Contents
- I. Introduction to Bee-Friendly Habitats
- II. The Importance of Creating Bee-Friendly Habitats
- III. Understanding the Needs of Bees
- IV. Selecting and Planting Bee-Friendly Flowers
- V. Providing a Water Source for Bees
- VI. Avoiding Harmful Pesticides and Chemicals
- VII. Creating Nesting Sites for Bees
- VIII. Maintaining and Caring for Bee-Friendly Habitats
- IX. Frequently Asked Questions about Creating Bee-Friendly Habitats
- 1. Why are bees important for our environment?
- 2. How can I create a bee-friendly habitat in my backyard?
- 3. What types of flowers are attractive to bees?
- 4. Do I need a big garden or yard to create a bee-friendly habitat?
- 5. Can I attract bees without attracting other pests like wasps?
- 6. How do I provide nesting sites for solitary bees?
- 7. Are there any bee-friendly alternatives to traditional lawn care?
- 8. How can I support bees during the winter months?
- 9. Can I keep honeybees in my backyard?
- 10. What other steps can I take to protect bees?
I. Introduction to Bee-Friendly Habitats

Welcome to the world of bee-friendly habitats! In this article, we will explore the importance of creating spaces that support and promote a healthy environment for bees. Bees play a crucial role in pollinating plants, which helps sustain our ecosystems and food supply.
Creating bee-friendly habitats is not only beneficial for these incredible creatures but also for us humans. By providing them with suitable environments, we can ensure their survival and contribute to the overall well-being of our planet.
Understanding Bee Behavior
To create effective bee-friendly habitats, it’s important to understand how these tiny insects behave. Bees are social creatures that live in colonies comprising thousands of individuals. They communicate through intricate dances and pheromones, working as a coordinated team to gather nectar and pollen.
Bee-friendly habitats need to provide ample food sources throughout the year. This includes planting a variety of flowers that bloom at different times, ensuring continuous availability of nectar and pollen.
The Importance of Native Plants
Native plants have evolved alongside local bees, making them excellent sources of food and shelter. These plants have developed natural adaptations that attract specific bee species by producing nectar in appropriate quantities and at ideal times.
Incorporating native plants into your garden or landscape can significantly enhance its appeal to bees while supporting local biodiversity. Researching which native plant species thrive in your area is an essential step towards creating a truly bee-friendly habitat.
Providing Shelter Options
In addition to food sources, bees also require suitable nesting sites within their habitat. Providing various options such as beehives or nesting blocks can encourage solitary bees like mason bees or leafcutter bees to take up residence in your garden.
Bee-friendly shelters should be placed in a location that receives adequate sunlight and protection from strong winds. These structures offer bees safe spaces to lay their eggs, ensuring the next generation’s survival.
Minimizing Chemical Use
Chemical pesticides and herbicides can be detrimental to bees’ health. To create truly bee-friendly habitats, it is crucial to minimize or eliminate the use of such chemicals in your garden or landscape.
Opt for organic pest control methods and natural alternatives whenever possible. This will help maintain a healthy balance between pests, beneficial insects, and pollinators like bees.
II. The Importance of Creating Bee-Friendly Habitats
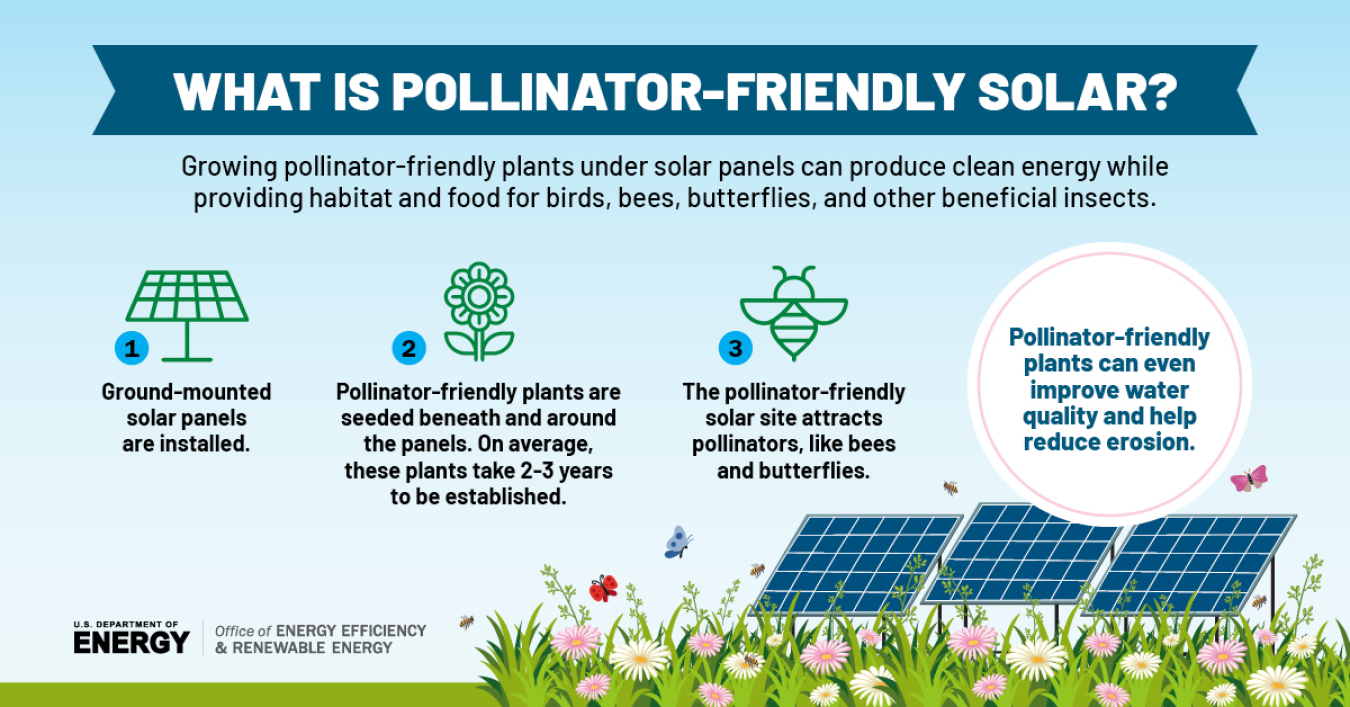
Creating bee-friendly habitats is crucial for the survival and well-being of bees, as well as for the overall health of our environment. Bees play a vital role in pollination, which is essential for the reproduction of many plants. Without bees, our food system would suffer greatly, as they are responsible for pollinating a wide variety of crops.
1. Enhancing Biodiversity
By creating bee-friendly habitats, we can contribute to enhancing biodiversity in our surroundings. Bees are attracted to diverse and abundant sources of nectar and pollen from various plant species. By planting a variety of flowering plants that bloom at different times throughout the year, we can provide bees with a continuous supply of food and support their population growth.
2. Supporting Native Bee Species
In addition to honeybees, there are numerous native bee species that also play an important role in pollination. These native bees have adapted to specific ecosystems and have unique relationships with certain plant species. By creating bee-friendly habitats that include native plants specific to your region, you can support these local bee populations and help maintain ecological balance.
3. Reducing Pesticide Use
Bee-friendly habitats promote natural pest control by attracting beneficial insects like ladybugs and lacewings that prey on pests harmful to crops. This can help reduce reliance on pesticides, which often have detrimental effects on bees’ health when they come into contact with them while foraging or through contaminated water sources.
4. Improving Water Sources
Bees require access to clean water for hydration purposes as well as nest building activities such as mud construction by certain solitary bee species. Including shallow water sources like birdbaths or creating small ponds in your bee-friendly habitat will ensure bees have a reliable and safe water supply, especially during hot summer months.
5. Educating and Raising Awareness
Creating bee-friendly habitats provides an opportunity to educate others about the importance of bees and their role in our ecosystem. By sharing knowledge about the benefits of supporting pollinators, we can raise awareness and inspire others to take action in their own communities. Together, we can make a significant impact on preserving bee populations for future generations.
III. Understanding the Needs of Bees

Bees are fascinating creatures that play a vital role in our ecosystem. They are not only responsible for pollinating flowers and plants, but they also contribute to the production of honey and beeswax. To create a bee-friendly habitat, it is crucial to understand their needs and provide an environment that supports their well-being.
The Importance of Food Sources
One of the primary needs of bees is access to a diverse range of food sources. Bees rely on nectar and pollen from flowers as their main source of nutrition. By planting a variety of flowering plants, you can ensure that there is always an abundant supply of food for bees throughout the year.
Nesting Sites
In addition to food sources, bees require suitable nesting sites to build their hives or nests. Different species have different preferences when it comes to nesting locations. Some prefer hollow trees or logs, while others may choose underground burrows or even man-made structures like bee boxes or hotels. Providing various options for nesting sites can attract different bee species and promote biodiversity in your garden.
Avoiding Pesticides
Pesticides pose a significant threat to bees’ health and survival. These chemicals can be toxic to bees when they come into contact with them while foraging for food or returning to their nests. To create a truly bee-friendly habitat, it is essential to avoid using pesticides in your garden altogether or opt for organic alternatives that do not harm these beneficial insects.
Water Sources
Like any other living creature, bees need access to water for hydration purposes. Providing shallow water sources such as birdbaths with rocks or floating platforms can make it easier for bees to drink without risking drowning incidents.
Protection from Predators
Bees face threats from predators such as wasps, birds, and certain insects. Creating a safe environment for bees involves minimizing potential predators’ presence in the vicinity of their nesting sites. You can achieve this by installing bird feeders away from bee activity areas or using physical barriers to deter larger predators.
By understanding and addressing the needs of bees, you can create a welcoming habitat that supports their survival and contributes to the overall health of our environment. Remember, every small effort counts when it comes to conserving these amazing creatures!
IV. Selecting and Planting Bee-Friendly Flowers

Creating a bee-friendly habitat is not only beneficial for our buzzing friends but also for our environment as a whole. One of the key steps in establishing such a habitat is selecting and planting flowers that attract bees. By providing them with a diverse range of nectar-rich blooms, we can support their survival and help maintain healthy ecosystems.
1. Choose Native Flowers
Selecting native flowers is crucial when it comes to creating an ideal environment for bees. Native plants have evolved alongside local pollinators, making them perfectly suited to each other’s needs. These plants provide the necessary pollen and nectar sources that bees depend on for their diet, ensuring they receive proper nutrition while helping to sustain local bee populations.
2. Opt for Variety in Blooming Periods
Bee-friendly gardens should include flowers that bloom at different times throughout the year, offering nectar sources during various seasons. This ensures consistent food availability for bees from early spring through late fall, supporting their overall well-being and encouraging them to stay in your garden longer.
3. Consider Flower Shape and Color
Different species of bees are attracted to specific flower shapes and colors due to their varying tongue lengths or visual preferences. Incorporating a variety of flower shapes—such as tubular, composite, or bell-shaped—can accommodate different types of bees seeking nourishment within your garden. Additionally, using vibrant colors like purple, blue, yellow or white will catch their attention more easily.
4. Avoid Pesticides
Pesticides can be harmful not only to unwanted insects but also to beneficial ones like bees in your garden ecosystem; therefore it’s important to avoid using them altogether if possible. Instead, opt for organic gardening methods that rely on natural pest control techniques. This will ensure a safe and healthy environment for bees to thrive.
5. Create Sheltered Areas
In addition to providing flowers as a food source, it’s essential to create sheltered areas within your garden for bees to rest and nest. Consider leaving patches of bare ground or creating small piles of rocks and branches where bees can find refuge. Additionally, you may want to install bee houses that mimic natural nesting environments.
By following these guidelines, you’ll be well on your way to establishing a bee-friendly habitat in your garden. Not only will you attract these important pollinators, but you’ll also contribute positively to the overall health of our ecosystem.
V. Providing a Water Source for Bees
When creating a bee-friendly habitat, it is essential to provide bees with a reliable water source. Just like humans, bees require water to survive and carry out their daily activities. By ensuring they have easy access to water, you can contribute to the overall well-being of these crucial pollinators.
1. The Importance of Water for Bees
Water serves various purposes in a bee’s life. Bees use it for maintaining hydration levels within their bodies and regulating temperature inside the hive. Additionally, they utilize water to dilute honey and feed larvae.
2. Creating Bee-Friendly Water Sources
To create suitable watering stations for bees, consider the following tips:
a) Shallow Containers or Birdbaths:
Bees prefer shallow water sources where they can land safely without drowning. Place containers or birdbaths with shallow edges in your garden or near flowering plants.
b) Add Pebbles or Stones:
To prevent accidental drowning, place pebbles or stones in the container as perches for bees to rest on while drinking.
c) Keep It Fresh:
Ensure that you regularly replace stagnant water with fresh supplies since bees prefer clean sources of water.
3. Enhancing Safety Measures at Watering Stations
In order to protect visiting bees from predators and contamination, take the following precautions:
a) Provide Cover:
Create shade near the watering stations by using plants or umbrellas; this will protect visiting bees from potential bird attacks and excessive heat exposure.
b) Avoid Chemical Contamination:
Keep the water source free from chemicals, such as pesticides or herbicides, which can be harmful to bees. Opt for natural alternatives when maintaining your garden.
c) Regular Maintenance:
Regularly clean and refill the water containers to prevent the growth of algae or bacteria that may harm bees.
By taking these simple steps to provide a water source for bees, you are actively contributing towards creating a bee-friendly habitat. Not only will this benefit the health and survival of these important pollinators, but it will also enhance the biodiversity and beauty of your garden.
VI. Avoiding Harmful Pesticides and Chemicals
In order to create a bee-friendly habitat, it is essential to avoid harmful pesticides and chemicals that can harm these important pollinators. By adopting natural and organic practices in your garden or outdoor space, you can provide a safe environment for bees to thrive. Here are some tips on how to minimize the use of harmful substances:
1. Embrace Natural Pest Control Methods
Instead of resorting to chemical pesticides, consider using natural pest control methods. For example, you can introduce beneficial insects like ladybugs or lacewings that feed on common garden pests such as aphids or whiteflies.
2. Practice Crop Rotation
Crop rotation is an effective way to prevent the buildup of pests and diseases in your garden while reducing the need for chemical treatments. By rotating crops each season, you disrupt the life cycles of pests and reduce their impact on plants.
3. Use Organic Fertilizers
Avoid synthetic fertilizers that may contain harmful chemicals by opting for organic alternatives instead. Organic fertilizers enrich the soil naturally without posing any risks to bees or other beneficial insects.
4. Choose Bee-Friendly Plants
Select plants that are attractive to bees and other pollinators while avoiding varieties treated with systemic pesticides (neonicotinoids). Look for labels indicating that plants have been grown without these chemicals.
5. Maintain Proper Garden Hygiene
Cleanliness plays a crucial role in preventing pest infestations without relying on pesticides heavily. Remove dead plant debris regularly, as it can harbor pests and diseases that may require chemical intervention if left unattended.
Remember, by taking steps towards avoiding harmful pesticides and chemicals, you not only create a safe haven for bees but also contribute to the overall health of your garden. Embrace natural solutions, promote biodiversity, and let nature thrive in harmony with your outdoor space.
VII. Creating Nesting Sites for Bees
When it comes to creating a bee-friendly habitat, it’s not just about providing food sources for bees. Another crucial aspect is offering nesting sites where these industrious insects can establish their colonies and raise their young. By incorporating nesting sites into your garden or outdoor space, you can help support the local bee population and contribute to their overall well-being.
1. Installing Bee Hotels
Bee hotels are artificial structures designed to mimic natural nesting environments for solitary bees. These beneficial insects are responsible for pollinating a wide variety of plants, making them an invaluable asset in any garden ecosystem. Place bee hotels in sunny locations around your property, preferably near flowering plants that provide ample food sources.
2. Creating Underground Burrows
Some species of bees prefer to nest underground rather than in vertical structures like trees or walls. To accommodate these ground-nesting bees, leave patches of bare soil undisturbed in your garden or create small mounds with loose soil that act as inviting burrowing spots.
3. Providing Hollow Stems and Tubes
Mason bees and leafcutter bees are known to nest inside hollow stems or tubes found in plants such as bamboo, reeds, or even old drinking straws. To attract these species, tie together bundles of hollow stems and place them horizontally in a sheltered area of your garden.
4. Leaving Leaf Litter Undisturbed
Certain types of solitary bees construct their nests by tunneling into dead plant material on the ground such as fallen leaves or twigs. By leaving some leaf litter untouched beneath shrubs and trees, you create favorable conditions for these cavity-nesting bees to thrive.
5. Incorporating Wood Blocks with Pre-Drilled Holes
Some bees, like carpenter bees, excavate their nests inside wooden structures. By providing them with pre-drilled holes in untreated wood blocks or logs, you offer these cavity-nesting species a safe and suitable habitat.
Remember that each bee species has unique nesting preferences, so it’s essential to offer a variety of options to attract diverse populations. By implementing these strategies and creating nesting sites tailored to different bee species’ needs, you can significantly contribute to the conservation of these vital pollinators.
VIII. Maintaining and Caring for Bee-Friendly Habitats
Creating bee-friendly habitats is a wonderful way to support the survival and well-being of these essential pollinators. Once you’ve established a bee-friendly garden or area, it’s important to maintain it properly to ensure its effectiveness in attracting and supporting bees. Here are some key steps you can take to care for your bee-friendly habitats:
1. Regularly Monitor the Health of Your Garden
Keep a close eye on your garden’s overall health by regularly inspecting plants for signs of disease or pest infestations. Address any issues promptly using organic methods, as chemical pesticides can harm bees and other beneficial insects.
2. Provide Adequate Water Sources
Besides nectar-rich flowers, bees also need water to thrive. Create shallow water sources like birdbaths or small ponds with rocks or floating objects as perches for easy access to drinking water.
3. Avoid Using Harmful Chemicals
Avoid using synthetic pesticides, herbicides, and fertilizers in your bee-friendly habitat as they can be toxic to bees and disrupt their natural behaviors.
4. Encourage Native Plants
Incorporating native plants into your habitat is highly beneficial since they have evolved alongside local pollinators, making them an excellent source of food and shelter.
5. Plant Flowers That Bloom at Different Times
To provide a consistent supply of nectar throughout the year, choose flowers that bloom at different times so that there are always food sources available for bees.
6. Regularly Weed Your Garden
Weeding helps prevent invasive plant species from overpowering native plants and competing for resources. This allows the native plants to thrive and continue supporting bee populations.
7. Create Nesting Sites
Provide nesting sites by leaving patches of bare ground or incorporating materials like hollow stems, wood blocks with drilled holes, or specialized bee houses where bees can lay their eggs and raise their young.
8. Educate Others About Bee Conservation
Spread awareness about the importance of bees and the need for bee-friendly habitats among your friends, family, and community. Encourage others to create their own bee-friendly spaces to multiply the positive impact on pollinator populations.
By following these maintenance practices, you can ensure that your bee-friendly habitat remains a welcoming sanctuary for bees, contributing significantly to their survival and overall biodiversity in your area. Remember, every effort counts when it comes to protecting these incredible creatures!
IX. Frequently Asked Questions about Creating Bee-Friendly Habitats
1. Why are bees important for our environment?
Bees play a crucial role in pollinating plants, which helps to sustain ecosystems and food production. They are responsible for pollinating a large percentage of the world’s crops, including fruits, vegetables, nuts, and oilseeds.
2. How can I create a bee-friendly habitat in my backyard?
To create a bee-friendly habitat, you can start by planting native flowering plants that provide nectar and pollen throughout the year. Avoid using pesticides or choose organic alternatives to protect bees from harmful chemicals.
3. What types of flowers are attractive to bees?
Bees are attracted to flowers with bright colors such as blue, purple, yellow, and white. Flowers with single petals or flat-topped clusters make it easier for bees to access nectar and pollen.
4. Do I need a big garden or yard to create a bee-friendly habitat?
No, you don’t need a large space to create a bee-friendly habitat. Even small gardens or balconies can be transformed into havens for bees by planting container gardens with bee-friendly plants.
5. Can I attract bees without attracting other pests like wasps?
A well-planned garden that focuses on attracting specific types of bees will not necessarily attract more wasps than usual. Providing suitable nesting sites for solitary bees can help increase their population while minimizing interactions with wasps.
6. How do I provide nesting sites for solitary bees?
You can provide nesting sites for solitary bees by leaving patches of bare soil or providing artificial nest boxes made from bamboo tubes or drilled wood blocks. These nesting sites should be located in a sunny area protected from strong winds.
7. Are there any bee-friendly alternatives to traditional lawn care?
Avoiding the use of synthetic fertilizers and pesticides on your lawn can make it more bee-friendly. Allow clover, dandelions, and other flowering weeds to grow as they provide valuable food sources for bees.
8. How can I support bees during the winter months?
Leaving some garden debris, such as fallen leaves or dead plant stems, provides overwintering sites for bees. You can also create small piles of twigs or logs to offer shelter to hibernating insects.
9. Can I keep honeybees in my backyard?
If you have enough space and are willing to commit time and effort, keeping honeybees can be a rewarding experience. However, proper research and understanding of beekeeping practices are essential before starting your own hive.
10. What other steps can I take to protect bees?
In addition to creating a bee-friendly habitat, you can support local beekeepers by purchasing their honey or products made from beeswax. By raising awareness about the importance of bees in your community, you can inspire others to take action as well.

Andrew Boyer is an accomplished individual with a deep-rooted passion for bees and their conservation. Born and raised in a small town in Oregon, Andrew developed an early fascination with nature and the environment. He pursued his education at the prestigious University of Oregon, where he obtained a Bachelor’s degree in Environmental Science with a specialization in Entomology. During his time at university, Andrew conducted extensive research on the behavior and ecological impact of bees, earning him recognition from his peers and professors. His dedication to the field led him to internships at local beekeeping associations, where he honed his skills in hive management and honey production. Andrew’s expertise in beekeeping and his commitment to environmental sustainability make him a valuable asset in the conservation of these vital pollinators.
