Contents
- I. Introduction to Beekeeping and Land Stewardship
- II. Benefits of Beekeeping for Land Stewardship
- III. Role of Bees in the Ecosystem
- IV. Sustainable Beekeeping Practices to Promote Land Stewardship
- V. Importance of Pollinator-Friendly Plants in Land Stewardship
- VI. Beekeeping and Organic Farming: Synergistic Relationship
- VII. Beekeeping as a Tool for Biodiversity Conservation
- VIII. The Role of Beekeepers in Land Conservation Efforts
- IX. Frequently Asked Questions about Beekeeping and Land Stewardship
- 1. Why is beekeeping important for land stewardship?
- 2. How does beekeeping contribute to sustainable agriculture?
- 3. Can beekeepers help protect endangered plant species?
- 4. What are some ways beekeepers can support land conservation efforts?
- 5. Are there any specific challenges faced by beekeepers practicing land stewardship?
- 6. How can individuals support beekeepers and land stewardship?
- 7. What other benefits do bees provide besides pollination?
- 8. Can I start beekeeping even if I don’t own vast tracts of land?
- 9. Are there any risks associated with keeping bees on private property?
- 10. How can I learn more about beekeeping and land stewardship practices?
I. Introduction to Beekeeping and Land Stewardship

Beekeeping is a fascinating practice that not only provides us with delicious honey but also plays a vital role in the ecosystem. It involves the management and care of bee colonies, allowing them to thrive and contribute to pollination. However, beekeeping goes beyond just reaping the sweet rewards; it encompasses land stewardship, which entails responsible management of the environment for both bees and other wildlife.
The Importance of Beekeeping
Beekeeping has gained significant attention in recent years due to the decline in global bee populations. Bees are essential pollinators that facilitate plant reproduction, contributing directly to crop production and biodiversity. Through their pollination efforts, they enable plants to bear fruits, vegetables, nuts, and seeds that sustain our food systems.
Environmental Benefits
By keeping bees on our land or supporting local beekeepers, we actively participate in preserving biodiversity and promoting sustainable agriculture. Bees play a crucial role as indicators of environmental health; their presence indicates a balanced ecosystem rich in flora and fauna. Additionally, maintaining healthy habitats for bees often leads to improved soil quality.
Promoting Land Stewardship
Land stewardship is an integral part of beekeeping practices aimed at preserving natural resources while minimizing negative impacts on ecosystems. This approach involves implementing sustainable agricultural methods such as organic farming or reducing pesticide use.
Educating Communities
In addition to managing beehives responsibly, beekeepers act as valuable educators within their communities regarding environmental conservation practices. They raise awareness about the importance of protecting pollinators like honeybees by sharing knowledge about sustainable gardening techniques or participating in outreach programs with schools or local organizations.
Cultivating Collaboration
Beekeeping and land stewardship often require collaboration between beekeepers, farmers, and landowners. By working together, they can create landscapes that support both bees and other wildlife. This collaborative effort promotes a balanced ecosystem where pollinators thrive, benefiting not only beekeepers but the entire community.
II. Benefits of Beekeeping for Land Stewardship
Beekeeping not only offers the opportunity to harvest honey and beeswax but also provides numerous benefits for land stewardship. Let’s explore some of the key advantages that beekeeping brings to the environment and our communities.
Promotes Pollination
One of the most significant benefits of beekeeping is its role in pollination. Bees are natural pollinators, transferring pollen from one flower to another, which allows plants to reproduce and bear fruit. By keeping bees on your land, you can enhance crop yields and promote biodiversity by ensuring that flowers are adequately pollinated.
Enhances Ecosystem Health
Beekeeping contributes to overall ecosystem health by supporting a diverse range of plant species. As bees collect nectar from various flowers, they inadvertently assist in cross-pollination, promoting genetic diversity among plants. This diversity helps ecosystems thrive by providing habitats for other wildlife species and maintaining a balanced ecological system.
Conserves Wild Bee Populations
The decline in wild bee populations due to habitat loss and pesticide use has raised concerns about potential negative impacts on ecosystems worldwide. By engaging in responsible beekeeping practices, such as using organic methods and avoiding harmful chemicals, we can help conserve wild bee populations while actively participating in their preservation.
Promotes Sustainable Agriculture
Beekeepers play an essential role in sustainable agriculture practices as they provide farmers with valuable pollinators that increase crop productivity naturally. By integrating beehives into agricultural landscapes, farmers reduce their reliance on synthetic fertilizers and pesticides while achieving higher yields through improved pollination services.
In conclusion,
Beekeeping offers multiple benefits for land stewardship – from promoting pollination and enhancing ecosystem health to conserving wild bee populations and supporting sustainable agriculture. By actively participating in beekeeping, individuals and communities can contribute to a healthier environment, increased agricultural productivity, and the preservation of important pollinators.
III. Role of Bees in the Ecosystem
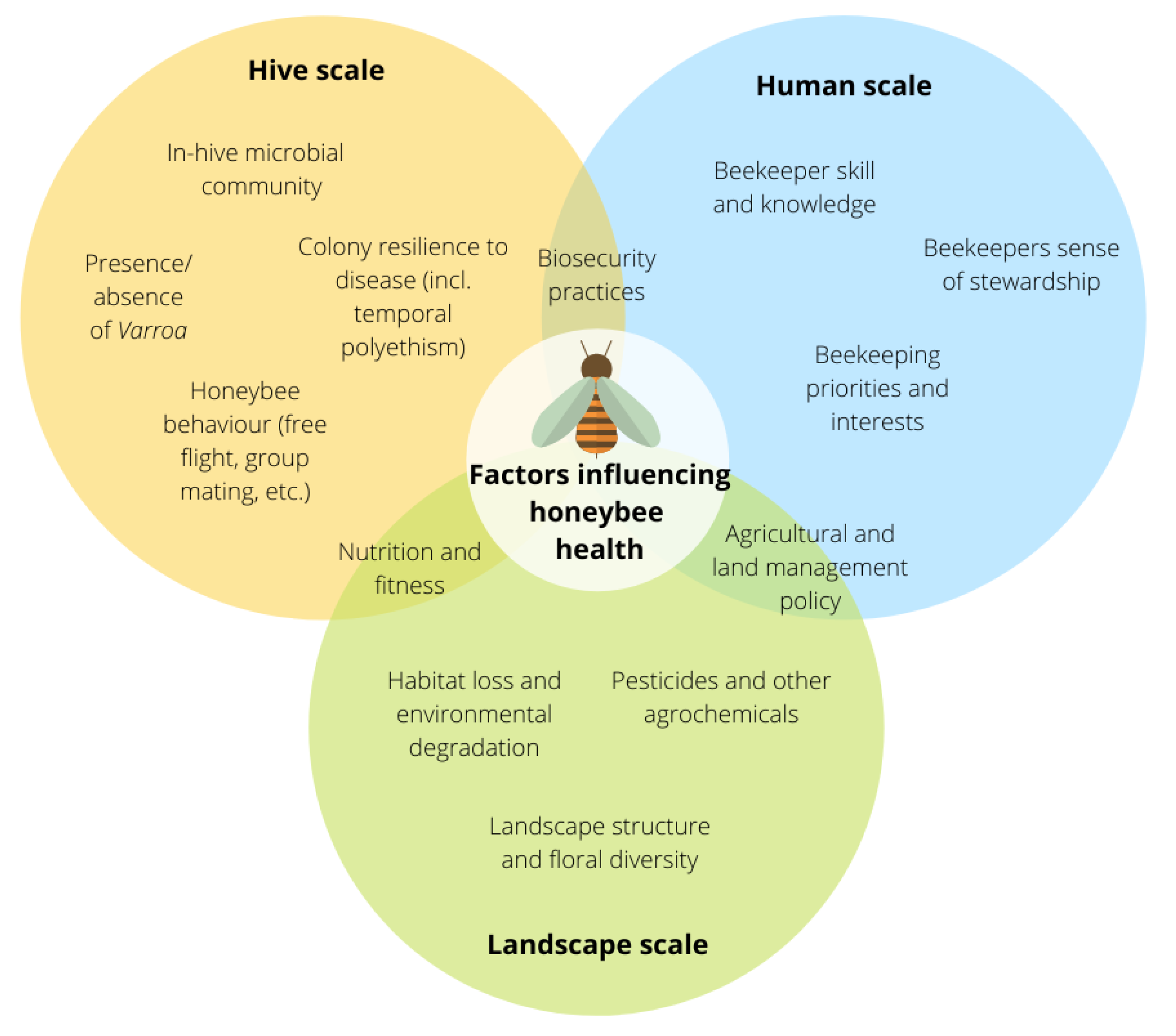
Bees play a vital role in maintaining the delicate balance of our ecosystem. These remarkable creatures are not just buzzing insects that produce honey; they are essential pollinators that contribute to the reproduction and survival of countless plant species.
Pollination and Plant Reproduction
The primary function of bees is to transfer pollen from male flower parts (anthers) to female flower parts (stigmas), enabling fertilization and subsequent seed production. This process, known as pollination, is crucial for plant reproduction.
When bees visit flowers in search of nectar or pollen, tiny grains of pollen stick to their bodies due to electrostatic forces. As they move from one flower to another, some of this pollen rubs off onto the receptive stigma, allowing fertilization to take place.
Biodiversity Preservation
By engaging in pollination activities, bees facilitate biodiversity preservation. They help maintain healthy populations of various plant species by ensuring their successful reproduction. In turn, this sustains diverse ecosystems by providing food sources and habitats for other organisms.
Without bees’ diligent efforts as pollinators, many plants would struggle with low reproductive success rates or even face extinction. Loss or decline in bee populations can have cascading effects on entire ecosystems.
Economic Importance
Beyond their ecological significance, bees also hold great economic importance for humans. Pollination services provided by bees contribute significantly to agricultural productivity and food security worldwide.
Crops such as fruits, vegetables, nuts, and oilseeds heavily rely on bee-mediated pollination for efficient fruit set and higher yields. The value added by these crops through bee pollination is estimated at billions of dollars annually.
Environmental Benefit
Furthermore, bees contribute to the overall environmental health. Their foraging behavior helps regulate plant populations and control weed growth. They also aid in the dispersal of seeds, enabling new plants to establish in different areas.
The presence of bees in an ecosystem indicates its ecological stability. Their absence or decline may disrupt the delicate balance and lead to cascading effects on other organisms within the environment.
Conclusion
In summary, bees are not just buzzing insects; they are vital contributors to our ecosystem. Through their role as pollinators, they ensure plant reproduction, preserve biodiversity, support agricultural productivity, and maintain environmental health. Recognizing the importance of bees is crucial for fostering sustainable land stewardship practices that prioritize their conservation.
IV. Sustainable Beekeeping Practices to Promote Land Stewardship

When it comes to beekeeping, adopting sustainable practices not only ensures the health and well-being of your bees but also promotes land stewardship. By implementing these practices, you can contribute to the preservation of our environment and support the overall ecosystem. Here are some key strategies for sustainable beekeeping:
1. Organic Beekeeping
Choosing organic methods in your beekeeping operations is an excellent way to minimize harmful impacts on both bees and the environment. By avoiding synthetic pesticides, antibiotics, and genetically modified organisms (GMOs), you can create a healthier habitat for your bees while reducing chemical contamination.
2. Natural Hive Management
Avoiding invasive hive management techniques is crucial for promoting sustainable beekeeping practices. Instead of using chemical treatments against pests or diseases, focus on enhancing colony resilience through natural methods such as selective breeding, providing adequate nutrition, and maintaining proper ventilation.
3. Native Plant Diversity
Promoting native plant diversity around your apiary provides a rich source of nectar and pollen for honeybees while supporting local ecosystems. Research which flowering plants are indigenous to your region and create pollinator-friendly habitats by planting them near your hives.
4. Integrated Pest Management (IPM)
An effective IPM approach involves monitoring pest levels regularly without relying solely on chemical interventions. Implementing physical barriers like screened bottom boards or employing biological controls such as introducing predator insects can help manage pests in a more eco-friendly manner.
5 .Water Conservation
Beekeepers should consider water conservation efforts since water scarcity affects both humans and honeybees alike. Collect rainwater or use drip irrigation systems instead of wasteful methods like hose spraying. Additionally, providing shallow water sources with floating platforms or rocks can prevent bees from drowning while quenching their thirst.
6. Responsible Honey Harvesting
When it’s time to harvest your honey, ensure responsible practices that prioritize bee welfare and hive sustainability. Leave enough honey for the bees to sustain themselves during colder months and avoid excessive extraction that could weaken the colony.
By adopting these sustainable beekeeping practices, you become an integral part of land stewardship efforts. Not only will you enjoy healthy and productive colonies, but you will also contribute positively to the preservation of our planet’s fragile ecosystems.
V. Importance of Pollinator-Friendly Plants in Land Stewardship
When it comes to land stewardship, one crucial aspect that often gets overlooked is the importance of pollinator-friendly plants. These plants play a vital role in supporting various pollinators, such as bees, butterflies, and birds, which are essential for maintaining biodiversity and ecological balance.
Enhancing Pollination Services
By incorporating pollinator-friendly plants into our landscapes, we can enhance the availability of suitable habitats and food sources for these important creatures. This leads to increased pollination services, benefiting both wild plant populations and agricultural crops. The more diverse and abundant the flowering plants are in an area, the greater the number of pollinators attracted.
Supporting Bee Health
Bees are among the most crucial pollinators worldwide; however their populations have been declining due to habitat loss and pesticide use. By planting a variety of native flowers rich in nectar and pollen throughout our lands, we can provide bees with a diverse diet that supports their health and well-being. In turn, healthy bee populations contribute to sustainable agriculture by ensuring efficient crop pollination.
Promoting Biodiversity
Pollinator-friendly plants not only attract bees but also support other beneficial insects like butterflies and moths. These insects serve as important links in food chains for birds and other wildlife species. Creating habitats with sufficient native plant diversity helps maintain a balanced ecosystem by providing shelter, food sources, nesting sites for these animals.
Ecosystem Resilience
Incorporating pollinator-friendly plants into land management practices promotes ecosystem resilience against environmental challenges such as climate change or invasive species invasion. By diversifying plant species composition through including native flowering plants adapted to local conditions, we can strengthen ecosystems and their ability to withstand disturbances.
Conserving Endangered Species
Many pollinators are currently facing the risk of extinction. By cultivating pollinator-friendly plants, we can create safe havens for endangered species and contribute to their conservation efforts. These plants act as stepping stones that enable the movement and gene flow of pollinators across fragmented landscapes, allowing populations to interconnect and persist.
VI. Beekeeping and Organic Farming: Synergistic Relationship
Beekeeping and organic farming share a mutual relationship that goes beyond the production of honey. The presence of bees in organic farms plays a crucial role in enhancing crop yields, promoting biodiversity, and supporting sustainable agricultural practices.
Pollination: Nature’s Gift to Organic Farms
One of the key benefits that beekeeping brings to organic farming is pollination. Bees are excellent pollinators, transferring pollen from male to female flower parts, which leads to fruit set and seed production. In an organic farm setting where synthetic pesticides are not used, bees play a vital role in ensuring successful pollination of crops such as fruits, vegetables, nuts, and berries.
Biocontrol: Natural Pest Management
Beyond their pollination services, bees also contribute to natural pest management in organic farms. Some species of bees have evolved specific behaviors that help control populations of harmful insects by preying on them or parasitizing their eggs or larvae. This natural biocontrol mechanism reduces the reliance on chemical pesticides in maintaining crop health.
Soil Fertility: Bees as Soil Builders
The activities of bees directly impact soil fertility through their interactions with flowers. As they collect nectar and pollen for food, they inadvertently transfer pollen grains between plants while simultaneously depositing small amounts of fecal matter (frass) onto the soil surface below. These tiny contributions enrich the soil with essential nutrients and microorganisms that facilitate plant growth.
Habitat Creation: Supporting Biodiversity
Beekeepers often provide suitable habitats for honeybees by creating beehives or apiaries within or near organic farms. These hives not only support thriving honeybee populations but also attract a diverse array of other pollinators, including native bees, butterflies, and even birds. The presence of these pollinators helps maintain biodiversity within the farm ecosystem.
Education and Awareness: Promoting Sustainable Practices
Beekeeping in an organic farming context provides an excellent opportunity for education and awareness about sustainable agricultural practices. It allows farmers to understand the interconnections between bees, crops, and the environment while also promoting responsible land stewardship. By incorporating beekeeping into their farming operations, organic farmers can inspire others to adopt eco-friendly practices.
VII. Beekeeping as a Tool for Biodiversity Conservation
Beekeeping is not only about honey production; it also plays a crucial role in biodiversity conservation. Bees, as pollinators, are responsible for the reproduction of many plant species, making them essential for the survival and growth of various ecosystems.
The Importance of Pollination
Pollination is a vital ecological process that enables plants to reproduce and produce fruits and seeds. It involves the transfer of pollen from the male part (stamen) to the female part (pistil) of flowers, leading to fertilization. Bees are one of nature’s most efficient pollinators due to their foraging behavior and ability to carry large amounts of pollen on their bodies.
By engaging in beekeeping practices, we can create ideal environments that support bee populations and enhance pollination services. This allows us to preserve floral diversity within ecosystems while ensuring the continued propagation of numerous plant species.
Enhancing Habitat Diversity
Beekeepers often maintain diverse landscapes around their hives by planting various flowering plants that provide nectar and pollen sources throughout different seasons. These efforts contribute directly to habitat diversification, attracting not only honeybees but also native wild bees and other beneficial insects.
Moreover, beekeepers can adopt sustainable land management practices such as avoiding pesticide use or implementing organic farming techniques. These actions help conserve soil health, reduce chemical contamination in surrounding areas, and promote overall ecosystem resilience.
Conserving Endangered Species
Some bee species face extinction due to habitat loss or degradation caused by human activities. By practicing responsible beekeeping methods focused on preserving natural habitats rather than exploiting them intensively for honey production alone, we can contribute significantly towards conserving endangered bees.
Additionally, beekeepers can participate in citizen science initiatives by monitoring and reporting bee populations and their behaviors. This data can aid scientists in better understanding the dynamics of bee populations, identifying threats to their survival, and implementing targeted conservation strategies.
The Ripple Effect
Beekeeping’s impact on biodiversity conservation extends beyond just bees. By ensuring the health and diversity of pollinator populations, we indirectly support the well-being of other wildlife species that rely on these pollinators for food or habitat resources.
Ultimately, by recognizing beekeeping as a tool for biodiversity conservation, we have an opportunity to protect not only bees but also entire ecosystems. Through responsible practices and active participation in preserving natural habitats, we can contribute towards maintaining healthy biodiversity levels for generations to come.
VIII. The Role of Beekeepers in Land Conservation Efforts
Beekeepers play a vital role in land conservation efforts, contributing to the preservation and restoration of natural habitats. By caring for honeybees and their hives, beekeepers indirectly support the wider ecosystem and promote biodiversity.
Promoting Pollination
One of the primary contributions of beekeepers to land conservation is through promoting pollination. Honeybees are highly efficient pollinators, transferring pollen from one flower to another as they collect nectar. This process is crucial for the reproduction of many plant species, including those that serve as food sources for other wildlife.
By maintaining healthy colonies and strategically placing their hives near agricultural fields or areas with diverse flora, beekeepers ensure that crops receive adequate pollination services. This not only increases crop yields but also enhances overall ecosystem health by supporting native plant populations.
Protecting Native Bees
Beekeeping practices can also contribute to protecting native bee populations. Although honeybees are not native to all regions, they often coexist with various species of solitary bees and bumblebees that play essential roles as pollinators in local ecosystems.
Beekeepers who prioritize sustainable practices create suitable environments for these native bee species by providing nesting sites, planting diverse flowering plants, and minimizing pesticide use around their apiaries. These efforts help maintain healthy populations of both managed honeybees and wild bees, ensuring resilient ecosystems capable of sustaining diverse flora and fauna.
Educating Communities
Beyond their practical contributions on the ground, beekeepers also play a significant role in educating communities about environmental conservation. As keepers of an emblematic insect species like honeybees, they have a unique opportunity to raise awareness about broader ecological issues and inspire action.
Beekeepers often engage in outreach programs, school visits, and public demonstrations to share their knowledge about bees’ importance and the need for preserving natural habitats. By fostering a sense of appreciation for nature and promoting sustainable practices, they encourage individuals to actively participate in land conservation efforts.
Collaborating with Conservation Organizations
Many beekeepers collaborate with local conservation organizations or participate in citizen science initiatives to contribute valuable data on pollinator populations. Through these partnerships, they help monitor bee health, track changes in habitat conditions, and identify potential threats to pollinators.
By sharing their observations with researchers and conservationists, beekeepers contribute valuable insights that inform land management strategies. This collaborative approach strengthens the connection between beekeeping communities and broader environmental stewardship efforts.
In conclusion, beekeepers are essential actors in land conservation endeavors. Their contributions through promoting pollination, protecting native bees, educating communities about environmental issues, and collaborating with conservation organizations help create a more sustainable future for both honeybees and the ecosystems they inhabit.
IX. Frequently Asked Questions about Beekeeping and Land Stewardship
Beekeeping and land stewardship go hand in hand, as both practices play a crucial role in maintaining a healthy ecosystem. If you’re new to beekeeping or interested in the connection between bees and the environment, here are some frequently asked questions that might provide further insights:
1. Why is beekeeping important for land stewardship?
Beekeeping plays a vital role in pollination, which is essential for the reproduction of many plant species. By keeping bees, we can help ensure that flowering plants receive adequate pollination, leading to better crop yields and overall biodiversity.
2. How does beekeeping contribute to sustainable agriculture?
Beekeepers work closely with farmers by providing their hives for pollination services on agricultural lands. This collaboration helps enhance crop productivity while reducing the need for chemical pesticides.
3. Can beekeepers help protect endangered plant species?
Absolutely! Beekeepers often focus on conserving local plant varieties by placing their hives near areas with rare or endangered plants. Bees visit these flowers, aiding in their reproduction and increasing their chances of survival.
4. What are some ways beekeepers can support land conservation efforts?
Beyond traditional beekeeping practices, many responsible beekeepers actively participate in habitat restoration projects by planting native wildflowers and creating suitable nesting sites for solitary bees.
5. Are there any specific challenges faced by beekeepers practicing land stewardship?
A significant challenge is ensuring that bees have access to diverse sources of nectar and pollen throughout the year since monoculture farming limits floral diversity. Beekeepers must carefully plan hive locations near varied floral resources.
6. How can individuals support beekeepers and land stewardship?
Supporting local beekeepers by purchasing their honey and beeswax products is a great way to contribute. Additionally, creating pollinator-friendly gardens at home with native plants, avoiding chemical pesticides, and spreading awareness about the importance of bees are all impactful actions.
7. What other benefits do bees provide besides pollination?
Besides pollination, bees produce honey, beeswax, propolis (a natural resin), and royal jelly (a nutrient-rich substance). These products have various uses in food production, cosmetics, medicine, and more.
8. Can I start beekeeping even if I don’t own vast tracts of land?
Absolutely! Beekeeping can be practiced on a small scale in urban areas as well. Many cities now allow rooftop or balcony beekeeping as long as certain regulations are followed to ensure safety for both the bees and humans.
9. Are there any risks associated with keeping bees on private property?
The primary risk is the potential for stings if not handled properly or if people have allergies to bee venom. However, with proper precautions such as using protective gear while working around hives and placing them away from high-traffic areas, these risks can be minimized.
10. How can I learn more about beekeeping and land stewardship practices?
To deepen your knowledge about beekeeping and its connection to land stewardship, consider joining local beekeeping associations or attending workshops offered by experienced apiarists. There are also numerous online resources available that provide valuable information for beginners.
Remember that embracing sustainable practices like responsible beekeeping ultimately contributes to preserving our environment’s health while fostering biodiversity for future generations.

Andrew Boyer is an accomplished individual with a deep-rooted passion for bees and their conservation. Born and raised in a small town in Oregon, Andrew developed an early fascination with nature and the environment. He pursued his education at the prestigious University of Oregon, where he obtained a Bachelor’s degree in Environmental Science with a specialization in Entomology. During his time at university, Andrew conducted extensive research on the behavior and ecological impact of bees, earning him recognition from his peers and professors. His dedication to the field led him to internships at local beekeeping associations, where he honed his skills in hive management and honey production. Andrew’s expertise in beekeeping and his commitment to environmental sustainability make him a valuable asset in the conservation of these vital pollinators.
