Contents
- I. Introduction to Pheromones and Chemical Signals
- II. Understanding Pheromones: Definition and Function
- III. Types of Pheromones and Their Effects
- IV. The Role of Pheromones in Animal Communication
- V. Pheromones in Humans: Myth or Reality?
- VI. How Pheromones Influence Behavior and Attraction
- VII. Pheromone Detection and Sensory Systems
- VIII. The Science behind Pheromone Production and Release
- IX. Pheromone-Based Products: Do They Really Work?
I. Introduction to Pheromones and Chemical Signals
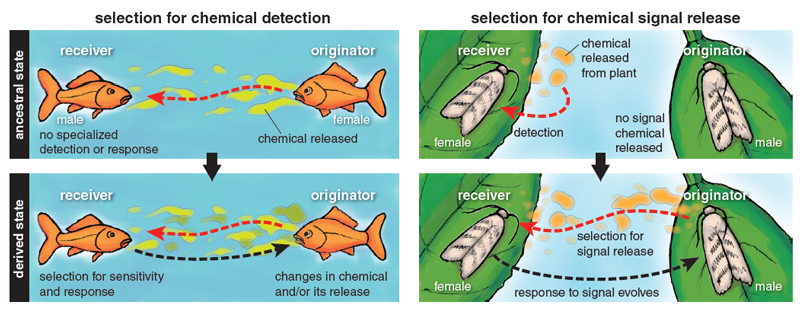
In the fascinating world of animal communication, there exists a secret language that is often undetectable to our human senses – pheromones and chemical signals. These invisible molecules play a crucial role in the social interactions and survival strategies of various species. From insects to mammals, pheromones are used as an effective means of communication.
So what exactly are pheromones? They are chemical substances secreted by animals that trigger specific responses in individuals of the same species. Unlike verbal or visual communication, which rely on sound or sight, pheromones work their magic through scent receptors.
1. The Power of Scent
Scent holds incredible power when it comes to animal behavior. Pheromones allow creatures to convey essential information such as territory marking, sexual attraction, alarm signals, or even aggression warnings without uttering a single word.
Insects like ants use trail-marking pheromones to guide their fellow colony members towards food sources or new nest locations. These tiny chemical trails act as invisible maps leading them in the right direction.
2. Mating Rituals and Sexual Attraction
Pheromonal cues also play a significant role in mating rituals among many species. In some cases, female moths emit sex-attractant pheromones that can be detected by males from miles away using their highly sensitive antennae.
Mammals like dogs have specialized glands that release unique odors during reproductive cycles which signal potential mates about readiness for breeding.
3. Alarm Signals and Defense Mechanisms
Pheromone signaling is not only limited to attracting mates but also serves as an alarm system for danger detection. For instance, bees release alarm pheromones when they perceive a threat to their hive, alerting other members to prepare for defense.
Even humans are not immune to the power of pheromones. Although our sense of smell may not be as acute as that of animals, research suggests that certain chemical signals can influence our social interactions and even subconscious attraction towards others.
II. Understanding Pheromones: Definition and Function
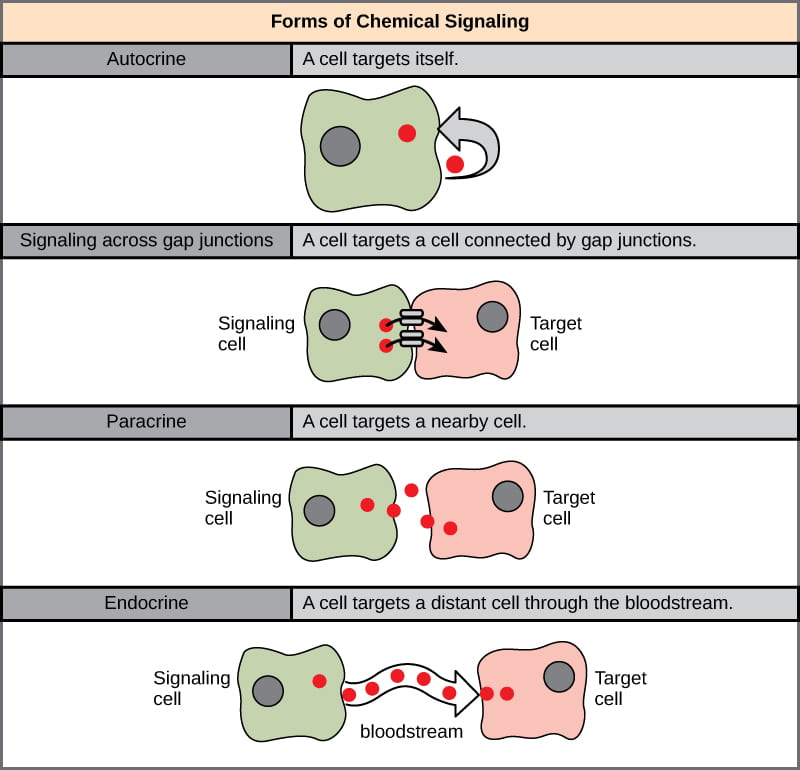
Pheromones are fascinating chemical compounds that play a crucial role in communication among animals, insects, and even humans. Derived from the Greek words “pherein” (to transfer) and “hormon” (to stimulate), pheromones are secreted by individuals of the same species to convey specific messages or signals.
The Definition of Pheromones
Pheromones can be defined as chemical substances released into the environment by an organism which then trigger a physiological or behavioral response in other members of the same species. These odorless chemicals are often perceived through specialized receptor cells located in the nasal passages or sensory organs.
The Function of Pheromones
The primary function of pheromones is to transmit information between individuals within a species, influencing their behavior and responses. They serve as powerful messengers, guiding social interaction, mating rituals, territorial marking, alarm signaling, and even aggression control.
One example of pheromone function is seen in ants. Ants release trail pheromones that act as a guide for other ants to follow when searching for food sources. This effective communication system ensures efficient foraging and resource allocation within their colonies.
In mammals like dogs or wolves, pheromonal cues emitted through urine marking help establish territories and communicate dominance hierarchies among pack members. Likewise, female moths release sex pheromones to attract males during mating season while simultaneously repelling rival females.
Pheromone Reception Mechanisms
To detect these chemical signals effectively, organisms possess specialized sensory systems designed specifically for detecting pheromonally-induced cues. In insects like bees, these receptors are located on their antennae, while mammals have a specialized organ called the vomeronasal organ (VNO) that detects pheromones.
Once the pheromone molecules bind to their respective receptors, they trigger a cascade of neurochemical reactions in the brain, resulting in various physiological and behavioral responses. These responses can range from attraction or repulsion to changes in hormone levels and even alterations in reproductive behavior.
The Role of Pheromones in Human Interaction
While often associated with animals and insects, pheromones also play a role in human interaction. Although their impact on humans is still not fully understood, studies suggest that specific chemical signals influence attraction between individuals and may affect mood or emotional states.
Although more research is needed to uncover the extent of pheromonal effects on human behavior, it is clear that these invisible chemical messengers have a significant impact on communication and social dynamics across various species.
III. Types of Pheromones and Their Effects

Pheromones are chemical substances secreted by organisms to communicate with others of the same species. These chemical signals play a vital role in various aspects of animal behavior, including mating, territorial marking, alarm signaling, and social bonding. Different types of pheromones have been identified across different species, each serving a specific purpose and producing unique effects.
Sex Pheromones
Sex pheromones are perhaps the most well-known type of pheromone. They play a crucial role in attracting individuals for mating purposes. In many animal species, these pheromones can be detected at long distances and trigger specific behaviors associated with courtship rituals.
Aggregation Pheromones
Aggregation pheromones are used by certain organisms to signal the presence of resources or suitable habitats to other members of their species. These chemicals help attract conspecifics to gather in groups or colonies for feeding or sheltering purposes.
Alarm Pheromones
When an individual within a group detects danger or perceives a threat, they release alarm pheromones as a warning signal to others nearby. Alarm pheromones can evoke defensive behaviors such as fleeing or adopting protective postures.
Territorial Pheromones
Territorial pheromones are utilized by animals to mark their territories and establish ownership over particular areas. By depositing these chemicals on surfaces within their territory, animals communicate boundaries and deter intruders from encroaching upon their space.
Trail Pheromon
IV. The Role of Pheromones in Animal Communication

Pheromones play a crucial role in animal communication, serving as chemical signals that transmit information between individuals of the same species. These chemical compounds are released by animals into their environment and can be detected by other members of their species, influencing various behaviors and social interactions.
1. Attracting Mates
One significant function of pheromones is to attract potential mates. In many species, males emit specific pheromones that signal their availability and desirability to females. These chemical cues can communicate information about genetic compatibility, health status, and reproductive readiness. By detecting these pheromones, females can assess the suitability of potential partners and make informed decisions while choosing a mate.
2. Territory Marking
Pheromones also play a key role in marking territories and establishing dominance within animal communities. Many animals release scent markers containing specific pheromonal signals to indicate ownership or defend their territory against intruders. These territorial messages help prevent conflicts between individuals by providing clear boundaries for resource access.
3. Alarm Signals
Certain types of pheromones act as alarm signals, alerting nearby individuals to potential threats or danger in the environment. When an animal detects these chemical cues released by another member of its species during times of distress or danger, it triggers immediate behavioral responses such as fleeing or defensive actions.
4. Social Bonding
Pheromonal communication also plays a vital role in forming social bonds among animals within the same group or community. By emitting specific bonding pheromones during grooming sessions or physical contact with others, animals create positive associations with each other and strengthen social cohesion within the group.
5. Trail Marking
Some species of animals, particularly insects like ants and bees, use pheromones to mark trails that lead to food sources or their nests. These chemical markers guide other members of the colony, ensuring efficient foraging and navigation within their environment.
V. Pheromones in Humans: Myth or Reality?
When it comes to pheromones, most people tend to think of animals and insects, but what about humans? Do we possess these chemical signals that can influence our behavior and attract potential mates? The topic of human pheromones has sparked much debate among scientists and researchers.
The Science Behind Human Pheromones
Scientific studies have shown that animals use pheromones as a means of communication, particularly for mating purposes. These chemical signals are released into the environment and detected by receptors in the nose or other sensory organs of the receiving individual. However, when it comes to humans, the existence and significance of pheromones are still not fully understood.
While some studies suggest that humans do produce certain chemicals that can affect our behavior and attraction towards others, there is no consensus in the scientific community regarding their existence. It is believed that if human pheromones do indeed exist, they may play a role in sexual attraction and mate selection.
The Controversy Surrounding Human Pheromones
One reason for the controversy surrounding human pheromones is the difficulty in isolating specific compounds as definitive evidence. Unlike animals where specific chemicals have been identified as pheromonal cues, identifying such compounds in humans has proven challenging due to variations among individuals and cultural factors.
Another point of contention is whether or not these alleged human pheromones would be consciously perceived by individuals. While animals rely heavily on their sense of smell for detecting pheromonal cues, humans have a less developed olfactory system compared to other mammals.
The Role of Olfactory Preferences
Despite these uncertainties surrounding human pheromones, research has shown that scent can influence human behavior and attraction. Olfactory preferences, or our individual likes and dislikes when it comes to smells, have been found to play a role in forming social bonds and mate selection.
Studies have demonstrated that individuals may be more attracted to certain scents or body odors associated with genetic compatibility. This suggests that while we may not possess the same pheromonal communication system as animals do, scent still plays a role in human interactions.
The Future of Human Pheromone Research
As our understanding of human biology and chemistry advances, it is likely that more research will be conducted on the topic of human pheromones. With advancements in technology and experimental techniques, scientists may be able to shed further light on this intriguing aspect of human behavior.
VI. How Pheromones Influence Behavior and Attraction
Pheromones, the chemical signals emitted by organisms, play a significant role in influencing behavior and attraction among individuals. These invisible messengers communicate information about an individual’s gender, reproductive status, social dominance, and even emotional state.
The Power of Scent
Our sense of smell is closely linked to our emotions and memories. It is through this powerful sense that pheromones exert their influence on behavior and attraction. When we encounter certain scents produced by others, it triggers a cascade of reactions within our brains that can affect our mood, desire for connection, and sexual attraction.
Social Bonding
Pheromones contribute to the formation of social bonds between individuals. In many species, including humans, these chemical signals help establish trust and familiarity among members of a group. They can promote cooperation, reduce aggression levels, and enhance overall social cohesion.
Mate Selection
In the realm of romantic relationships, pheromones play a crucial role in mate selection. These chemical signals carry information about an individual’s genetic compatibility with potential partners. Research suggests that people are more attracted to individuals whose pheromone profiles complement their own immune system genes – a phenomenon known as “scent-based attraction.”
Sexual Arousal
Pheromones also have the ability to stimulate sexual arousal in both men and women. Certain scents can trigger physiological responses such as increased heart rate or dilation of blood vessels – signs commonly associated with sexual excitement.
Affection and Emotional Well-being
Beyond sexual attraction, pheromones can also influence feelings of affection and emotional well-being between individuals. The release of certain pheromones, such as those produced by a mother or during moments of intimacy, can create a sense of comfort, security, and bonding.
VII. Pheromone Detection and Sensory Systems
The detection and perception of pheromones in organisms play a crucial role in their social interactions, reproductive behaviors, and overall survival. Pheromones are chemical signals released by an individual to communicate with others of the same species, influencing various physiological and behavioral responses.
1. Olfactory Receptors
The olfactory receptors are responsible for detecting pheromones in most organisms. These specialized sensory cells are located in the nasal cavity or antennae, depending on the species. When a pheromone molecule enters the nose or antenna, it binds to specific receptors present on these cells, triggering a cascade of biochemical events that generate neural signals.
2. Vomeronasal Organ (VNO)
In addition to olfactory receptors, some animals possess a vomeronasal organ (VNO) dedicated solely to pheromone detection. The VNO is an auxiliary olfactory system found in reptiles, amphibians, and certain mammals like rodents and carnivores. It detects volatile chemical compounds emitted by conspecifics during mating or territorial disputes.
3. Signal Processing
Once pheromone molecules are detected by either olfactory receptors or VNOs, they initiate signal transduction pathways within sensory neurons that transmit information to higher brain regions for processing and interpretation. These neural circuits analyze the incoming signals based on factors such as concentration gradients, temporal patterns of release, and context-dependent cues provided by other sensory modalities.
4. Behavioral Responses
Pheromonal cues received through olfaction or VNO activation can trigger various behavioral responses in individuals within a species-specific context. This can include sexual attraction between potential mates, aggression or submission during territorial disputes, alarm signals to warn others of danger, or the formation of social hierarchies within a group.
5. Species-Specificity and Pheromone Diversity
One fascinating aspect of pheromones is their species-specific nature. Each species produces and detects unique pheromonal blends that are recognized by conspecifics while remaining undetectable or ineffective for individuals of other species. This specificity ensures accurate communication within a particular species while minimizing interference from unrelated organisms.
VIII. The Science behind Pheromone Production and Release
Pheromones are fascinating chemical signals that play a crucial role in communication among various species. These chemical messengers are produced and released by organisms to convey information about their presence, attract mates, mark territories, or warn others of danger. Understanding the science behind pheromone production and release can provide valuable insights into the intricate world of chemical signaling.
1. Pheromone Biosynthesis
The process of pheromone production begins within specialized cells or glands present in an organism’s body. These cells contain enzymes and precursors necessary for synthesizing pheromones. The biosynthesis pathway involves a series of enzymatic reactions that convert precursor molecules into specific pheromonal compounds.
For example, in insects, pheromones are often derived from fatty acids or amino acids through complex enzymatic transformations. The genes responsible for encoding these enzymes play a vital role in determining the type and quantity of pheromones produced by an individual.
2. Storage and Release Mechanism
Once synthesized, pheromones need to be stored until they can be effectively released to elicit a response from other individuals. Depending on the organism, this storage may occur within specialized glands or secretory structures located on the surface of the body.
Different species employ diverse mechanisms for releasing their pheromones into the environment. In some cases, they may rely on passive diffusion through pores or cuticular openings on their bodies. Others may require specific behaviors such as rubbing body parts together or performing distinctive displays to disperse their chemical signals effectively.
3. Reception and Interpretation
Pheromonally-receptive individuals possess sensory receptors that detect these chemical signals. These receptors are often located on specialized sensory organs, such as antennae or vomeronasal organs, depending on the species.
Once detected, pheromones bind to specific receptor proteins on the surface of receptor cells. This binding triggers a cascade of molecular events that ultimately leads to the transmission of nerve impulses to the brain. The interpretation of these signals in the brain enables individuals to respond appropriately by engaging in behaviors like mating, territorial defense, or avoidance of potential threats.
4. Species-Specificity and Communication
Pheromone communication is highly species-specific due to variations in receptor specificity and sensitivity among different organisms. Each species has evolved unique pheromonal blends that allow them to distinguish between conspecifics (members of their own species) and heterospecifics (members of other species).
The intricate chemistry behind pheromone production and release ensures that these chemical signals remain specific and effective within their ecological contexts. Through millions of years, organisms have fine-tuned their ability to produce and interpret these chemical messages accurately.
IX. Pheromone-Based Products: Do They Really Work?
Pheromones are chemical signals secreted by animals, including humans, to communicate with others of the same species. In recent years, pheromone-based products have gained popularity in various industries, promising to enhance attractiveness and improve social interactions. But do these products really work as advertised? Let’s delve into the science behind pheromones and their effectiveness.
The Science Behind Pheromones
Pheromones play a crucial role in animal behavior and mating rituals. They can trigger specific responses in other individuals, such as attraction or territorial marking. While the existence of human pheromones is still debated among scientists, some studies suggest that certain chemicals emitted by humans may influence social interactions.
However, it’s important to note that the effectiveness of pheromones varies from person to person due to individual differences in scent production and reception. Additionally, factors like personal hygiene practices and genetic compatibility can affect how others perceive these chemical signals.
Evidence for Pheromone-Based Products
Manufacturers of pheromone-based products claim that their formulations can boost confidence levels, increase sexual attraction, or foster better relationships. Despite these claims, scientific evidence supporting their efficacy remains limited.
A study UPDATED in the journal “Archives of Sexual Behavior” examined the effects of a popular pheromone-based product on women’s perception of men’s attractiveness. The findings indicated no significant difference between those who used the product and those who did not.
Another study conducted at Stockholm University analyzed whether synthetic human-like compounds could elicit gender-specific responses related to sexual attraction. The results suggested only minimal effects on participants’ perceptions.
While these studies provide some insights into the potential influence of pheromones, more research is needed to establish a definitive link between these chemical signals and their impact on human behavior.
The Placebo Effect
It’s worth considering the placebo effect when evaluating the effectiveness of pheromone-based products. The belief that a product will work can influence our perception and behavior, leading us to perceive positive changes even if they are not directly caused by the product itself. This psychological phenomenon may explain why some individuals report positive experiences with pheromone-based products despite limited scientific evidence.
Conclusion
Pheromone-based products claim to enhance attractiveness and improve social interactions. However, while there is some evidence suggesting the potential influence of pheromones on human behavior, further research is needed to fully understand their effects. Factors like individual differences in scent production and reception, personal hygiene practices, genetic compatibility, and the placebo effect all contribute to the complexity of this topic. So before investing in such products, it’s essential to approach them with a critical mindset.

Andrew Boyer is an accomplished individual with a deep-rooted passion for bees and their conservation. Born and raised in a small town in Oregon, Andrew developed an early fascination with nature and the environment. He pursued his education at the prestigious University of Oregon, where he obtained a Bachelor’s degree in Environmental Science with a specialization in Entomology. During his time at university, Andrew conducted extensive research on the behavior and ecological impact of bees, earning him recognition from his peers and professors. His dedication to the field led him to internships at local beekeeping associations, where he honed his skills in hive management and honey production. Andrew’s expertise in beekeeping and his commitment to environmental sustainability make him a valuable asset in the conservation of these vital pollinators.
