinators.
1. Providing Diverse Forage
A key aspect of supporting pollinators through beekeeping is ensuring the availability of diverse forage. Bees rely on a variety of flowering plants for nectar and pollen collection, which sustains their colonies and allows them to fulfill their role as effective pollinators.
Beekeepers can enhance this by planting diverse floral resources in their vicinity, such as wildflowers or native plant species that bloom at different times throughout the year. This not only benefits honeybees but also supports other important native pollinators.
2. Reducing Pesticide Use
To protect both honeybees and other pollinators, it is crucial to minimize pesticide use near beehives and surrounding areas. Pesticides can have detrimental effects on bees’ health, leading to reduced colony strength or even complete hive loss.
Beekeepers should educate themselves about alternative pest management methods that are less harmful to bees while still maintaining effective control over pests or diseases affecting their hives.
3. Promoting Genetic Diversity
Maintaining genetic diversity within honeybee populations is vital for their resilience against diseases and environmental changes. Beekeepers can achieve this by introducing new queen bees from different lineages into their colonies periodically.
This practice helps prevent inbreeding depression while promoting stronger honeybee stocks better adapted to local conditions.
4. Educating Others
Beekeeping enthusiasts have a unique opportunity to educate the public about the importance of pollinators and their conservation. By sharing their knowledge, experiences, and enthusiasm, beekeepers can inspire others to take action in protecting these valuable creatures.
Engaging with schools, community groups, or local organizations allows beekeepers to spread awareness about pollinator-friendly practices and the role bees play in food production.
5. Participating in Citizen Science
Beekeepers can actively contribute to scientific research by participating in citizen science initiatives focused on studying pollinators. These projects provide valuable data that helps researchers better understand bee populations, diseases, and environmental factors affecting their survival.
By monitoring hive health or reporting sightings of wild bees through designated platforms or apps, beekeepers become an essential part of efforts to conserve pollinators on a larger scale.
VI. Role of Bees in Plant Biodiversity and Ecosystem Health
Bees play a crucial role in maintaining plant biodiversity and ensuring the health of ecosystems. As they go about their daily activities, bees perform vital tasks that contribute to the overall balance and functioning of natural environments.
Pollination: A Key Contribution
One of the primary roles bees fulfill is pollination. As they visit flowers to collect nectar and pollen, bees inadvertently transfer pollen grains from male flower parts (stamens) to female flower parts (pistils). This cross-pollination process leads to fertilization, allowing plants to produce fruits, seeds, and new plants.
Pollination by bees is essential for a diverse range of flowering plants, including both wild species and agricultural crops. Without this pollinator service provided by bees, many plant species would struggle to reproduce effectively or even face extinction. Moreover, over 75% of global food crops depend on animal pollinators like bees for successful fruit set.
Biodiversity Maintenance
The intricate relationship between bees and flowering plants contributes significantly to plant biodiversity maintenance. By facilitating cross-pollination among various plant species as they move from one flower source to another, bees enable genetic diversity within populations. This diversity strengthens the resilience of plant communities against diseases and environmental changes.
Furthermore, different bee species exhibit preferences for specific types of flowers based on factors such as color or shape. These preferences result in selective pollination patterns that promote specialized relationships between certain bee species and particular plants. These interactions foster coevolutionary processes where both parties adapt over time for mutual benefit.
Ecosystem Services Beyond Pollination
Beyond their crucial role in pollinating flowering plants, bees provide additional ecosystem services that contribute to overall ecosystem health. Bees’ foraging activities help regulate plant populations by controlling herbivorous insect populations that might otherwise become excessive and cause ecological imbalances.
Furthermore, the presence of bees in an ecosystem can enhance soil fertility. As bees visit flowers, they inadvertently transfer pollen grains containing microorganisms, including beneficial bacteria and fungi. These microorganisms can enrich the soil microbiome, supporting nutrient cycling processes and promoting healthier plant growth.
VII. The Relationship between Beekeeping and Sustainable Agriculture
Beekeeping plays a crucial role in promoting sustainable agriculture by providing essential pollination services, enhancing crop yields, and fostering ecological balance. Through their intricate process of collecting nectar and pollen, bees inadvertently facilitate the reproduction of flowering plants, including many fruits, vegetables, and nuts that make up our agricultural system.
Pollination Services for Increased Crop Yields
One of the primary contributions of beekeeping to sustainable agriculture is its provision of pollination services. Bees transfer pollen grains from the male parts (anthers) to the female parts (stigma) of flowers during their foraging activities. This transfer enables fertilization and subsequent fruit or seed development, resulting in increased crop yields.
By actively managing beehives near agricultural fields or orchards, beekeepers ensure that an adequate number of bees are available to visit flowers during their blooming period. The presence of these diligent pollinators significantly enhances fruit set and quality for various crops such as apples, strawberries, almonds, blueberries, cucumbers, melons – just to name a few.
Promoting Biodiversity and Ecological Balance
Beekeeping also contributes to supporting biodiversity within agricultural landscapes. Honeybees are generalist foragers that collect nectar from a wide range of plant species throughout their flight radius. In doing so, they foster floral diversity by visiting different types of flowering plants.
This diversity in turn attracts other wild pollinators like bumblebees and solitary bees who may specialize in certain plant species or have different preferences than honeybees when it comes to feeding on nectar or collecting pollen.
The Role of Bee Products in Sustainable Agriculture
In addition to pollination, beekeeping offers various products that have practical applications in sustainable agriculture. The most well-known product is honey, a natural sweetener produced by bees from flower nectar. Honey has multiple uses as a food ingredient and also possesses medicinal properties.
Another valuable product is beeswax, which can be used for making candles, cosmetics, and even as an ingredient in various ointments or balms. Beeswax acts as a natural preservative and provides moisture-locking properties to the products it is incorporated into.
Furthermore, propolis – a resinous substance collected by bees from tree buds – has antimicrobial properties and finds application in organic farming practices to control certain plant diseases without resorting to synthetic chemicals.
VIII. Beekeeping as a Tool for Habitat Restoration
Beekeeping plays a crucial role in habitat restoration efforts, offering numerous benefits to the environment and biodiversity. By creating suitable habitats for bees, beekeepers contribute to the preservation of pollinators and the restoration of ecosystems.
1. Enhancing Biodiversity
Beekeeping promotes biodiversity by providing a safe sanctuary for bees. Bees are essential pollinators that facilitate the reproduction of flowering plants, ensuring genetic diversity within plant populations. By maintaining beehives in specific areas, beekeepers help ensure that plants receive adequate pollination and thrive.
2. Pollination Services
Beekeeping contributes to habitat restoration by providing much-needed pollination services to surrounding flora. As bees collect nectar from flowers to produce honey, they inadvertently transfer pollen between plants, enabling fertilization and seed production.
3. Supporting Native Plant Species
Through their foraging activities, bees play a vital role in supporting native plant species’ growth and distribution. As they visit various flowers in search of nectar and pollen, bees aid in cross-pollination between different plant individuals within the same species.
4. Creating Wildlife Habitats
The presence of beehives not only benefits bees but also creates habitats for other wildlife species such as birds and insects. The structures built by beekeepers offer shelter opportunities while also attracting other beneficial insects that assist with pest control or serve as additional pollinators.
5. Restoring Ecosystem Functioning
Beekeeping contributes to restoring ecosystem functioning by helping maintain healthy populations of key plant species through effective pollination services provided by bees.
Incorporating beekeeping into habitat restoration initiatives can yield significant positive outcomes for both the environment and local communities. By supporting bees, beekeepers play a crucial role in preserving biodiversity and restoring ecosystems, ultimately contributing to a more sustainable future.
IX. Challenges and Solutions in Beekeeping for Ecological Restoration
Beekeeping for ecological restoration is a vital practice that plays a significant role in promoting biodiversity, enhancing pollination, and restoring ecosystems. However, beekeepers often encounter various challenges that can hinder their efforts towards ecological restoration. In this section, we will explore some of these challenges and provide potential solutions to overcome them.
Predation and Pests:
One of the primary challenges faced by beekeepers is predation by animals such as bears, skunks, raccoons, and rodents. These predators can cause significant damage to beehives and disrupt the overall health of the bee colonies. Additionally, pests like varroa mites can weaken bees’ immune systems.
To address these challenges, beekeepers can implement measures such as installing electric fences around beehives to deter large predators. Regular monitoring and treatment for pests like varroa mites using organic methods or integrated pest management techniques are also crucial for maintaining healthy colonies.
Habitat Loss:
The loss of natural habitats due to urbanization or intensive agriculture has a direct impact on bees’ foraging resources. Bees rely on diverse floral resources throughout the year for nectar and pollen collection essential for their survival.
One solution to combat habitat loss is through establishing flowering landscapes or wildflower meadows adjacent to apiaries. These areas provide additional sources of food for bees while supporting local plant biodiversity.
Pesticide Use:
The widespread use of pesticides in conventional agriculture poses a significant threat to bees’ health and well-being. Exposure to insecticides can lead to decreased fertility rates, impaired navigation abilities, weakened immune systems, and ultimately colony collapse disorder (CCD).
To mitigate pesticide-related risks, beekeepers can opt for organic farming practices and collaborate with farmers who use sustainable pest management methods. Educating the public about the importance of reducing pesticide usage and advocating for stricter regulations on pesticide application are also essential steps towards protecting bees.
Climate Change:
The changing climate patterns, including rising temperatures and unpredictable weather events, pose challenges for beekeeping. Bees rely on specific temperature ranges to thrive, and extreme weather conditions can disrupt their natural cycles.
Beekeepers can adapt to these challenges by implementing strategies such as providing shade structures or relocating hives to more suitable microclimates. Regular monitoring of hive conditions and adjusting management practices accordingly will help mitigate the negative impacts of climate change on beekeeping activities.
In conclusion, while beekeeping for ecological restoration offers numerous benefits, it is not without its challenges. By acknowledging these obstacles and implementing appropriate solutions like addressing predation risks, combating habitat loss, reducing pesticide use, and adapting to climate change effects in a proactive manner, we can promote successful ecological restoration through responsible beekeeping practices.

Andrew Boyer is an accomplished individual with a deep-rooted passion for bees and their conservation. Born and raised in a small town in Oregon, Andrew developed an early fascination with nature and the environment. He pursued his education at the prestigious University of Oregon, where he obtained a Bachelor’s degree in Environmental Science with a specialization in Entomology. During his time at university, Andrew conducted extensive research on the behavior and ecological impact of bees, earning him recognition from his peers and professors. His dedication to the field led him to internships at local beekeeping associations, where he honed his skills in hive management and honey production. Andrew’s expertise in beekeeping and his commitment to environmental sustainability make him a valuable asset in the conservation of these vital pollinators.
