Contents
- I. Introduction to Waggle Dance Communication
- II. The Importance of Waggle Dance Communication in Bees
- III. How Waggle Dance Communication Works
- IV. Factors Influencing Waggle Dance Communication
- V. The Role of Waggle Dance Communication in Foraging
- VI. Benefits of Understanding Waggle Dance Communication for Beekeepers
- VII. Frequently Asked Questions about Waggle Dance Communication
- What is the purpose of waggle dance communication?
- How does a honeybee perform a waggle dance?
- Why do bees use dances instead of direct communication?
- Do all honeybees know how to interpret these dances?
- Can humans understand or decode waggle dances?
- Are there different types of waggle dances?
- Do other bee species use similar communication methods?
- Can environmental factors affect waggle dance behavior?
- What happens if a foraging bee cannot find a previously indicated food source?
- How do scientists study waggle dance communication?
I. Introduction to Waggle Dance Communication
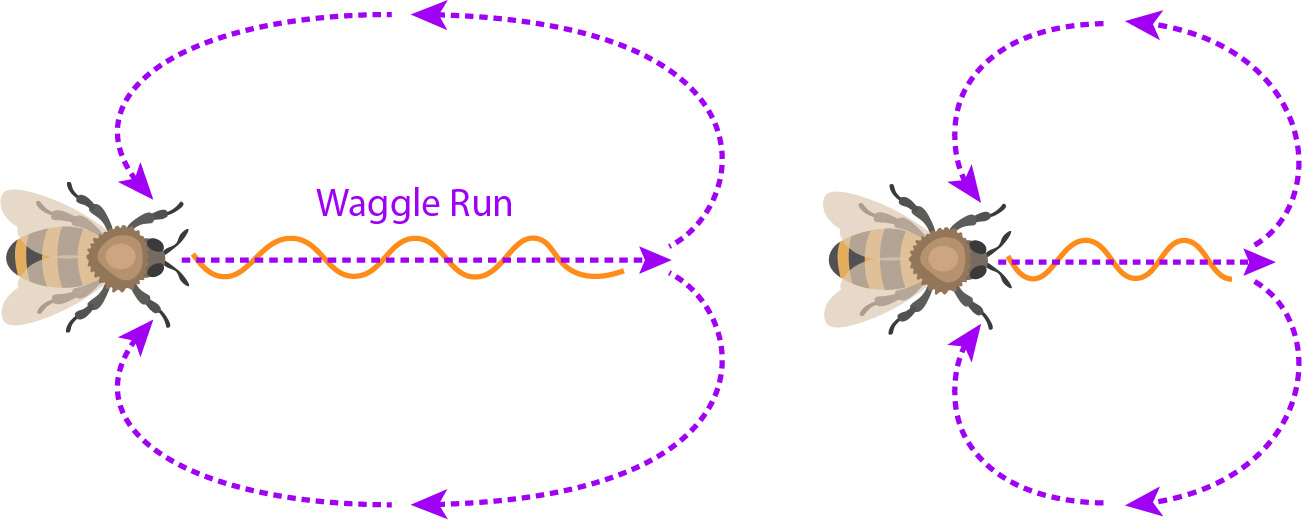
Waggle dance communication is a fascinating behavior exhibited by honeybees, where they convey vital information about food sources and locations to other members of the hive. This unique form of communication has been studied extensively by scientists and provides insights into the complex social organization and intelligence of these remarkable insects.
The Purpose of Waggle Dance
The main purpose of the waggle dance is to provide precise directions to other honeybees about the direction, distance, and quality of a food source. It serves as a navigational tool for foraging bees, enabling them to efficiently locate nectar-rich flowers or pollen sources.
How Does it Work?
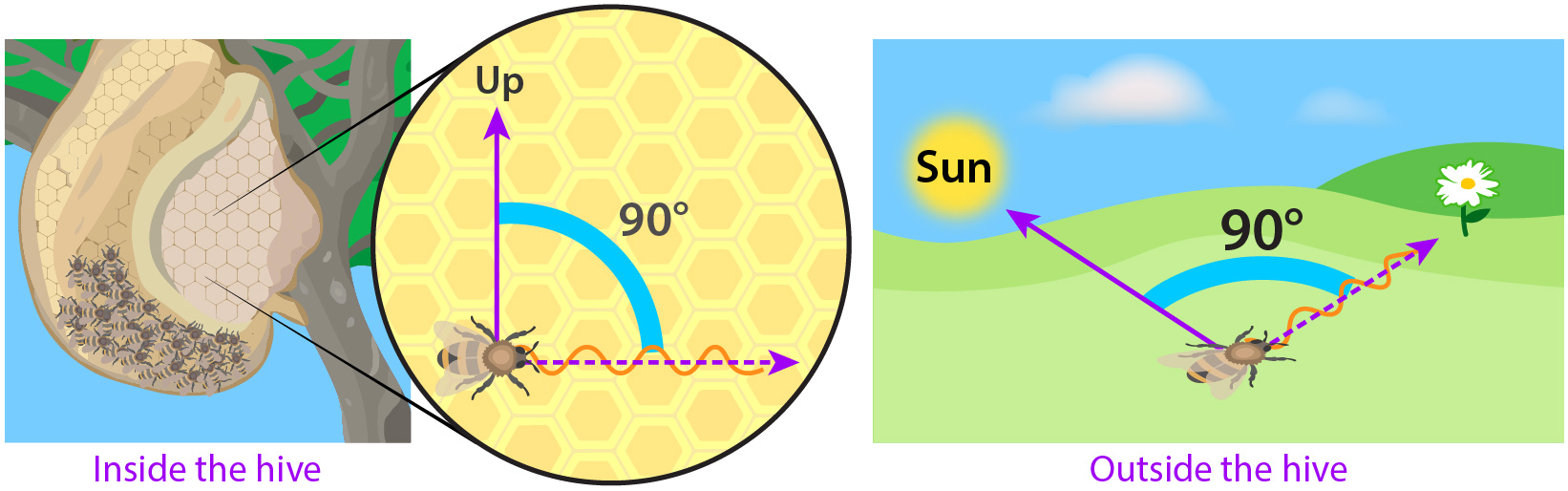
The waggle dance consists of intricate movements performed by worker bees inside the hive. The dancer bee moves in a figure-eight pattern while waggling its abdomen from side to side. The angle at which it performs this movement relative to vertical indicates the direction in which the food source can be found in relation to the sun’s position.
In addition, the duration or length of time spent waggling conveys information about distance: longer waggles indicate greater distances, while shorter ones represent closer proximity. By communicating both direction and distance through their dance, bees are able to effectively communicate complex spatial information without using words or sounds.
Other Bees’ Interpretation
Honeybees that observe this waggle dance use their sensory perception skills to interpret its meaning. They closely follow these intricate movements made by the dancing bee and decode important details embedded within them.
To determine exact location coordinates relative to their surroundings, observing bees rely on polarized light patterns from sunlight filtering through cracks in their hive walls or tree branches outside. This helps them orient themselves and understand the direction indicated by the dancer bee.
The Importance of Waggle Dance
Waggle dance communication plays a vital role in ensuring the survival and productivity of honeybee colonies. By effectively communicating where abundant food sources can be found, bees are able to optimize foraging efforts, thus maximizing their chances of survival as well as the overall success of their colony.
Understanding waggle dance communication not only provides us with insights into how bees navigate and communicate but also sheds light on their sophisticated social structure. It highlights the remarkable ability of these tiny creatures to convey complex information without verbal language, showcasing their intelligence and adaptability.
II. The Importance of Waggle Dance Communication in Bees
Bees are fascinating creatures that have developed unique ways to communicate with each other. One such form of communication is the waggle dance, which plays a vital role in their survival and success as a colony. The waggle dance is an intricate behavior performed by worker bees to convey important information about food sources, including distance, direction, and quality.
1. Sharing Precise Information
The waggle dance allows bees to share precise details about the location of food sources with remarkable accuracy. Through a series of figure-eight movements and tail waggles inside the hive, a bee can communicate the exact distance and direction of the food source relative to the position of the sun. This information is crucial for other foragers to navigate their way towards valuable nectar or pollen-rich areas efficiently.
2. Efficient Resource Allocation
The ability to communicate through waggle dances enables bees to allocate their resources effectively. By sharing information about fruitful feeding grounds, they can avoid wasting time and energy on less productive areas. This efficient resource allocation ensures that individual bees can focus on collecting abundant resources while maintaining overall colony productivity.
3. Cultural Transmission
The waggle dance also plays a significant role in cultural transmission within bee colonies. Younger worker bees learn how to perform this complex behavior by observing more experienced dancers in the hive’s dark chambers. This cultural exchange ensures that knowledge about reliable food sources is passed down from one generation of workers to another, allowing for continued success even as individual bees come and go.
4 Enhancing Colony Survival
The effectiveness of waggle dance communication contributes directly to colony survival and resilience against environmental challenges like changes in floral availability or habitat disturbances caused by human activities. By sharing information about food sources, bees can adapt their foraging strategies and respond to changing circumstances, thus increasing the chances of survival for the entire colony.
5. Symbolic Language
Besides its practical value, the waggle dance represents a remarkable example of symbolic language in the animal kingdom. The specific movements and patterns performed by dancing bees convey meaning to other members of the colony, allowing them to interpret and act upon this shared knowledge. This form of communication highlights the sophistication and intelligence present within bee communities.
III. How Waggle Dance Communication Works
The waggle dance is a fascinating form of communication used by honeybees to convey information about the location of food sources to other members of their colony. This intricate dance involves precise movements and patterns that can be deciphered by fellow bees, allowing them to navigate and find valuable resources.
The Language of Waggle Dance
In the waggle dance, a foraging bee performs a series of figure-eight movements while vibrating its abdomen. The angle and duration of the waggle run indicate the direction and distance to the food source respectively. By observing these cues, bees are able to interpret the information encoded in this unique dance language.
Recruitment Process
Waggle dancing serves as a recruitment tool within the honeybee colony. When a successful forager returns to the hive, it performs the waggle dance on vertical surfaces such as combs or walls. Other worker bees closely follow these dances, tracking both direction and distance cues provided by their dancing counterparts.
If multiple bees return with information about different food sources, they may compete through more vigorous or longer dances in an attempt to recruit more followers for their respective sources. This competition ensures that resources are efficiently allocated within the colony.
Dance Variation and Adaptation
The complexity of waggle dances varies depending on factors such as resource quality and distance from the hive. Bees adjust their dancing behavior based on environmental conditions, allowing them to effectively communicate different types of information.
In situations where food is located nearby, bees perform shorter waggles with smaller angles to indicate proximity rather than exact distance measurements. On the other hand, when resources are farther away or require extensive navigation efforts, longer waggles with larger angles provide more precise directions for their fellow bees.
Communication Accuracy and Reliability
Waggle dance communication is remarkably accurate, with bees successfully guiding their nestmates to specific food sources. However, the accuracy can be influenced by various factors such as wind speed, terrain obstacles, or the behavior of other foragers within the colony.
Despite these challenges, honeybees have evolved to minimize errors in communication through continuous feedback loops and recalibration. By incorporating sensory information from their surroundings and adjusting dance parameters accordingly, they maintain a high level of reliability in sharing vital information for survival.
IV. Factors Influencing Waggle Dance Communication

Waggle dance communication is a fascinating behavior observed in honeybees, where foragers communicate the location of food sources to their hive mates through specific dance movements. This intricate dance language is influenced by various factors that shape its effectiveness and accuracy.
Spatial Orientation
The spatial orientation of the waggle dance plays a crucial role in conveying information about the direction and distance of the food source. Honeybees are highly sensitive to changes in their surroundings, such as alterations in light intensity or magnetic fields, which help them accurately interpret and follow the directions provided by the dancer.
Food Source Quality
The quality of a food source significantly influences how bees communicate its location. Bees perform longer duration dances when they discover rich nectar sources or abundant pollen, indicating higher desirability and value to their hive mates. Similarly, dances for lower-quality resources tend to be shorter or less vigorous.
Hive Environment
The internal conditions within the hive can impact waggle dance communication. Factors such as temperature, humidity, noise levels, and population density can all affect how well bees perceive and decode these dances. For instance, high noise levels may interfere with precise interpretation while crowded conditions could limit visibility during observation.
Time of Day
The time at which waggle dances occur also plays a role in communication efficiency. Bees adjust their dancing behavior based on external factors like sunlight availability or floral rhythms related to certain plant species that bloom at specific times of day. Timing synchronization allows other bees to synchronize their departure from the hive accordingly.
Dance Accuracy
The accuracy of waggle dance communication depends on multiple factors working together harmoniously. The precision with which a bee performs the dance, including the duration, orientation, and intensity of movements, directly influences how accurately hive mates can interpret the communicated information. The clearer and more consistent the dance signals, the higher the chances of successful foraging.
Overall, waggle dance communication in honeybees is a complex system influenced by various factors. From spatial orientation to environmental conditions and even time-related cues, these elements shape how bees convey vital information about food sources to their fellow hive members. Understanding these factors provides valuable insights into this remarkable form of communication among bees.
V. The Role of Waggle Dance Communication in Foraging
Waggle dance communication is a fascinating behavior observed in honeybees, where they use intricate movements to convey vital information about food sources to their fellow hive members. This unique form of communication plays a crucial role in guiding foragers towards abundant nectar and pollen-rich locations.
The Dance Language
The waggle dance involves a bee performing a figure-eight pattern while waggling its abdomen from side to side. The angle and duration of the waggle portion indicate the direction and distance respectively, relative to the sun, of the foraging site. By following these cues, other bees can navigate precisely towards the desired location.
This dance language is highly effective because it allows bees to communicate both spatial information (direction and distance) as well as qualitative information (quality and quantity of resources). Through this intricate choreography, honeybees are able to provide accurate instructions regarding fruitful foraging grounds.
Recruitment Process
Once a scout bee discovers a valuable food source, it returns to the hive and initiates recruitment through waggle dances. The more attractive the resource encountered by the scout bee, the longer and more vigorous its dance becomes. This difference in intensity helps prioritize better food sources while encouraging collective decision-making within the colony.
Other worker bees attentively observe these dances before deciding which ones to follow based on factors such as duration or intensity. As more workers join specific dances representing particular locations or resources, momentum builds up until there is an optimal number of individuals committed to visiting that specific site.
Fine-Tuning Information Flow
Honeybee colonies have developed mechanisms that fine-tune information flow during waggle dance communication. For example, scouts may compete for attention by performing dances simultaneously. In such cases, bees assess the dances and make decisions based on factors like dance quality or proximity to the hive entrance.
The communication network within a honeybee colony is highly dynamic, with constant adjustments made based on the changing availability and profitability of food sources. This flexibility ensures that bees can quickly adapt their foraging efforts to optimize resource exploitation.
Implications for Conservation
Understanding waggle dance communication has broader implications beyond the fascinating world of honeybees. Researchers have leveraged this knowledge to improve agricultural practices, enhance pollination efficiency, and support conservation efforts.
By deciphering the intricacies of waggle dance communication, scientists can gain insights into how bee colonies make decisions collectively. This understanding allows for effective management strategies that promote sustainable beekeeping practices while safeguarding pollinators’ vital role in maintaining ecosystem health.
VI. Benefits of Understanding Waggle Dance Communication for Beekeepers
Understanding waggle dance communication can provide numerous benefits for beekeepers. By deciphering the intricate language of bees, beekeepers can gain valuable insights into their hive’s health, behavior, and productivity. Let’s explore some of the key advantages:
Promotes Hive Management
Waggle dance communication allows beekeepers to monitor and manage their hives more effectively. Through decoding the dances performed by worker bees, beekeepers can determine the location and quality of nectar sources or pollen-rich areas. This information helps them make informed decisions regarding hive placement, ensuring optimal foraging opportunities for their colonies.
Enhances Honey Production
With a deeper understanding of waggle dances, beekeepers can maximize honey production. By identifying abundant nectar sources through observation or even video recording inside the hive, they can strategically place hives in areas where bees are likely to find rich food sources efficiently. This targeted approach results in increased honey yields and higher-quality products.
Predicts Swarming Behavior
The waggle dance also serves as an early warning system for potential swarming events within a colony. By interpreting specific characteristics of these dances such as duration or intensity, experienced beekeepers can anticipate when their bees might be preparing to swarm. This insight enables them to take preventive measures such as providing additional space or manipulating colony dynamics to discourage swarming.
Aids Pollination Services
Beekeeping is not only about honey production but also plays a crucial role in pollination services for agricultural crops and wild plants alike. Understanding waggle dance communication empowers beekeepers to steer their colonies towards specific floral resources that require pollination assistance at different times throughout the year. This targeted pollination can significantly improve crop yields and ensure the health of diverse ecosystems.
Facilitates Research and Education
Knowledge of waggle dance communication provides a fascinating avenue for research and education. Beekeepers who are familiar with decoding these dances can contribute valuable data to scientific studies on bee behavior, ecology, and conservation. Moreover, sharing this knowledge with the wider community helps raise awareness about the importance of bees in our environment, promoting their protection and sustainable management.
VII. Frequently Asked Questions about Waggle Dance Communication
Curious about waggle dance communication? Below are some frequently asked questions to help you understand this fascinating behavior among honeybees.
What is the purpose of waggle dance communication?
The purpose of waggle dance communication is for honeybees to share information about the location of food sources, such as nectar and pollen. By performing specific dance moves, a foraging bee can convey the direction and distance of a food source to other members of the colony.
How does a honeybee perform a waggle dance?
A honeybee performs a waggle dance by moving in a figure-eight pattern while waggling its abdomen from side to side. The angle at which it performs the wiggle relative to gravity indicates the direction in relation to the sun. The duration and intensity of the waggling also provide information about distance.
Why do bees use dances instead of direct communication?
Honeybees use dances as an efficient way to communicate because they can convey detailed information about food sources without physically transporting them back to the hive. This method allows multiple bees to gather accurate location data quickly, saving time and energy for individual foragers.
Do all honeybees know how to interpret these dances?
No, not all honeybees know how to interpret waggle dances immediately. Young worker bees need training from experienced foragers before they can understand and respond appropriately. Through repeated exposure and learning, they gradually become proficient in decoding these intricate movements.
Can humans understand or decode waggle dances?
While researchers have made significant progress in deciphering certain aspects of waggle dances, full comprehension remains challenging due to their complexity. Scientists use techniques such as video recordings and measurements to analyze the dances in detail, but there is still much to learn about their subtleties and variations.
Are there different types of waggle dances?
Yes, honeybees perform different types of waggle dances depending on the distance and quality of the food source. For shorter distances, they may perform “round” dances without waggling, indicating that the food source is nearby. For longer distances, more intense waggling movements are observed.
Do other bee species use similar communication methods?
While waggle dance communication is most commonly associated with honeybees (Apis mellifera), some other bee species also employ similar communication methods. Bumblebees, for example, perform vibrations known as “buzz runs” to communicate information about food sources within their colonies.
Can environmental factors affect waggle dance behavior?
Absolutely! Environmental factors such as temperature, humidity, and light conditions can influence how honeybees perform their waggle dances. Bees have been observed adjusting their dance patterns based on external conditions to ensure accurate communication within their specific context.
What happens if a foraging bee cannot find a previously indicated food source?
If a foraging bee cannot find a previously indicated food source during its search flight based on another bee’s dance instructions, it may return to the hive without collecting any resources. It may then engage in further exploration or rely on other bees’ information until it discovers an alternative food source.
How do scientists study waggle dance communication?
To study waggle dance communication in controlled environments or observe wild colonies undisturbedly, researchers often use marked bees or radio-frequency identification (RFID) tags. They also employ advanced technology, such as high-speed cameras and tracking systems, to capture and analyze the intricate details of the dances.

Andrew Boyer is an accomplished individual with a deep-rooted passion for bees and their conservation. Born and raised in a small town in Oregon, Andrew developed an early fascination with nature and the environment. He pursued his education at the prestigious University of Oregon, where he obtained a Bachelor’s degree in Environmental Science with a specialization in Entomology. During his time at university, Andrew conducted extensive research on the behavior and ecological impact of bees, earning him recognition from his peers and professors. His dedication to the field led him to internships at local beekeeping associations, where he honed his skills in hive management and honey production. Andrew’s expertise in beekeeping and his commitment to environmental sustainability make him a valuable asset in the conservation of these vital pollinators.
